Intimidated by prescribing hormones? Here's what you need to know to prescribe safely and effectively.
cdc.gov/reproductivehe…

The most common estrogen used is ethinyl estradiol (EE). There are 4 gen of progestins.
The (a) type of progestin and (b) amount of each component are what make each OCP unique.
Pill pack:
💊💊💊💊💊💊💊
💊💊💊💊💊💊💊
💊💊💊💊💊💊💊
✖️✖️✖️✖️✖️✖️✖️
- Monophasic = same amt EE & progestin in each pill. These are the most common!
- Estrogenic = consistent EE dose + varying progestin dose as the pill pack progresses.
- Multiphasic = a varying amount of EE and progestin each week
- Stop the active pills x1wk, allow a withdrawal bleed, then restart.
- Prescribe extra estrogen (e.g., Premarin 1.25mg x7d). If that doesn’t work, you can repeat once.
If your fix fails, look for a structural cause of the bleeding (eg, endometrial polyp).
💊 Make sure OCPs are safe for your patient.
💊Pick a progestin.
💊Pick EE & progestin doses
💊Find out how often a withdrawal bleed is desired.
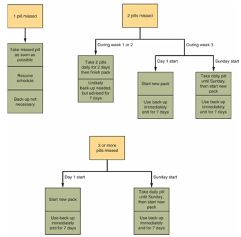
💊Choose when to start the pills.
💊Troubleshoot problems
💊 Stop 2mo prior to desired preg
🌟 Inspired by Dr. Michael Thomure (St Louis University REI) ⚜️
🌟 Speroff’s Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology & Infertility
🌟 C.D.C. Medical Eligibility Criteria