💥KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in CKD
Tweetorial
☄️Comprehensive Care in DM & CKD
☄️Glycemic Monitoring & Targets
☄️Lifestyle Interventions
☄️Anti-glycemic Rx
👉🏽 tinyurl.com/yyth59kn
1/
@goKDIGO @Kidney_Int
#KDIGO
Tweetorial
☄️Comprehensive Care in DM & CKD
☄️Glycemic Monitoring & Targets
☄️Lifestyle Interventions
☄️Anti-glycemic Rx
👉🏽 tinyurl.com/yyth59kn
1/
@goKDIGO @Kidney_Int
#KDIGO
💥Before reviewing the guidelines, note the difference between the:
⚡️Recommendations
⚡️Practice Points
💥Recommendations are based on strong evidence whereas for the Practice Points the evidence is insufficient or inconclusive👇🏽
2/

⚡️Recommendations
⚡️Practice Points
💥Recommendations are based on strong evidence whereas for the Practice Points the evidence is insufficient or inconclusive👇🏽
2/


💥Comprehensive Care is needed for pts. with DM & CKD to ⬇️ risk of
CV disease & Kidney Disease progression👇🏽
✅ Glycemic Control
✅ BP Control
✅ Lipid Rx
✅ Nutrition
✅ Exercise
✅ Smoking Cessation
🌟RAS Blockade & SGLT2i👇🏽
🌟Anti-platelet Rx👇🏽
3/
CV disease & Kidney Disease progression👇🏽
✅ Glycemic Control
✅ BP Control
✅ Lipid Rx
✅ Nutrition
✅ Exercise
✅ Smoking Cessation
🌟RAS Blockade & SGLT2i👇🏽
🌟Anti-platelet Rx👇🏽
3/

💥 RAS blockade w/ ACEi or ARB is recommended in pts. w/ DM, HTN & Albuminuria & the dose should be titrated to the highest approved dose tolerated by the pt.
⚡️Monitoring of serum creatinine & K during Rx w/ RAS blockers👇🏽
4/
⚡️Monitoring of serum creatinine & K during Rx w/ RAS blockers👇🏽
4/
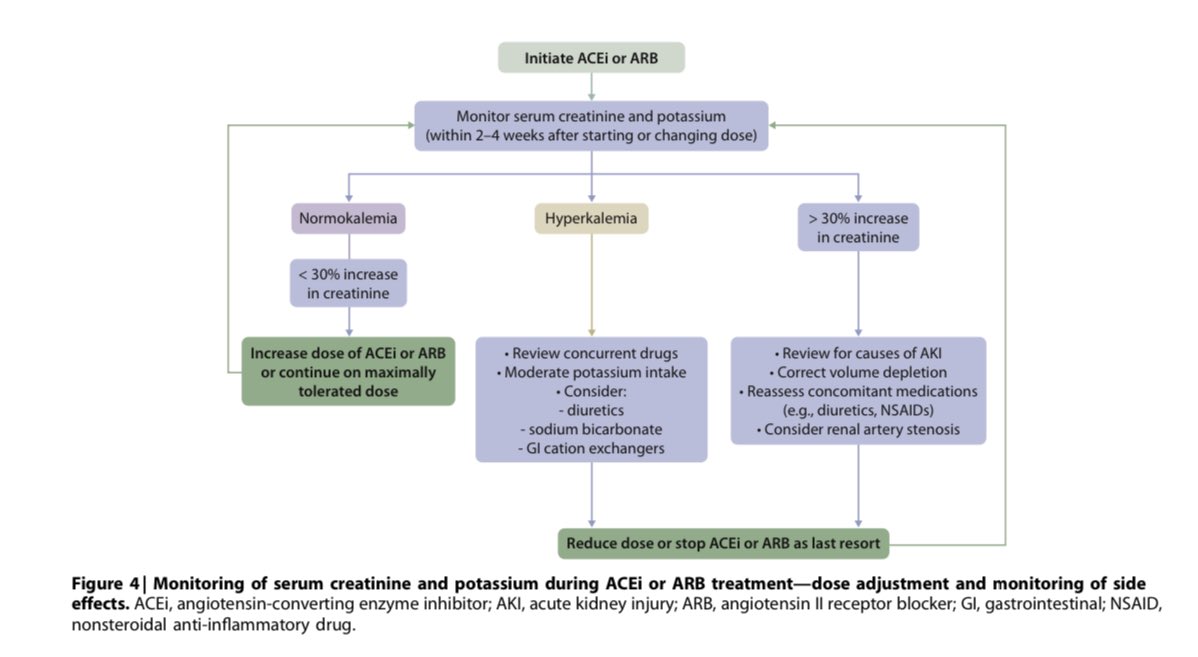
💥RAS blockade may be considered in pts. w/ DM, Albuminuria & no HTN
⚡️Benefits of RAS blockade in this group are less studied but it may be beneficial due to the strong correlation b/w the severity of albuminuria & ESKD in DM
👉🏽 nature.com/articles/hr200…
5/
⚡️Benefits of RAS blockade in this group are less studied but it may be beneficial due to the strong correlation b/w the severity of albuminuria & ESKD in DM
👉🏽 nature.com/articles/hr200…
5/

💥RAS blockade in T1DM patients with no Albuminuria & no HTN is generally not considered beneficial
⚡️In T1DM patients, RAS blockade did not slow progression of CKD or ⬇️ the incidence of albuminuria over 5 years👇🏽
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19571282/
6/
⚡️In T1DM patients, RAS blockade did not slow progression of CKD or ⬇️ the incidence of albuminuria over 5 years👇🏽
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19571282/
6/

💥RAS Blockade in T2DM w/ no Albuminuria & no HTN is gen. not considered beneficial
⚡️One study showed ⬇️ in incident albuminuria but ⬆️CV events👇🏽
⚡️Another review showed benefit in normoalbuminuric pts. on albuminuria progression but most pts. had HTN👇🏽
7/

⚡️One study showed ⬇️ in incident albuminuria but ⬆️CV events👇🏽
⚡️Another review showed benefit in normoalbuminuric pts. on albuminuria progression but most pts. had HTN👇🏽
7/


💥Here is a list of the different formulations of ACEi & ARBs:
⚡️Recommended starting dose
⚡️Recommended max. daily dose
⚡️Dose adjustment in CKD
⚡️Removal during hemodialysis
8/
⚡️Recommended starting dose
⚡️Recommended max. daily dose
⚡️Dose adjustment in CKD
⚡️Removal during hemodialysis
8/

💥Glycemic Monitoring & Target
⚡️Monitor HbA1c 2x/year or more often if BG control is poor
⚡️Target AIC: <6.5% to <8.0%
⚡️Accuracy of HbA1c is ⬇️ in CKD esp. in ESKD👇🏽
⚡️Continuous Glucose Monitoring can be used when A1c is not reliable👇🏽
9/



⚡️Monitor HbA1c 2x/year or more often if BG control is poor
⚡️Target AIC: <6.5% to <8.0%
⚡️Accuracy of HbA1c is ⬇️ in CKD esp. in ESKD👇🏽
⚡️Continuous Glucose Monitoring can be used when A1c is not reliable👇🏽
9/

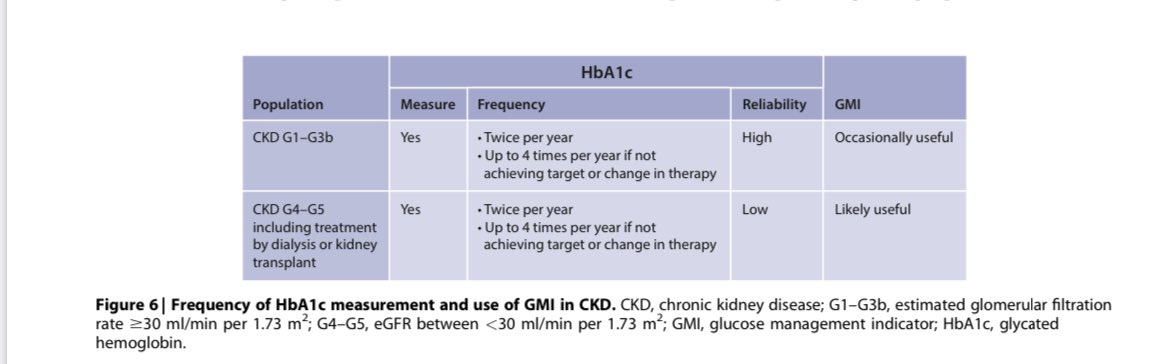


💥Lifestyle Interventions
❇️ Protein intake:
⚡️0.8 g/kg/day in pts. w/ DM & Non-dialysis CKD
⚡️1.0-1.2 g/kg/day for pts. on dialysis👇🏽
❇️ Sodium intake <2 g/day (<5 g NaCl/day)👇🏽
❇️ Physical Activity of moderate intensity for at least 150 min./wk
10/



