Last year the Geneva-based Mixed Migration Centre commissioned me to look into the effects of the pandemic on urban migrants. Months of research showed me that COVID-19 is an "arrival city" disease like no other before.
Allow me to discuss what I found.
mixedmigration.org/articles/hot-z…
Allow me to discuss what I found.
mixedmigration.org/articles/hot-z…
After drawing on large-scale data from the IOM, OECD, the World Bank and national- or local-level data from hundreds of sources and studies, here's what I found: Pandemics have always hit the nexus of migration and cities, but none to the extent, or in the manner, of this one 

I found three major worldwide effects of the pandemic on urban migration-origin communities:
- Concentration of infection in immigration districts
- The largest 'reverse migration' event in history
- Huge stranded populations of noncitizen migrants
I'll discuss in detail.
- Concentration of infection in immigration districts
- The largest 'reverse migration' event in history
- Huge stranded populations of noncitizen migrants
I'll discuss in detail.

I should note that many of the migrants and migration districts affected involve 'internal' or regional rural-to-urban migrant populations, who are majorities in some East Asian and African cities.
Human movement has always been related to the spread of epidemics--as have big cities (though rural areas are often hit harder).
Leaders naively assume shutting borders will halt the spread. In fact, it usually amplifies it. I wrote about this last year
foreignaffairs.com/articles/canad…
Leaders naively assume shutting borders will halt the spread. In fact, it usually amplifies it. I wrote about this last year
foreignaffairs.com/articles/canad…
Immigration has never been a big source of disease spread. (It's the travel of domestic populations--business and tourism).
eg the million migrants who entered Europe 2015-16 caused no measurable rise in infectious disease rates, per several studies:
ijidonline.com/article/S1201-…
eg the million migrants who entered Europe 2015-16 caused no measurable rise in infectious disease rates, per several studies:
ijidonline.com/article/S1201-…
But historically, DOMESTIC flight from cities has been a big factor in spreading disease--and it's been the well-off and privileged doing it.
It has hurt them. For instance, in the 1918 pandemic, mortality in cities was 1 in 100, in rural areas 1 in 10.
sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/…
It has hurt them. For instance, in the 1918 pandemic, mortality in cities was 1 in 100, in rural areas 1 in 10.
sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/…
I've also written about the intuition-challenging fact that cities are almost always safer than rural areas during pandemics.
But what happened in 2020 was many countries created a lot of strong incentives for people to try to flee cities.
theglobeandmail.com/opinion/articl…
But what happened in 2020 was many countries created a lot of strong incentives for people to try to flee cities.
theglobeandmail.com/opinion/articl…
So, why is COVID-19 more of an urban-migrant pandemic than previous one? A body of research (ie this study) shows that the migration dimensions are much more intense than even the SARS epidemic of 2003.
I identify three key reasons.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
I identify three key reasons.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
FIRST, the demographics are different. The number of cities with majority or plurality migration-origin populations--who maintain physical and communication links to their origin places--has grown A LOT since 2000, especially in Asia and Africa.
un.org/en/development…
un.org/en/development…
SECOND, long-distance quick travel is far more available and affordable. The number of international air passengers per year has risen from 2 billion in 2004 to 4.5 billion in 2019 -- and the largest share of that growth is in Asia-Pacific.
statista.com/statistics/564…
statista.com/statistics/564…
THIRD and I think most crucially, migration-origin communities, even extremely poor ones, are able to stay linked electronically, to their villages and one another
eg Africans using mobile phones rose from 0.67 per 100 in 2000 to ~83 per 100 today.
eg Africans using mobile phones rose from 0.67 per 100 in 2000 to ~83 per 100 today.
As a consequence of these three changes, this has been the first global pandemic where the people fleeing cities have not been the privileged and wealthy but the urban poor. And they're not fleeing the disease itself but the loss of economic opportunities. We'll get into this.
We got a preview of this during the West African *regional* Ebola pandemic in 2014-15.
Despite intense efforts by governments to restrict movement, urban-rural movement rates actually registered HIGHER than typical years -- for those three reasons
reliefweb.int/sites/reliefwe…
Despite intense efforts by governments to restrict movement, urban-rural movement rates actually registered HIGHER than typical years -- for those three reasons
reliefweb.int/sites/reliefwe…
So let's look at the three big effects of the pandemic on urban migrant communities.
A key argument of mine: A huge error has been a policy focus on immigrants/domestic migrants while they're moving/settling. What we've neglected is the ALREADY SETTLED communities; they're key
A key argument of mine: A huge error has been a policy focus on immigrants/domestic migrants while they're moving/settling. What we've neglected is the ALREADY SETTLED communities; they're key
ONE--the concentration of COVID-19 infection in immigration-settlement districts ("arrival cities").
In developed countries, due to the "suburbanization of immigration" over the last 20 years, this has made it a disease overwhelmingly of inner-suburban apartment districts

In developed countries, due to the "suburbanization of immigration" over the last 20 years, this has made it a disease overwhelmingly of inner-suburban apartment districts


If you want more detail on this, I wrote about it in some detail last summer. Note how COVID maps almost perfectly on skin colour and income -- a good proxy for immigration background in those cities.
https://twitter.com/DougSaunders/status/1299807185493524480?s=20
What's SIGNIFICANT is that tracing data appear to show these districts haven't become "disease sinks" because of the kinds of people or their housing (though HVAC in low-cost rental apartment units deserves a close look).
Rather, it's their role in the economy. "Essential."
Rather, it's their role in the economy. "Essential."
Traditionally these were "stepping-stone" neighbourhoods -- you got out, after maybe a generation. Rising housing prices have protracted this. And, ie per this economic study, prices can drive up infection-concentrating "disease segregation" effects
cambridge.org/core/journals/…
cambridge.org/core/journals/…
What about in less wealthy countries? There, we've seen a powerful concentration of the disease in slums, favelas and other informal settlements -- which are places of settlement for internal and regional rural-urban migrants. 
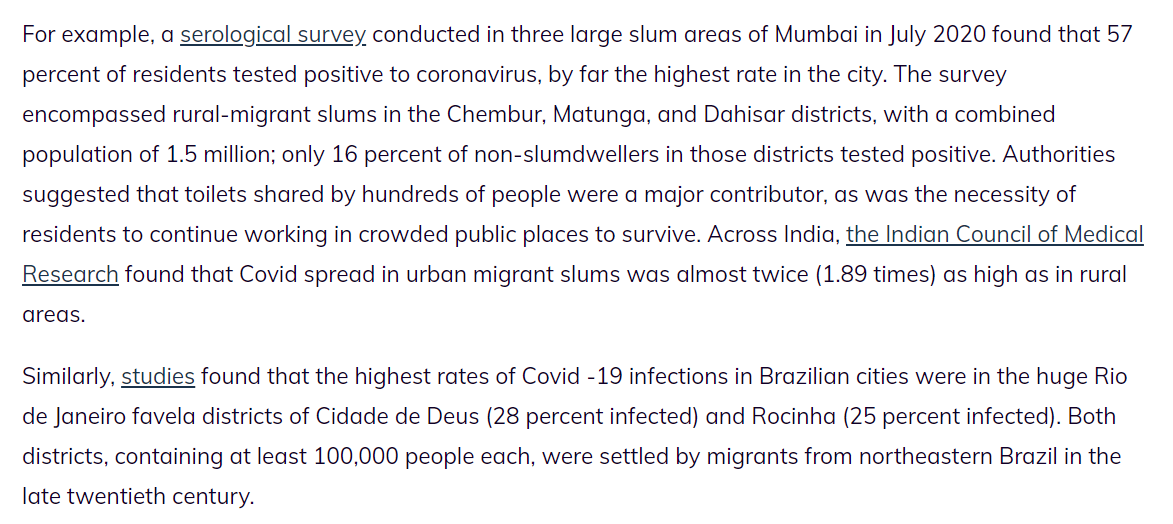
Worse than the infection rates in slums are the economic effects of curfew, which causes infection-spreading out-migration, amplified by governments using pandemic as cover to demolish settlements and scatter people.
theglobeandmail.com/opinion/articl…
theglobeandmail.com/opinion/articl…
(The fact that a large proportion of slum-dwellers are employed in domestic service in wealthier areas means that the slums are both vectors of infection in better-off neighbourhoods, but also that families can be ruined and flee to villages if their employers hard-quarantine)
TWO--the huge urban-to-rural migration.
This time it's not the elite. And it's not people fleeing the disease, but people fleeing the disease economy.
Scholars were pointing out in 2009 that quarantine measures in a tech society will drive out-migration
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
This time it's not the elite. And it's not people fleeing the disease, but people fleeing the disease economy.
Scholars were pointing out in 2009 that quarantine measures in a tech society will drive out-migration
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
As the World Bank noted this summer, we've seen "a chaotic and painful process of mass return" that has "disproportionately affected internal migrant workers" 

India might have had the biggest reverse migration--"the second largest exodus since Partition." How large? We'll never know, because India tried to ban movement, so people fled at night and discreetly. Sometimes virus-fearing villages beat them back.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
But I also looked at Peru and many sub-Saharan countries, where stealth reverse migrations were very big. 

So, what about non-poor countries. We read a lot about people migrating out of cities in the West. Were they return migrations?
There were shock urban-rural migrations -- for example, a million people probably left Paris:
leparisien.fr/high-tech/17-d…
There were shock urban-rural migrations -- for example, a million people probably left Paris:
leparisien.fr/high-tech/17-d…
And in northern Italy, when rumours of the coming lockdown spread through text messages, huge throngs of people rushed to the trains to go back to their family villages in the south
theguardian.com/world/2020/mar…
theguardian.com/world/2020/mar…
Unlike in poor countries, those urban-rural returns tended to be better-off people and were considerably smaller in scale. But data showed that they played a big role in virus spread--18% of Italy's first-wave deaths can be attributed to return migration
voxeu.org/article/intern…
voxeu.org/article/intern…
So, given how much back-to-village migration contributed to spread, is the solution to restrict it more?
Not necessarily. In Wuhan, this study shows travel bans only slowed spread 3-5 days. Distancing, handwashing, contact tracing etc did more.
science.sciencemag.org/content/368/64…
Not necessarily. In Wuhan, this study shows travel bans only slowed spread 3-5 days. Distancing, handwashing, contact tracing etc did more.
science.sciencemag.org/content/368/64…
And this econometric study of 135 countries found "no effects" on disease spread caused by “international travel controls, public transport closures and restrictions on movements across cities and regions."
iza.org/publications/d…
iza.org/publications/d…
Given the strong risk that movement restrictions will ampify rather than attenuate disease spread, it's better, I conclude, to use policy to address "the predominantly economic anxieties that motivate internal migrants to seek flight during a pandemic."
THREE
Least reported upon of the three effects is the huge number of long-term migrants who were and are trapped in places where they have no citizenship and suddenly have no means of economic livelihood.
Such people are MAJORITIES in many Gulf cities
Least reported upon of the three effects is the huge number of long-term migrants who were and are trapped in places where they have no citizenship and suddenly have no means of economic livelihood.
Such people are MAJORITIES in many Gulf cities

In September, the IOM estimated that there were still 2.75 million people facing this flight -- and this was AFTER countries like India had completed military missions to rescue large numbers of stranded labour-migrant nationals
iom.int/news/immediate…
iom.int/news/immediate…
Scholars refer to the "involuntary immobile." They faced a perfect storm in Mexico, where
- huge numbers of northbound Central Am. migrants were stranded at the closed US border
- The US deported at least 40K people southward
- Many gave up refuge attempts and flooded cities
- huge numbers of northbound Central Am. migrants were stranded at the closed US border
- The US deported at least 40K people southward
- Many gave up refuge attempts and flooded cities

One consequence was the collapse of remittance flows -- which are the largest source of income in poor countries and regions, far larger than all foreign aid combined.
The @WorldBank estimates a 20% drop--a loss of $109 billion to vulnerable regions
worldbank.org/en/news/press-…
The @WorldBank estimates a 20% drop--a loss of $109 billion to vulnerable regions
worldbank.org/en/news/press-…
In conclusion, all three of the populations I discuss here fall outside what is usually considered "migration governance." Settled migration-district populations, reverse-migrant groups, stranded populations -- that's where the pandemic hit hardest. As might the next big crisis 

If you'd like a downloadable copy of this paper, with full references, I've posted one here
researchgate.net/publication/34…
researchgate.net/publication/34…
It appears alongside a lot of even more interesting research in the 2020 MIXED MIGRATION REVIEW
(Published by the Mixed Migration Centre, which is part of the Danish Refugee Council)
Well worth downloading a copy:
mixedmigration.org/resource/mixed…
(Published by the Mixed Migration Centre, which is part of the Danish Refugee Council)
Well worth downloading a copy:
mixedmigration.org/resource/mixed…
For more detail on the concentration of COVID and segregation in the same neighbourhoods --
I also a policy brief on how to prevent urban-periphery neighbourhoods becoming "trap districts," drawing on the international workshops on this I held in June.
robertboschacademy.de/en/perspective…
I also a policy brief on how to prevent urban-periphery neighbourhoods becoming "trap districts," drawing on the international workshops on this I held in June.
robertboschacademy.de/en/perspective…
My 4 recommendations here:
- Recognize the new importance of specific neighborhoods for immigration settlement and integration
- Make physical mobility easier for residents
- Invest in opportunities for advancement WITHIN neighborhoods
- Give the next generation a better chance
- Recognize the new importance of specific neighborhoods for immigration settlement and integration
- Make physical mobility easier for residents
- Invest in opportunities for advancement WITHIN neighborhoods
- Give the next generation a better chance
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh








