Today I will share the core of #TBRchapter1 – The History of
Money
The previous tweets can be found here
theory.
– Dennis Lockhart, Chairman of the board of the Federal
Reserve Bank of Atlanta (2012)
#TBRchapter1
– Paul Volcker (2013)
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
built their empires around a monetary system based on gold.
Maintaining the value of one’s currency was key to keeping
power. Soldiers were kept happy by regular payments of wages in gold and silver coins.
#TBRchapter1
was debased.
#TBRchapter1
commonly known as the bezant, was used widely throughout
Europe and the Mediterranean. The bezant was possibly the most successful means of payment in world history. These gold coins existed from 491 to 1453
#TBRchapter1
the bubonic plague and a series of fijinancial crashes hammered Europe, the role of the bezant as money was replaced by silver coins in many European countries.
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
most important advantage is that it forces governments to be
disciplined in their fiscal policy because they cannot turn on
the printing press to finance budget deficits.
#TBRchapter1
inflation for almost two hundred years up until the dissolution
of the gold standard in 1914
#TBRchapter1
and often the only way – to pay for a war
#TBRchapter1
continued apace, leading to the creation of a massive credit
bubble in the 1920s. This led eventually to the market crash of
1929, after which the world economy collapsed and fell into a
deep economic crisis
#TBRchapter1
substantial like gold or silver, banks can create virtually limitless amounts of money by creating new loans. All money is created in the form of credit. If all loans were to be paid off,
all money would disappear
#TBR
#TBRchapter1
Appendix I). Central bankers, however, continue to claim that
this time, all will be well. If turning on the printing presses would lead to prosperity, then Africa would not be a poor continent
#TBRchapter1
portion of all outstanding liabilities as available reserves. In 1900 this was around 30%, and has now declined to just 3%.
Fractional banking started at the end of the Middle Ages
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
#TBR
way, which did indeed stimulate the French economy. Law eventually got himself into trouble pursuing another business
opportunity. In 1717, he founded the Mississippi Company.
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
Because of all this newly printed money, people began to distrust paper money. The French government quickly implemented some strict new rules. Maximum prices were set to curb inflation ..
gold instead of paper money when selling goods. In a last attempt to protect the paper money system, all trade in precious metals was forbidden as of 13 November 1793
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
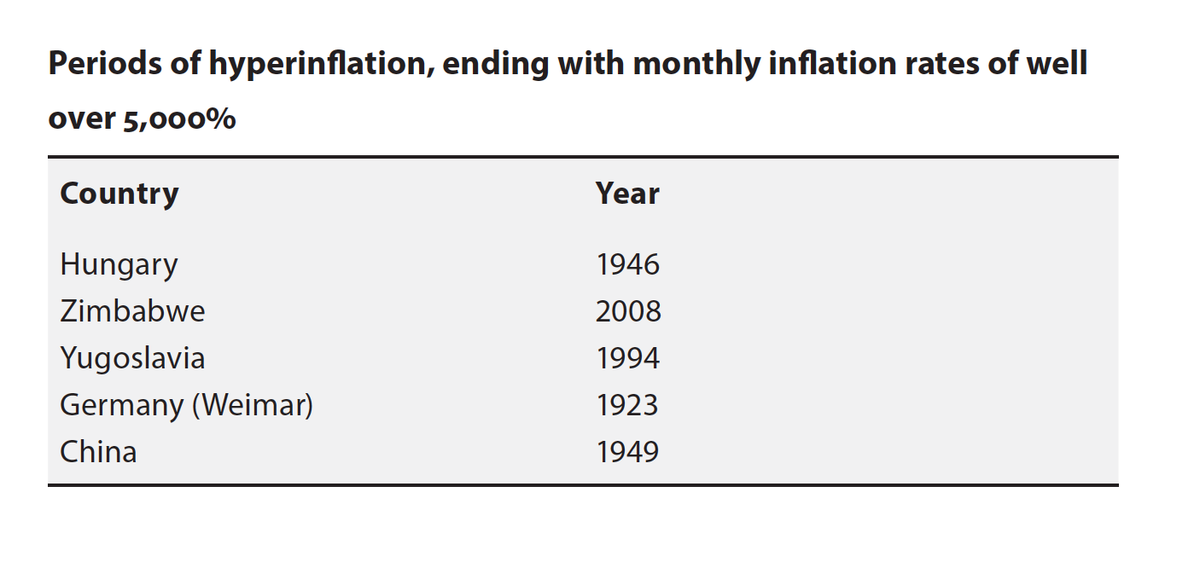
of over 50% within a year. Hyperinflation is so harmful because money loses its value and power. We could well call it the death of money.
#TBRchapter1
and people revert almost immediately to bartering. A good example of the dangers of fiat money is the hyperinflation
that scourged Germany’s Weimar Republic in the beginning
of the 1920s.
#TBRchapter1
#TBRchapter1
consequence, central banks such as the Fed and the ECB create over one trillion dollars (5tr now!?-wm) in new money every year in order to support their governments. And still, they claim they are fighting inflation.
en.cdfund.com/download-the-b…