❇️ Protein intake:
⚡️0.8 g/kg/day in pts. w/ DM & Non-dialysis CKD
⚡️1.0-1.2 g/kg/day for pts. on dialysis👇🏽
❇️ Sodium intake <2 g/day (<5 g NaCl/day)👇🏽
❇️ Physical Activity of moderate intensity for at least 150 min./wk
10/




💥 Anti-glycemic Rx in Pts. w/ T2DM & CKD
⚡️Lifestyle therapy:
☄️Exercise, Nutrition & Wt. loss
⚡️1st-line Drug Rx:
☄️Metformin + SGLT2i
⚡️Additional Drug Rx is guided by patient preference, comorbidities, eGFR & cost
☄️GLP-1 RA is preferred👇🏽
11/

⚡️Lifestyle therapy:
☄️Exercise, Nutrition & Wt. loss
⚡️1st-line Drug Rx:
☄️Metformin + SGLT2i
⚡️Additional Drug Rx is guided by patient preference, comorbidities, eGFR & cost
☄️GLP-1 RA is preferred👇🏽
11/


💥T2DM + CKD pts. w/ eGFR of
> or = 30 ml/min benefit from both Metformin & SGLT2i
⚡️Metformin: good anti-glycemic effect but modest impact on long term DM complications
⚡️SGLT2i: weak anti-glycemic effect but large effect on ⬇️ CKD progression & CVD
12/
> or = 30 ml/min benefit from both Metformin & SGLT2i
⚡️Metformin: good anti-glycemic effect but modest impact on long term DM complications
⚡️SGLT2i: weak anti-glycemic effect but large effect on ⬇️ CKD progression & CVD
12/
💥DAPA-CKD Trial was published on 9/24/20
⚡️KDIGO guidelines were written prior to DAPA-CKD publication & will be updated to reflect the eGFR cutoff
⚡️Dapagliflozin showed renal benefit in CKD w/ & w/o T2DM w/ eGFR of 25-75 ml/min & ACR 200 mg/g or > 👇🏽
13/
⚡️KDIGO guidelines were written prior to DAPA-CKD publication & will be updated to reflect the eGFR cutoff
⚡️Dapagliflozin showed renal benefit in CKD w/ & w/o T2DM w/ eGFR of 25-75 ml/min & ACR 200 mg/g or > 👇🏽
13/

💥In drug naive pts. (those not on Metformin or SGLT2i), which drug should be started first?
☄️No high-quality data comparing initiation of Metformin vs. initiation of SGLT2i
☄️In most large trials, SGLT2i was added to Metformin
14/
☄️No high-quality data comparing initiation of Metformin vs. initiation of SGLT2i
☄️In most large trials, SGLT2i was added to Metformin
14/
💥In drug naive pts (not on Metformin or SGLT2i):
1. Start Metformin & add SGLT2i
2. It may be practical to start low dose of both agents to manage glycemia & get organ protection benefits of SGLT2i👇🏽
⚡️Metformin & SGLT2i dose adjustment in CKD👇🏽
15/

1. Start Metformin & add SGLT2i
2. It may be practical to start low dose of both agents to manage glycemia & get organ protection benefits of SGLT2i👇🏽
⚡️Metformin & SGLT2i dose adjustment in CKD👇🏽
15/


💥If a pt. w/ T2DM + CKD w/ eGFR of >30ml/min is achieving glycemic target w/ Metformin alone:
⚡️Then try to lower the Metformin dose & add SGLT2i
⚡️Addition of SGLT2i is unlikely to cause hypoglycemia but yet offer the Kidney & CV benefits
16/
⚡️Then try to lower the Metformin dose & add SGLT2i
⚡️Addition of SGLT2i is unlikely to cause hypoglycemia but yet offer the Kidney & CV benefits
16/
💥Based on current evidence:
⚡️Metformin must be stopped if eGFR drops to <30 ml/min
⚡️If Canagliflozin is initiated at eGFR of >30 ml/min, then it can be continued till the start of kidney replacement therapy (as was done in the CREDENCE Trial)
17/

⚡️Metformin must be stopped if eGFR drops to <30 ml/min
⚡️If Canagliflozin is initiated at eGFR of >30 ml/min, then it can be continued till the start of kidney replacement therapy (as was done in the CREDENCE Trial)
17/


💥If glycemic target is NOT met w/ Metformin + SGLT2i then GLP-1 RA is preferred because of it’s demonstrated CV benefits & possible kidney benefits👇🏽
⚡️Consider Pt. Factors when selecting a glucose lowering drug to add to Metformin & SGLT2i👇🏽
18/
⚡️Consider Pt. Factors when selecting a glucose lowering drug to add to Metformin & SGLT2i👇🏽
18/

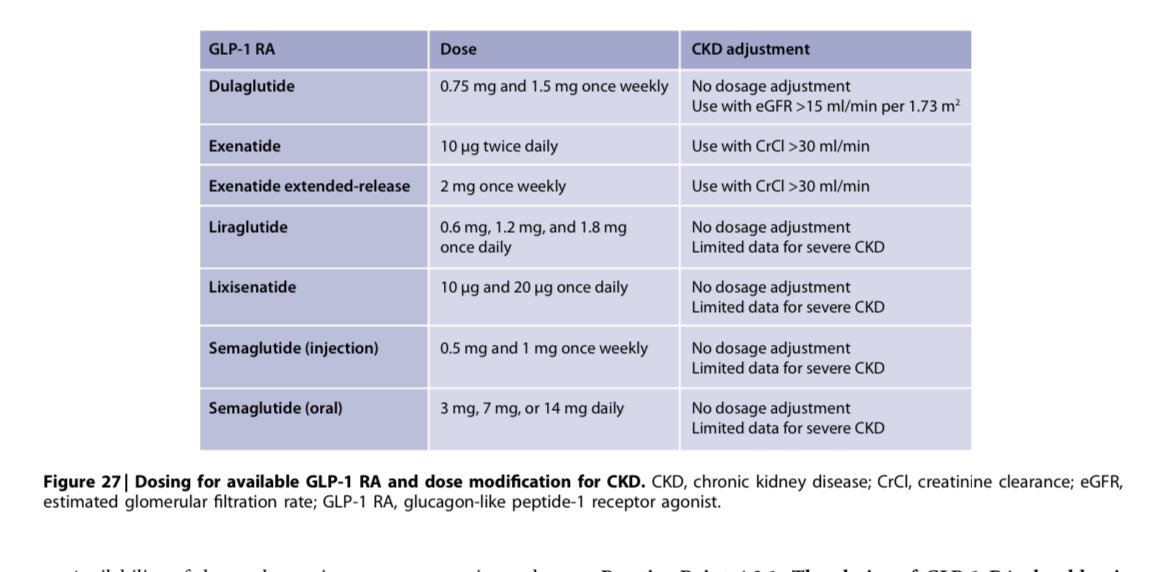
💥Most GLP-1 RA are injectable drugs except Semaglutide
⚡️Side effects include GI symptoms
⚡️Contraindicated in pts. w/ h/o medullary thyroid ca, MEN-2, acute pancreatitis
⚡️GLP-1 RA should NOT be used w/ DPP-4 Inh.
⚡️GLP-1 RA dose adjustment in CKD👇🏽
19/
⚡️Side effects include GI symptoms
⚡️Contraindicated in pts. w/ h/o medullary thyroid ca, MEN-2, acute pancreatitis
⚡️GLP-1 RA should NOT be used w/ DPP-4 Inh.
⚡️GLP-1 RA dose adjustment in CKD👇🏽
19/
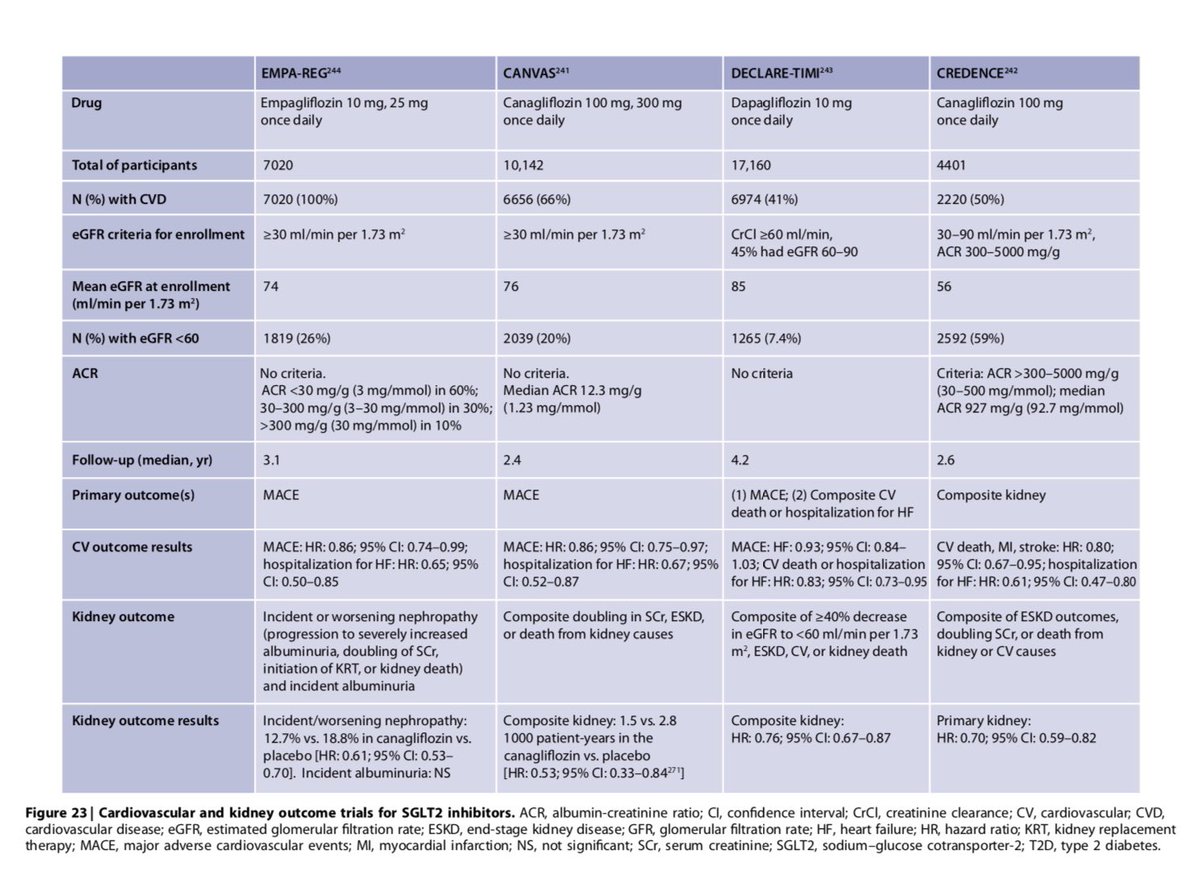
💥Large Trial Data - Summary
⚡️Overview of the large, placebo-controlled trials assessing the benefits of SGLT2i, GLP-1 RA & DPP-4 inhibitors👇🏽
⚡️CV & Kidney Outcome Trials for SGLT2i👇🏽
⚡️CV & Kidney Outcome Trials for GLP-1 RA👇🏽
20/


⚡️Overview of the large, placebo-controlled trials assessing the benefits of SGLT2i, GLP-1 RA & DPP-4 inhibitors👇🏽
⚡️CV & Kidney Outcome Trials for SGLT2i👇🏽
⚡️CV & Kidney Outcome Trials for GLP-1 RA👇🏽
20/


💥Summary of DM management in CKD
⚡️Comprehensive Care
⚡️Lifestyle Interventions
⚡️RAS Blockade
⚡️T2DM: Initiate metformin & SGLT2i if eGFR criteria met
⚡️T2DM: If BG target not reached w/ Metformin + SGLT2i then GLP-1 RA is preferred
21/
⚡️Comprehensive Care
⚡️Lifestyle Interventions
⚡️RAS Blockade
⚡️T2DM: Initiate metformin & SGLT2i if eGFR criteria met
⚡️T2DM: If BG target not reached w/ Metformin + SGLT2i then GLP-1 RA is preferred
21/
💥Here is the link to the complete KDIGO 2020 Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease
👉🏽 tinyurl.com/yyth59kn
💥Link to the Executive Summary of the 2020 KDIGO Diabetes Management in CKD Guideline
👉🏽 tinyurl.com/yydxghoy
End/

👉🏽 tinyurl.com/yyth59kn
💥Link to the Executive Summary of the 2020 KDIGO Diabetes Management in CKD Guideline
👉🏽 tinyurl.com/yydxghoy
End/


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




















