Love to see this new work from @fleventy5 @jfkelso @maxplanckpress outlining Neandertal and Denisovan Y chromosomes. New evidence of genetic mixture of Neandertals and third population closer to today's people. @ScienceMagazine
science.sciencemag.org/content/369/65…
science.sciencemag.org/content/369/65…
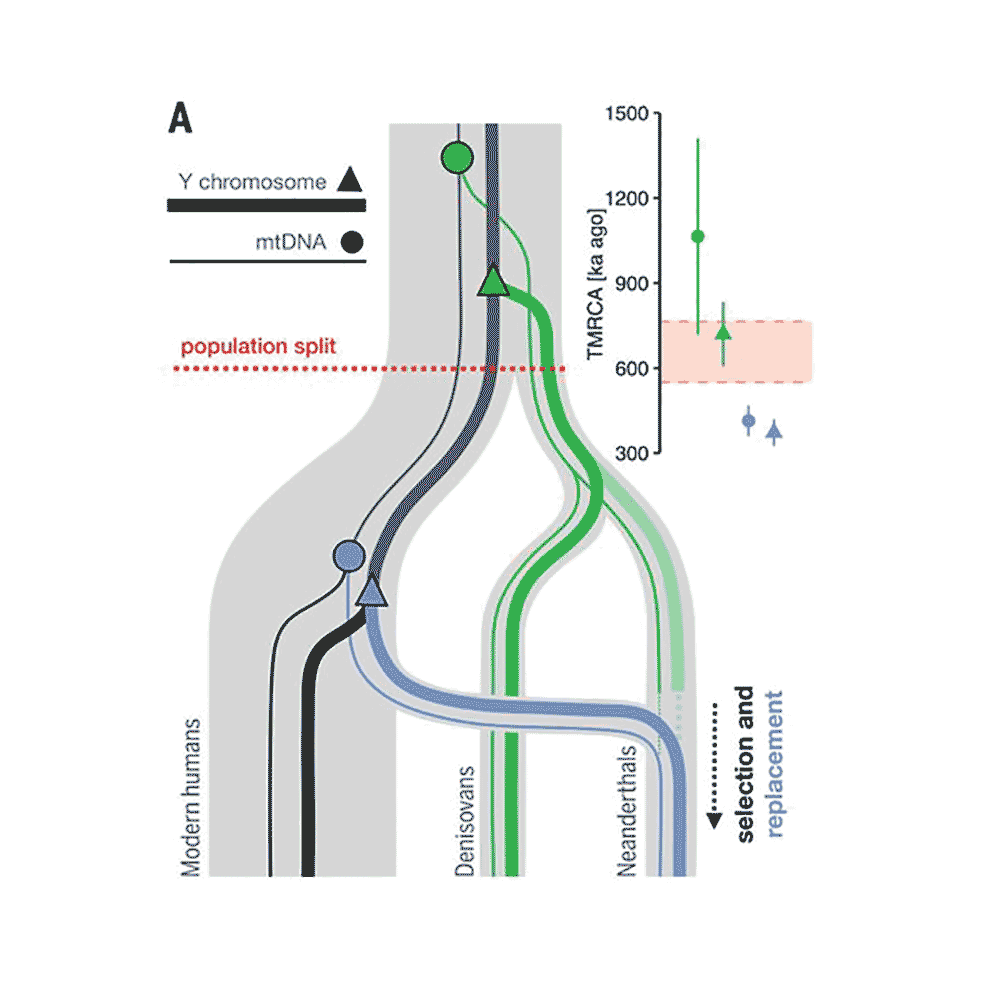
I strongly hesitate to use the term "modern humans" in this context. The Y chromosome of Neandertals is from a Y clade that is extinct today, outside the range of present-day Y variation. What we don't know is where that Y clade fit into our structured ancestral populations.
Both the Y chromosome (~250ka) and mtDNA (~200ka) of modern humans have MRCA younger than the time we think that today's populations of modern people began to differentiate (~300ka). Of course, any of these dates could be wrong...
...but a likely hypothesis is introgressive replacement of Y and mtDNA in some early modern populations from others. The reason for such adaptive introgression in these populations would be the same as Neandertals: small population size, high drift, deleterious fixed mutations.
The story is not (or not only) that Neandertals picked up these gene systems from "moderns", but that most early moderns also picked them up. The term "moderns" to most people connotes one panmictic gene pool. But we now know that our ancestors were anything but that.
People on various channels are asking me, if Neandertals got their mtDNA and their Y chromosome from "modern" humans, how can we consider them a distinct species? After all, both their maternal and paternal lines came from us! This is a good question to be asking.
If you're wondering, it's worth a look at the ancient DNA papers that are generating these results. Very few of them use the term "Homo neanderthalensis" at all. As a concept, it has not been useful for explaining the genetic patterns.
One last thing about the new paper: It's very interesting in light of all the mtDNA and Y introgression that Denisovan Y chromosome divergence is right on the expected 700ka time range.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh