It is reasonable to ask: why close restaurants and pubs if there are so few outbreaks associated with those environments? However, this is misreading and misinterpreting the data on outbreaks and clusters. 1/10 
If I went out 5 days ago and caught the virus in a restaurant, it will have multiplied silently inside me for 3 days; then I will have started shedding virus, and potentially infecting others, for 2 days; today I become symptomatic, self-isolate, and get a test. 2/10
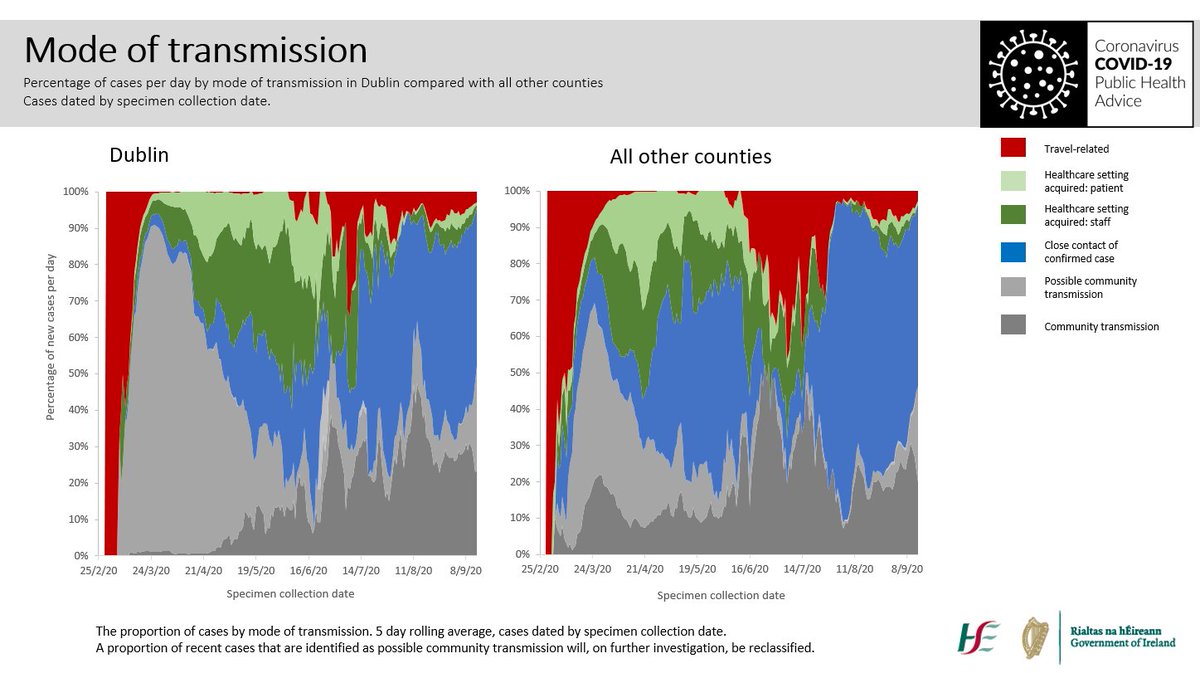
Public health only ask me about my contacts for the 48 hours before I developed symptoms. They don’t need to know where I got the virus; that happened 5 days ago. They want to know where the virus is going, who I might have infected, and prevent onward transmission. 3/10
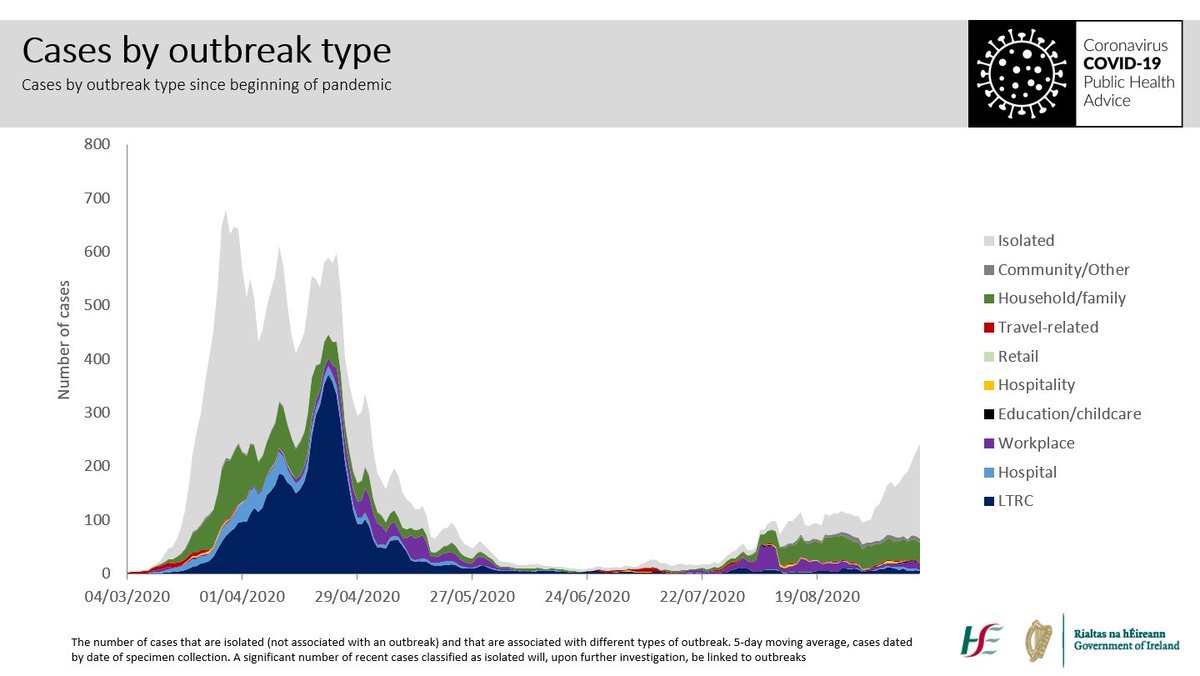
My contacts are tested, and unfortunately two of my family are infected. It’s now a household outbreak, and I am a case of community transmission. Even though I got it in a restaurant and brought it home. 4/10
We would like to go back and find out where people are getting the virus, but we don’t have the time or resources to pursue this academic exercise. 5/10
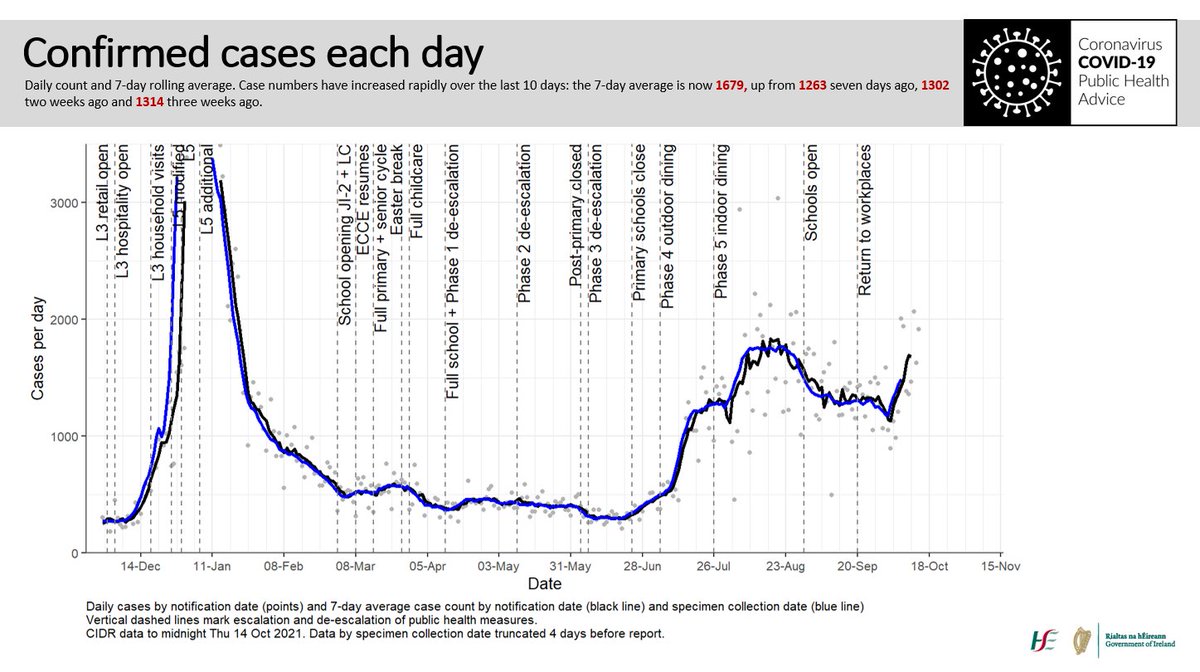
We have lots of international evidence from better resourced systems on how the virus transmits: we know that social settings, including bars and restaurants, drive community transmission. 6/10
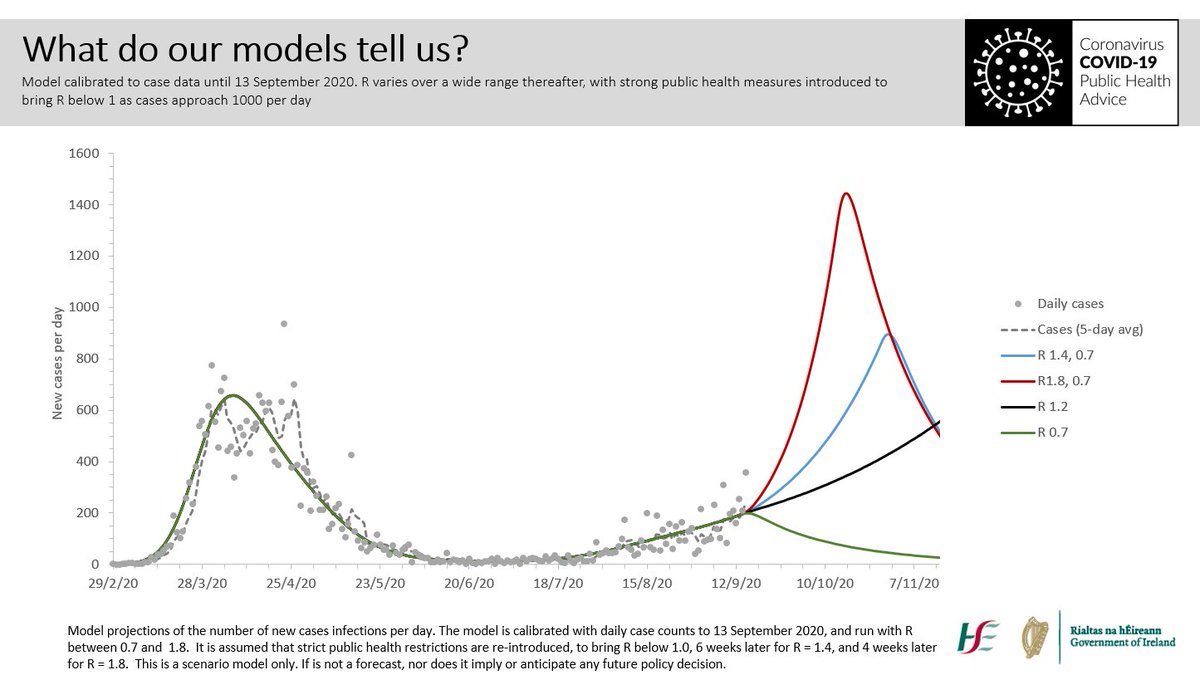
We know that in Dublin at least one in three cases are community transmission. Where is this happening? Wherever we mix socially: our houses, gyms, bars, restaurants. Sadly, unless we stop mixing in these settings, we know the disease will spiral out of control. 7/10 
This is really difficult. Restaurant and gastropub owners have worked very hard to minimize the risk of transmission. Their livelihoods and our safety are at stake, and their work allows us to socialize and enjoy ourselves safely when the level of the virus is low. 8/10
However, the level of the virus is rising again rapidly, and we have to radically reduce mixing between households. 9/10 
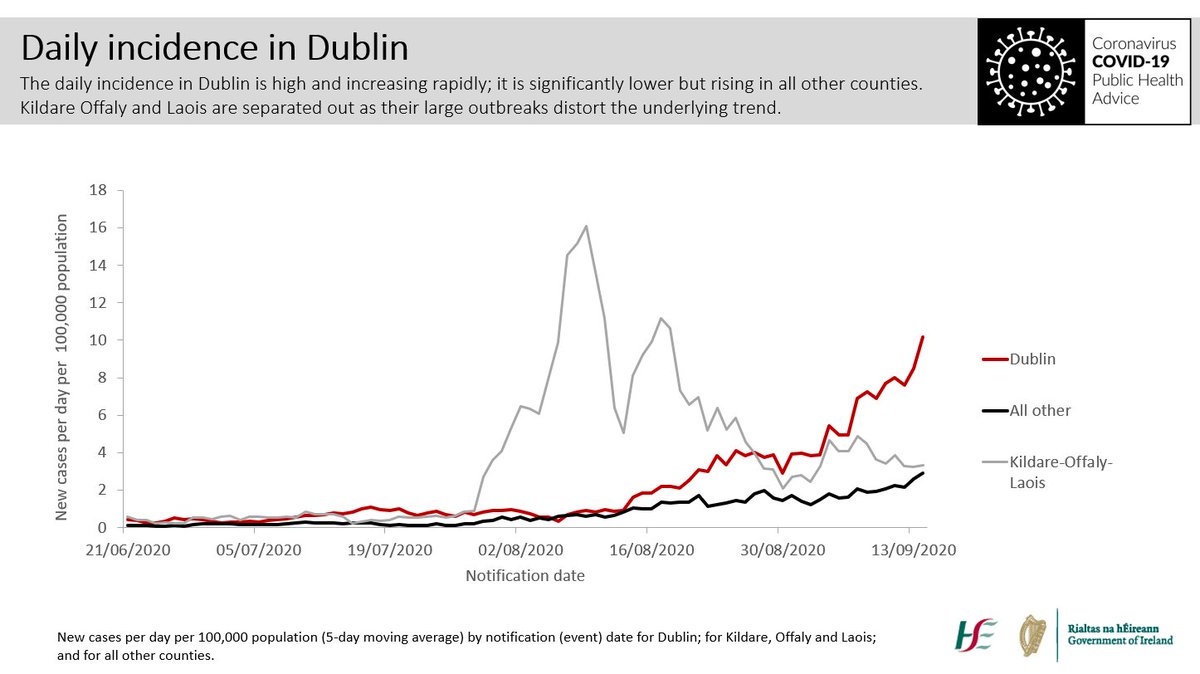
If we don’t, this virus will kill some of us, saturate our health system, close schools, and create a bigger shock to our economy. It’s devastating for those businesses affected, but we must act now, while targeted measures might still get the virus back under control. 10/10 
...for clarity on above, of course our colleagues in public health would track down the source if they had the resources to do so, but they don’t, and must prioritise the management of cases, outbreaks and onward transmission.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh