NMAT Review
Must Know: Biology Part 1 [Thread]
Here are some key notes about basic biological knowledge. (Topics: Properties of life, Types of Cell, Cell Cycle, Cell Division, Ontogeny etc.)
Must Know: Biology Part 1 [Thread]
Here are some key notes about basic biological knowledge. (Topics: Properties of life, Types of Cell, Cell Cycle, Cell Division, Ontogeny etc.)
1.Properties of Life:
-All organisms consist of one or more cells.
-All living things are highly ordered.
-All living things respond to stimuli.
-Homeostasis
-Evolutionary Adaptation
-Energy Utilization
-Capable of growth, development and reproduction
-All organisms consist of one or more cells.
-All living things are highly ordered.
-All living things respond to stimuli.
-Homeostasis
-Evolutionary Adaptation
-Energy Utilization
-Capable of growth, development and reproduction
3.Three Domains of Life
Domain Bacteria
-consisted of all the unicellular prokaryotic organisms.
Domain Archaea
-consisted of all the extreme bacteria and some species of algae.
Domain Eukarya
-consisted of all the unicellular, multicellular, colonic or filamentous organisms.
Domain Bacteria
-consisted of all the unicellular prokaryotic organisms.
Domain Archaea
-consisted of all the extreme bacteria and some species of algae.
Domain Eukarya
-consisted of all the unicellular, multicellular, colonic or filamentous organisms.
4.Kingdoms 1/2
Bacteria
-Prokaryotic organisms with a peptidoglycan cell wall.
Archaebacteria
- Prokaryotes that lack a peptidoglycan cell wall
Animalia(Eukarya)
- Eukaryotic, multicellular, motile, heterotrophic .
Bacteria
-Prokaryotic organisms with a peptidoglycan cell wall.
Archaebacteria
- Prokaryotes that lack a peptidoglycan cell wall
Animalia(Eukarya)
- Eukaryotic, multicellular, motile, heterotrophic .
5.Kingdoms 2/2 (Eukarya)
Plantae
-Eukaryotic, multicellular, nonmotile, usually terrestrial, photosynthetic organisms
Fungi
-Eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, nonmotile organisms, with cell walls of chitin
Monera
-Eukaryotic, unicellular, photosynthetic, heterotrophic
Plantae
-Eukaryotic, multicellular, nonmotile, usually terrestrial, photosynthetic organisms
Fungi
-Eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, nonmotile organisms, with cell walls of chitin
Monera
-Eukaryotic, unicellular, photosynthetic, heterotrophic
7.Cell Theory
-All living things are composed of one or more cells.
-Cells are the smallest living things, the basic unit of organization of all organisms.
-Cell arise only by division of a previously existing cell.
-Cells carry genetic information in the form of DNA.
-All living things are composed of one or more cells.
-Cells are the smallest living things, the basic unit of organization of all organisms.
-Cell arise only by division of a previously existing cell.
-Cells carry genetic information in the form of DNA.
12.Interphase
-cellular components are copied. 90% of the cell cycle.
•G1 Phase (Organelle Replication)
•S (Synthesis) Phase (DNA Replication)
•G2 Phase (Safety Gap)
-cellular components are copied. 90% of the cell cycle.
•G1 Phase (Organelle Replication)
•S (Synthesis) Phase (DNA Replication)
•G2 Phase (Safety Gap)
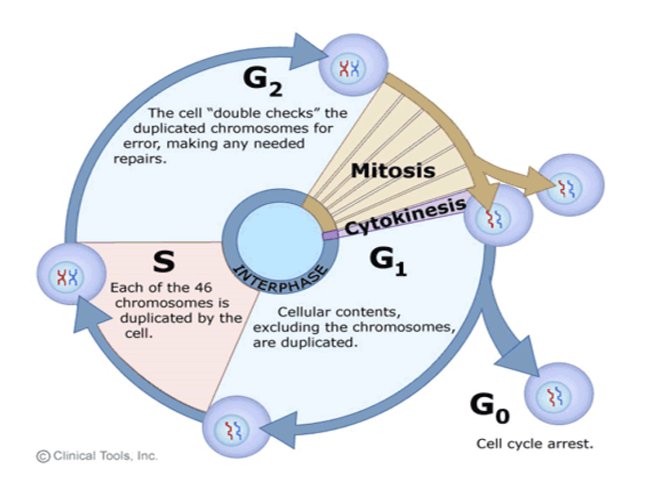
14.Mitosis
Prophase-nuclear envelope starts to disappear as chromosomes condensed
Metaphase-chromosome pairs align at the equatorial plate
Anaphase-spindle fibers pulls the sister chromatids apart towards the opposite poles
Telophase-sister chromatids are now on opposite poles
Prophase-nuclear envelope starts to disappear as chromosomes condensed
Metaphase-chromosome pairs align at the equatorial plate
Anaphase-spindle fibers pulls the sister chromatids apart towards the opposite poles
Telophase-sister chromatids are now on opposite poles

18.Prophase 1
Mnemonics: LeZyPaDiDi
Crossing-over/Recombination
-Each set exchanges bits of DNA with the other and recombines, thus creating genetic variation.
Synapsis
-the fusion of chromosome pairs at the start of meiosis.
Mnemonics: LeZyPaDiDi
Crossing-over/Recombination
-Each set exchanges bits of DNA with the other and recombines, thus creating genetic variation.
Synapsis
-the fusion of chromosome pairs at the start of meiosis.
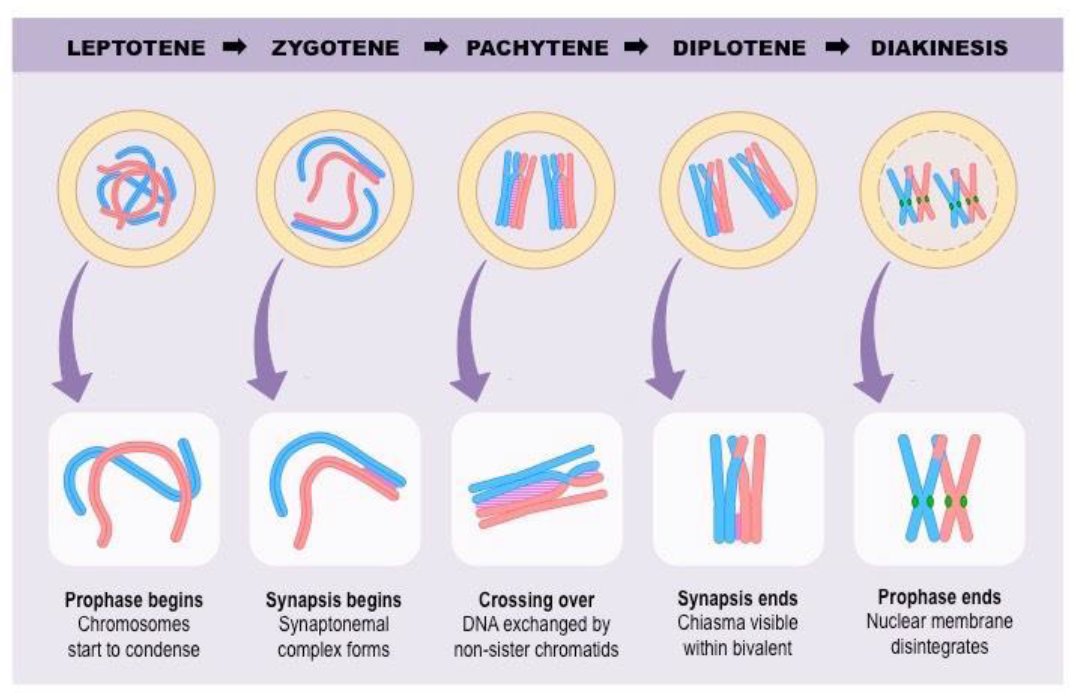
21.Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis
Spermatogenesis
-the formation of sperm cells
Oogenesis
-the formation of egg cells
* Spermiogenesis
-the transformation of spermatids to spermatozoa(sperms) by differentiation.
Spermatogenesis
-the formation of sperm cells
Oogenesis
-the formation of egg cells
* Spermiogenesis
-the transformation of spermatids to spermatozoa(sperms) by differentiation.

22.Ontogeny
-all the developmental events that occur during the existence of a living organism.
Fertilization
-is the union of a human egg and sperm, usually occurring in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
-all the developmental events that occur during the existence of a living organism.
Fertilization
-is the union of a human egg and sperm, usually occurring in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
23.Stages of Early Embryonic Development 1/5
Morulation
-The cleavage or segmentation of the ovum by which a morula is formed.
Morula
-a solid ball of cells resulting from division of a fertilized ovum, and from which a blastula is formed
Morulation
-The cleavage or segmentation of the ovum by which a morula is formed.
Morula
-a solid ball of cells resulting from division of a fertilized ovum, and from which a blastula is formed
24.Stages of Early Embryonic Development 2/5
Blastulation
-is the formation of a blastula from a morula.
Blastula
-an animal embryo at the early stage of development when it is a hollow ball of cells.
Blastulation
-is the formation of a blastula from a morula.
Blastula
-an animal embryo at the early stage of development when it is a hollow ball of cells.
25.Stages of Early Embryonic Development 3/5
Gastrulation
-ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm form.
Gastrula
-an embryo at the stage following the blastula, when it is a hollow cup-shaped structure having three layers of cells.
Gastrulation
-ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm form.
Gastrula
-an embryo at the stage following the blastula, when it is a hollow cup-shaped structure having three layers of cells.
26.Stages of Early Embryonic Development 4/5
Neurulation
-germ layers develop a nervous system
Neurula
-a vertebrate embryo at the early stage of development in which neurulation occurs
Neurulation
-germ layers develop a nervous system
Neurula
-a vertebrate embryo at the early stage of development in which neurulation occurs
@threadreaderapp unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh