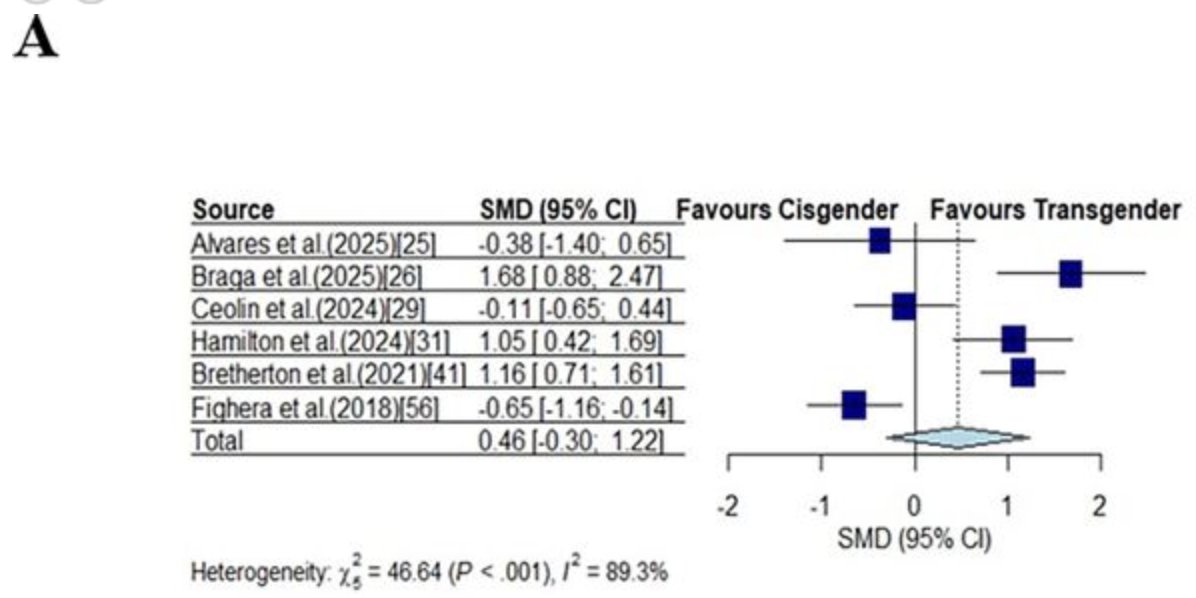
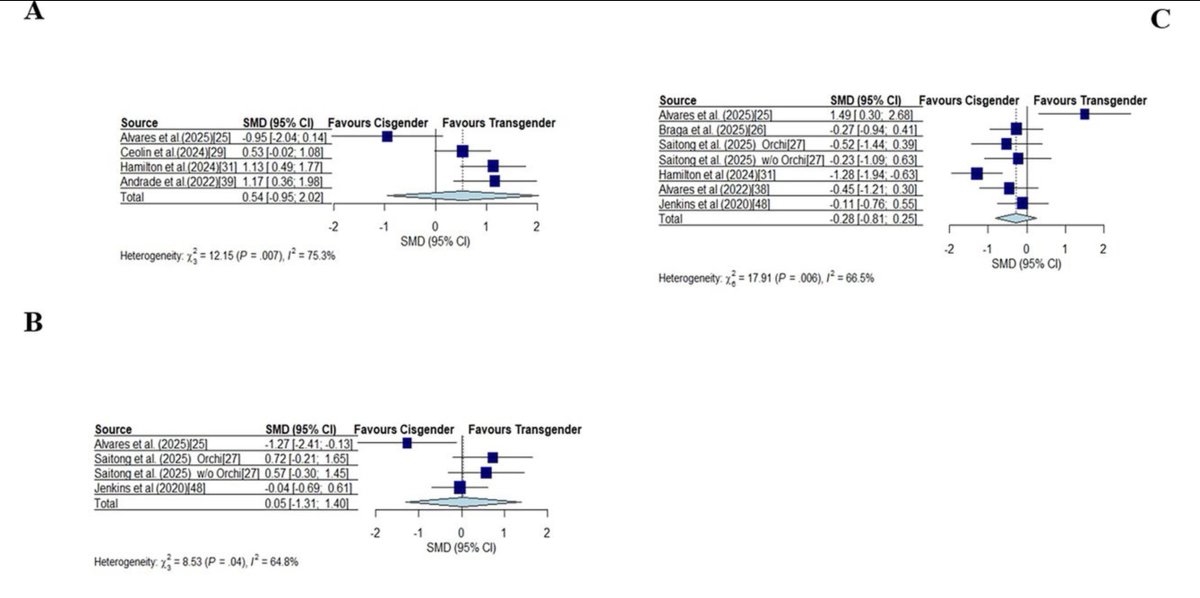
I am delighted to announce that Hilton and Lundberg, 2020 is now published! @TLexercise
‘Transgender Women in the Female Category of Sport: Perspectives on Testosterone Suppression and Performance Advantage’
link.springer.com/article/10.100…
‘Transgender Women in the Female Category of Sport: Perspectives on Testosterone Suppression and Performance Advantage’
link.springer.com/article/10.100…

Anyone wishing to spot changes from our pre-print:
1. We included a section on pre-pubertal differences (that is, even young boys outperform young girls, thus the performance gap is not solely down to pubertal T).
1. We included a section on pre-pubertal differences (that is, even young boys outperform young girls, thus the performance gap is not solely down to pubertal T).
2. We extended our analysis of CV capacity changes and potential impact on endurance performance (although we had acknowledged a likely effect, we have drilled deeper into mechanism).
3. We have *significantly* extended our discussion of impact on athlete transwomen and the mitigating effects of exercise (that is, moderate training can mitigate or even reverse muscle/strength loss during T suppression).
The remaining differences are minor, and represent no significant change from the pre-print.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh