In the Netherlands there is much ado about a new ENCO study showing NUCLEAR is cheap. It apparently convinced more than half of parliament. But it is riddled with errors and was rushed through without any check. If the errors are corrected the conclusion reverses. (short thread)
The same ministry (@MinisterieEZK) commissioned a peer reviewed study earlier this year (by Kalavasta) that showed nuclear is more expensive.
Why did they commission this new non-peer reviewed study from a group that is mainly doing nuclear security studies?
Why did they commission this new non-peer reviewed study from a group that is mainly doing nuclear security studies?
Fortunately the writers of the Kalavasta study already reacted to the new pro-nuclear ENCO study. They point out the main problems with the new study that are glaringly obvious for most experts.
Let me summarise in this thread.
content1a.omroep.nl/urishieldv2/l2…
Let me summarise in this thread.
content1a.omroep.nl/urishieldv2/l2…

1st problem: higher costs for wind and solar in 2040 than 2020! Without sources to defend that.
Google "learning curves for solar and wind" and you see that they become cheaper very predictably. ENCO makes a big beginners error that is disqualifying in and off itself.
Google "learning curves for solar and wind" and you see that they become cheaper very predictably. ENCO makes a big beginners error that is disqualifying in and off itself.
ENCO is extremely optimistic about the nuclear costs.
They clearly belong to the first of 2 groups regarding Nuclear.
Group 1: "But NEXT time the power plant will be MUCH cheaper! I KNOW it!
Group 2: "Let's extrapolate historical data. Oh, they are becoming more expensive."
They clearly belong to the first of 2 groups regarding Nuclear.
Group 1: "But NEXT time the power plant will be MUCH cheaper! I KNOW it!
Group 2: "Let's extrapolate historical data. Oh, they are becoming more expensive."
It's interesting to note that the Kalavasta study (the one that found nuclear was more expensive) also used similarly optimistic costs for nuclear.
So not exactly nuclear haters, the people at Kalavasta.
So not exactly nuclear haters, the people at Kalavasta.
2nd problem: nuclear must be on 95% of the time.
This is possible when you give it priority over wind and solar (which have zero marginal costs).
But it means completely changing the electricity market and throttling wind and solar.
The ENCO authors seem to be unaware of this.
This is possible when you give it priority over wind and solar (which have zero marginal costs).
But it means completely changing the electricity market and throttling wind and solar.
The ENCO authors seem to be unaware of this.
3rd problem: they use wrong underlying energy system data.
They assume 50% wind and solar when the climate agreement points to 60% and PBL to 70% in 2030. Etc.
This gets nerdy but simplified: "Why on earth couldn't they use the correct and open source Dutch energy system data?"
They assume 50% wind and solar when the climate agreement points to 60% and PBL to 70% in 2030. Etc.
This gets nerdy but simplified: "Why on earth couldn't they use the correct and open source Dutch energy system data?"
4th problem: their energy system model is childishly simplistic compared to the Kalavasta study, not specific for the Dutch situation, and based on outdated sources, as admitted by ENCO.
Result: the all important system costs that ENCO adds to wind and solar are much too high.
Result: the all important system costs that ENCO adds to wind and solar are much too high.
By the way: I make energy system models at the @TUeindhoven (NEONresearch.nl) and Zenmo.com. This was the first thing that stood out for me: system costs for wind and solar where unrealistically high, especially for a system with only 50% wind and solar.
Another aside: cheap batteries (as promised on the @Tesla battery day) could not only bring down the system costs for wind and solar even further but also give nuclear a higher capacity factor. It's a novel idea that doesn't get enough airtime I think.
5th problem: no peer review
You can feel the frustration of the Kalavista writers that noticed ENCO mainly has knowledge of security analysis in the nuclear industry. They offered to explain their methodology and maybe review the ENCO study. No response apparently.
You can feel the frustration of the Kalavista writers that noticed ENCO mainly has knowledge of security analysis in the nuclear industry. They offered to explain their methodology and maybe review the ENCO study. No response apparently.

All in all it is VERY unusual that anybody is this harsh about a study commissioned by the government in the Netherlands. That's not because this ENCO study is 'pro nuclear' but simply because it is severely flawed.
Makes me wonder if the nuclear community is a bit out of touch.
Makes me wonder if the nuclear community is a bit out of touch.
I forgot to link to the ENCO study. Here it is with its most important graphic.
rijksoverheid.nl/binaries/rijks…
rijksoverheid.nl/binaries/rijks…
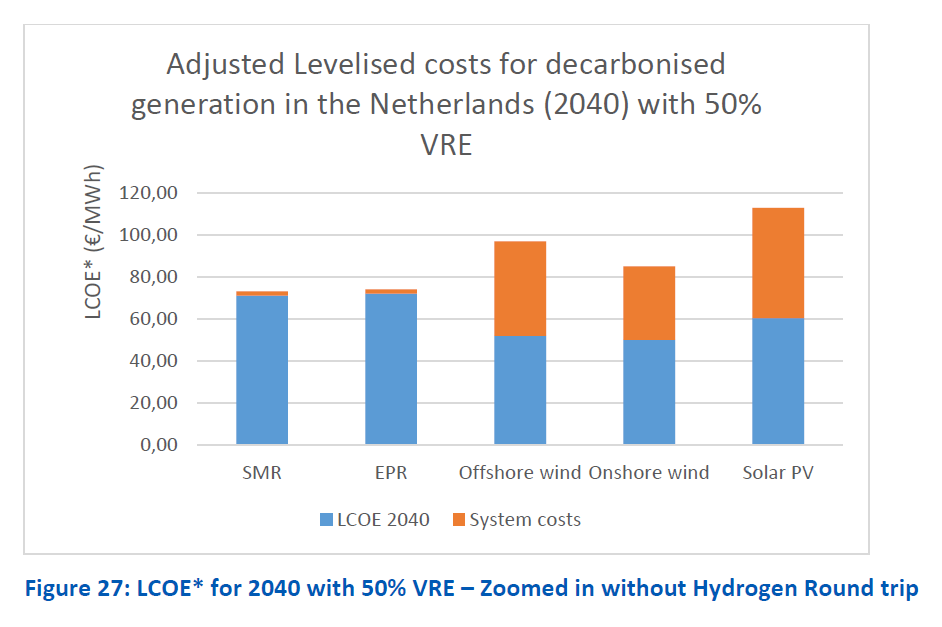
And somehow the omroep.nl link I provided to the Kalavasta rebuttal is not workin for many people. So here is a working link: nvde.nl/wp-content/upl…
I must issue a correction: I said nuclear running 95% of the time meant changing the market rules. That was incorrect. Nuclear could underbid solar and wind (by offering negative prices) and get higher prices when solar&wind where lacking.
Thx @EnzoDiependaal & @JoostGreunsven!
Thx @EnzoDiependaal & @JoostGreunsven!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh











