(Especially when thinking about self-applied behavioural science)
'Beyond Willpower' by @angeladuckw , @katy_milkman and #DavidLaibson
Here are my favourite notes and quotes (Thread)👇
"Men are rather reasoning than reasonable animals for the most part governed by the impulse of passion." ~ Alexander Hamilton (1802)
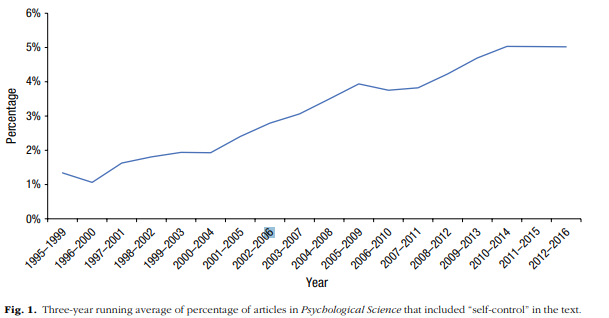
Useful to remember that inquiry on the topic stretches back 1000's of years.
~ Persistence of self-control failures even when known
~ People incorrectly predict their ability to solve SCF's
~ The pervasiveness of temptations in the modern world
Should behaviour (exercising, eating healthy, going to bed early) - more valuable in the long-run.
Want behaviour (staying on the couch, staying up late) is more alluring in the moment.
"When people pursue the option with more enduring value, they experience self-control success; when they pursue the option that is more tempting right now, they experience self-control failure."
1) Multiple sequential selves with inconsistent preferences
2) Multiple coexisting selves
3) multiple-attribute choices
commonplace."
Why?
"Succeeding at self-control requires people to do MORE THAN DECIDE to forego what they want in order to do what they should."
1) Situational strategies OR
2) Cognitive strategies
&
3) Self-deployed Strategies OR
4) Other-deployed control strategies
- Commitment Devices
- Temptation Bundling
- Situation Modification
- Behavior Therapy
- Goals
- Mental Contrasting
- Implementation Planning
- If-then Planning Prompts
- Self-monitoring
- Psychological Distancing
- Mindfulness
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
- Descriptive Social Norms
- Social Labeling
- Making the Future Self-relatable
- Joint Evaluation
- Fresh-start Framing
- Licensing Prevention
- Hard Paternalism
- Microenvironments
- Defaults
- Active Choice
- Enhanced Active Choice
- Choosing in Advance
- Planned Interruptions
Self-deployed:
Put a greater “burden” on the individual but, once mastered, can, in theory, be applied across domains.
Other-deployed:
Easier to carry out but do not build the capacity of individuals to exercise self-control (or self-knowledge).
"Optimal strategies depend not only on their likelihood of success but also on their ease of execution."
1) Direct comparability
2) Complementary and substitution effects
3) Gist thinking, personal rules and habits
4) Executive function activation
5) General intervention robustness