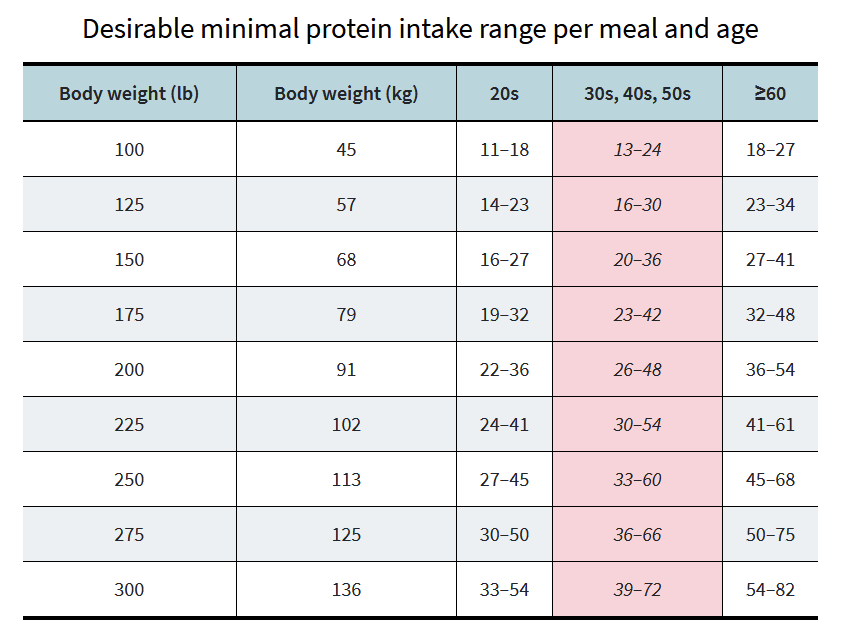
How much protein do you need per day?
As with most things in nutrition, there’s no simple answer. Your ideal intake of calories and protein depends on your health, body composition, main goal, and the type, intensity, duration, and frequency of your physical activity.
[thread]
As with most things in nutrition, there’s no simple answer. Your ideal intake of calories and protein depends on your health, body composition, main goal, and the type, intensity, duration, and frequency of your physical activity.
[thread]
If you’re healthy and sedentary:
Aim for 1.2–1.8 g/kg (0.54–0.82 g/lb).
Keep in mind that your body composition is more likely to improve if you add regular activity, especially resistance training, than if you merely hit a protein target.
Aim for 1.2–1.8 g/kg (0.54–0.82 g/lb).
Keep in mind that your body composition is more likely to improve if you add regular activity, especially resistance training, than if you merely hit a protein target.

If you’re of healthy weight, active, and wish to keep your weight:
Aim for 1.4–2.0 g/kg (0.64–0.91 g/lb).
People who are trying to keep the same weight but improve their body composition (more muscle, less fat) may benefit from the higher end of the range.
Aim for 1.4–2.0 g/kg (0.64–0.91 g/lb).
People who are trying to keep the same weight but improve their body composition (more muscle, less fat) may benefit from the higher end of the range.

If you’re of healthy weight, active, and wish to build muscle:
Aim for 1.6–2.4 g/kg (0.73–1.10 g/lb).
Intakes as high as 3.3 g/kg may help experienced lifters minimize fat gain when bulking.
Aim for 1.6–2.4 g/kg (0.73–1.10 g/lb).
Intakes as high as 3.3 g/kg may help experienced lifters minimize fat gain when bulking.

If you’re of healthy weight, active, and wish to lose fat:
Aim for 1.6–2.4 g/kg (0.73–1.10 g/lb), skewing toward the higher end of this range as you become leaner or if you increase your caloric deficit (by eating less or exercising more).
Aim for 1.6–2.4 g/kg (0.73–1.10 g/lb), skewing toward the higher end of this range as you become leaner or if you increase your caloric deficit (by eating less or exercising more).

If you’re overweight:
Aim for 1.2–1.5 g/kg (0.54–0.68 g/lb).
This range, like all the others in this list, is based on your total body weight.
Aim for 1.2–1.5 g/kg (0.54–0.68 g/lb).
This range, like all the others in this list, is based on your total body weight.

Those are the basics, but there’s a lot more nuance when it comes to your optimal protein intake.
Read the full guide on optimal protein intake: examine.com/guides/protein…
Read the full guide on optimal protein intake: examine.com/guides/protein…
Oh, and here’s our protein intake calculator to make it super-easy for you to quickly find out your optimal protein intake:
examine.com/nutrition/prot…
examine.com/nutrition/prot…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh