Really nice to see this WHO analysis in JAMA (along w 3 RCTs) put to bed the importance of corticosteroids in ventilated patients w COVID-19. A lot of good stuff here.
So what to do w steroids in those requiring supp O2 only? /1
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
So what to do w steroids in those requiring supp O2 only? /1
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
RECOVERY results suggest a mortality benefit in this population (supp O2 only), and I have seen basically every patient in this category receive dex, appropriately... but there are enough odd features of this single open-label trial that make me wonder. /2
Much of this nuance is explained well in this thread by @FranciscoMarty_
The main thing that nags me personally is how ridiculously high the mortality was in RECOVERY - 26.2% among those requiring O2 and receiving usual care /3
https://twitter.com/FranciscoMarty_/status/1293550705865822208?s=20
The main thing that nags me personally is how ridiculously high the mortality was in RECOVERY - 26.2% among those requiring O2 and receiving usual care /3
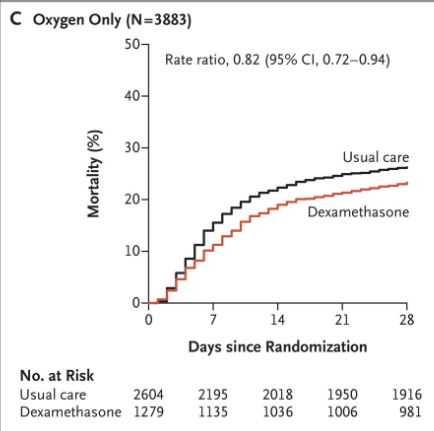
This is much higher than what I've seen reported in other high-resource settings. Eg study from Boston 👇 found 15% mortality among ALL admitted patients (42% critically ill) /4
thelancet.com/journals/eclin…
thelancet.com/journals/eclin…
Maybe @EricMeyerowitz can explain to me why mortality for people on supp O2 was so different in RECOVERY, but this, along with the even more dubious effect of dex in those not on O2, makes me question reflexively giving steroids to pts admitted with COVID-19 on low-flow O2 /end
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh