Russian economy is super fragile. It's critically dependent upon the:
1. Export of natural resources
2. Technological import
It has always been so. That's why Russia could never win a major war without massive economic help of the West. Without Western allies Russia's doomed🧵
1. Export of natural resources
2. Technological import
It has always been so. That's why Russia could never win a major war without massive economic help of the West. Without Western allies Russia's doomed🧵

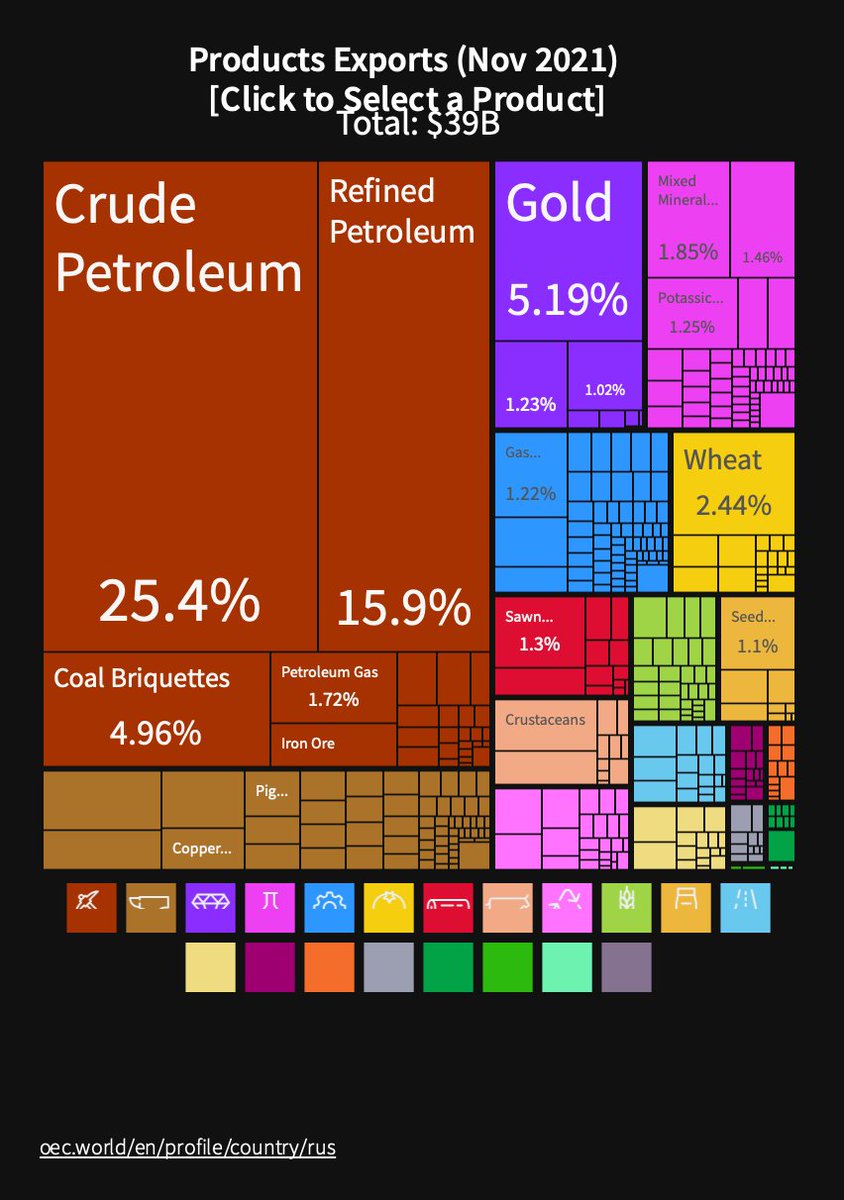
Let's have a look at Russian export structure. As you see, carbohydrates comprise its lion share with 1) metals 2) precious metals and stones 3) chemical products, mostly fertilisers, following. Russian economy is quite simply and based on the export of natural resources 
Where Russia takes resources to export? There is a trend northward. Until WWII Russia relied on Azerbaijan oil. In 1948 it found it in Tatarstan. In 1960 - in West Siberia. Now it relies on the Arctic. The older southern deposits deplete and you *have* to go north to find them 

Let's have a look on the largest gas/oil projects of Putin's era. Overall they give a pretty good picture of how it goes with extraction of natural resources. TL;DR the cost of extraction in Russia grows quickly and dependence on foreign financial + technological assistance, too 

Deposit Vostok Oil has 1/3 of Russian oil. The first well was drilled in 2020, in 2021 they started planning a pipeline route. They also must build a railway, a pipeline and a new port. All in the Arctic, at enormous cost. Singaporean Trafigura, Vitol, etc. invested in project 

In 2013 Russia started extracting oil from its first shelf deposit. Prirazlomnoye. Now it's 2022 and its still the only one. Why? It's expensive. Experts argue it's profitable only when the oil price is above 70-100 usd (estimates vary). This oil is sour, has a lot of sulphur 

Bazhenov Formation is a geological stratum covering more than 1 million km. It's the sediment of a prehistoric sea containing more oil than all currently extracted Russian deposits. But Russia lacks technology to extract it profitably. They do research but with no results so far 

Now let's discuss liquefied gas production. There are two Arctic facilities - Yamal LNG and Arctic LNG2. Yamal LNG is finished, first production line started in 2016. French "Total" owns 20%, Chinese "CNPC" - 20%, Silk Road Fund - 9,9%. It includes plant, seaport, airport, etc 

Arctic LNG2 - another project for producing and exporting the liquefied natural gas is still under construction, they estimate it's 39% ready. Investors include French Total, Chinese CNPC and CNOOC, Japanese Mitsui and Jogmec 

Until recently Putin aspired to increase the gas export to Europe. He built a Nordstream-1 pipeline connecting Russian Ust-Luga with Germany. He started building a liquified gas plant in Ust-Luga which was supposed to start production in 2023 and reach full capacity in 2024 

Russian relations with the West declining, Putin tried to get closer with China. In 2019 they commenced exporting gas through the Power of Siberia pipeline. They are also building Amur Gas processing plant there. Production commenced in 2021 and should reach full capacity in 2025 

This plant belongs to the Russian Gazprom. However, it took loans from the Bank of China, China Construction Bank Corporation and China Development Bank. Most of machines and equipment for gas production were supplied by the German "Linde Group" 

Sounds good, doesn't it? Putin prepares for the War on the West and diversifies his export markets? And yet, he project is terribly unprofitable. China is the only market and ofc Chinese set the lowest possible prices. The project is purely political, economically detrimental 

Power of Siberia pipeline is extremely costly. Why? Because contractors were Putin's friends, Rotenberg and Timchenko. In 2018 Sberbank SIB analysts concluded that the alternative route for the pipeline would be five times cheaper. And it was rejected in favour of costlier option 

Analysts speculated that the pipelines construction in Russia is systematically conducted not in the interest of state owned companies which finance them, but in favour of well-connected "contractors" who built them. And they purposefully design them as costly as possible 

These analysts suggested that the entire pipeline construction in Russia is conducted in a way so that "contractors" could enrich. In other words, state-owned companies work at a loss, so that Putin's friends could work at a profit. Analysts were fired of course 

Russia is critically dependent upon the West regarding its exports. It needs Western technological & managerial assistance to extract & export natural resources. There are ofc purely Russian projects with no Western investors/contractors. They just don't work and remain on paper 

Putin tries to "diversify" his exports re-orienting them to China. But Chinese are no idiots. Re-orienting its export flows towards China Russia comes to the one-buyer market. Chinese don't care about "friendship" and exploit Russia, setting the prices far below break-even point 

If Xi Jinping really urged Putin to wait with his invasion till the end of Beijing Olympics, that's hilarious. That would show enormous Chinese disregard to Russian interests and unthinkable compliance of Putin. Xi asked, Putin obeyed & waited till the spring mud, his army stuck 

China can't compensate the loss of European market. It also can't compensate it technologically. Even on Far Easter gas plants they used German machines. Import from China is significant bur far below imports from Europe which supplies Russia with most means of production 

And ofc China can't compensate Europe as an investor. Most of Russian-Chinese investment cooperation is BS. Chinese sign whatever the non-binding agreements Putin wants, then don't invest anything. There's zero progress on 81 out of total 88 such projects that were agreed upon 

The very idea that expanding on Chinese one-buyer market can compensate the losses on Western multi-buyers market is insane. China perfectly understand Russian neediness and will use its leverage fully. "Friendship" of a declining empire with a rising superpower is a delusion 

Chinese policy towards Russia may have an element of revenge in it. Deng Xiaoping told that imperialistic powers inflicted a lot of damage on China during its weakness. Japan ofc made the most of devastation. But Russia ***including the USSR*** took the most of advantage of China 

I don't know what Xi Jinping thinks of his relations with the northern neighbour. But I won't be surprised if he views using his leverage fully as a sort of retaliation. In the past you exploited our weakness under a BS pretext of friendship. Now, as you are weaker, we will 

So there are three factors that don't allow Russia to compensate their export losses on Chinese market. Firstly, China is using its leverage, as there's no one else to buy. Secondly, Putin's friends organise construction of infrastructure as costly as possible in order to enrich 

The problem is not jus them "stealing". In fact, it would be much better if they just directly took billions from the budget of Russian state-owned companies. The problem is that state companies can't just openly transfer money onto the offshore accounts of Putin's friends 

Since Putin's friends can't just openly take money from government budget, they organise a lot of BS "construction" acting as contractors. And they purposefully maximise the cost. They destroy at least 10 rubles in order to steal 1. That's why everything is so unprofitable 

And finally, re-orienting towards China takes time. You can't do it overnight no matter how much you need it. Even if Putin's friends didn't participate (impossible) and China would altruistically cooperate (impossible) it would take many years. Economy will collapse much earlier 

This is exacerbated by the depletion of southern deposits which are easier and cheaper to extract. Why does Russia go further and further north for oil and gas extraction? Because all southern and cheaper ones are being depleted. That's why Russian oil is so expensive to produce 

How expensive it is? We can't know for sure because Russian legislation and Putin's executive order classifies such information. And yet, we can consider some expert estimates 

In 2019 the IHS Market concluded that the cost of production of Russian oil is some of the highest in the world. They estimate it as 42$ for onshore and 44$ for offshore projects. You can ask, are this estimates reliable? In fact there is a corroborating evidence 

Since mid 2010s Russia's constantly launching new and new "tax manoeuvres" in oil and gas industry? What does it even mean? It means that government is introducing new and new tax and tariff benefits for oil and gas exports. Eventually it aims to reduce export rate tariff to zero 

Why is Russia doing these "tax manoeuvres"? Cuz it ran out of cheap oil. Easy to extract deposits are over and new ones lie in very harsh terrain (when technologically possible to develop). Cost of production rising, Putin has to reduce tax burden to zero to keep companies afloat 

Today I covered Russian exports, next time I'll talk of its technological imports and technological dependence. If you want to support my work, you can sign up to my Patreon. End of🧵patreon.com/kamilkazani922
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh