Today's @bopinion post is about Nigeria. I expect its conclusions will not come as a surprise to most Nigerians, but it's good for Americans to be thinking about Nigeria and its problems. bloomberg.com/view/articles/…
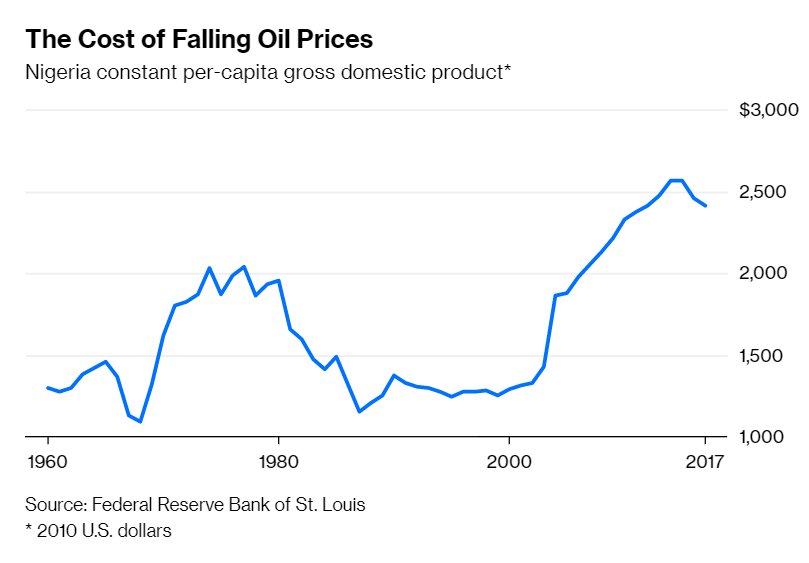
Nigeria is very dependent on oil, for its government revenues and for its foreign exchange earnings.
When oil prices fall, Nigeria's people suffer.
When oil prices fall, Nigeria's people suffer.
And like many oil-rich countries, the government tries to cushion the blow by subsidizing fuel (this is more expensive than you might think, since Nigeria can't refine all of its own oil).
When oil prices rise again, this puts a strain on govt. budgets.
When oil prices rise again, this puts a strain on govt. budgets.

To escape the doom spiral of the Resource Curse, Nigeria should look to a country that seems to have beaten the curse: Botswana.
openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/hand…
openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/hand…
Botswana's approach is basically:
1. Pour resource revenues into a Sovereign Wealth Fund
2. Depreciate the currency
3. Use SWF to stabilize the budget
4. Invest a bunch in education, health and infrastructure
1. Pour resource revenues into a Sovereign Wealth Fund
2. Depreciate the currency
3. Use SWF to stabilize the budget
4. Invest a bunch in education, health and infrastructure

But Nigeria is missing one big piece: Investment in education.
(It could also stand to invest more in health.)
thenationonlineng.net/nigerias-disap…
(It could also stand to invest more in health.)
thenationonlineng.net/nigerias-disap…
Instead of subsidizing fuel, Nigeria needs to subsidize education (which doubles as child care) and health. This will provide jobs, relieve poverty, and - most importantly - build human capital.
(end)
(end)

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh











