This month US Americans got a small glimpse of what a coup might feel like, and they are rightly outraged. One might hope this would provoke some reflection on the *actual* coups that the US itself has perpetrated around the world. Here are some of them:
1953: Mohammed Mossadegh, the progressive, democratically elected leader of Iran, was deposed in a US- and British-backed coup because he sought to restore national control over Iran's oil reserves. 
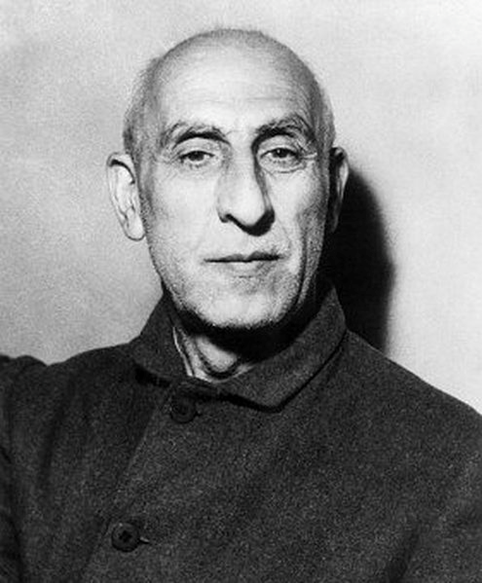

1954: Jacobo Árbenz, the progressive, democratically elected leader of Guatemala, was deposed in a US-backed coup because he sought to restore land to small farmers and Indigenous communities that had been dispossessed by US fruit companies. 
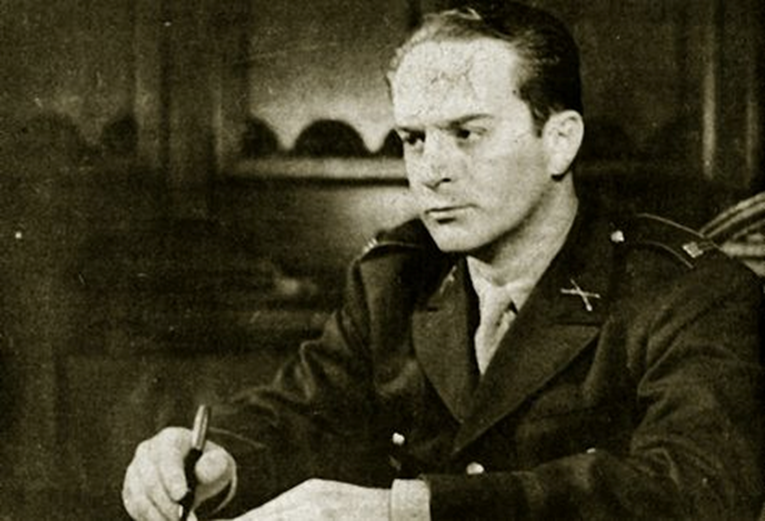

1961. Patrice Lumumba, the first democratically elected leader of the Republic of Congo, was assassinated in a coup backed by the US, UK and Belgium, because he sought to restore control over the country's mineral reserves. They installed the Mobutu dictatorship in his place. 

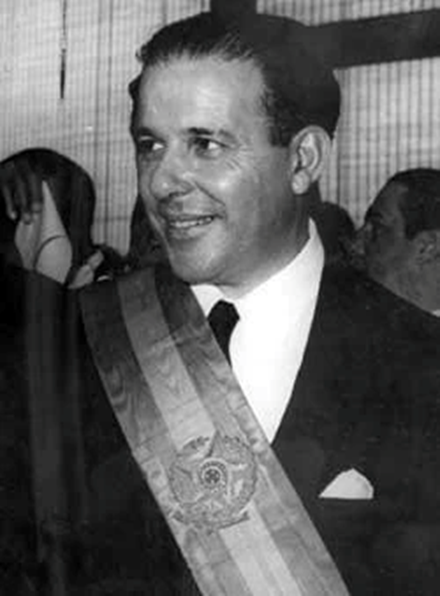
1964. João Goulart, the progressive, democratically elected leader of Brazil, was deposed by a US-backed coup and replaced with a right-wing military junta. 

1967. Sukarno, the first leader of independent Indonesia, was deposed in a US-backed coup that installed a right-wing military dictatorship. As part of this operation, the US collaborated in the massacre of 500,000 left-wing peasants and workers. 
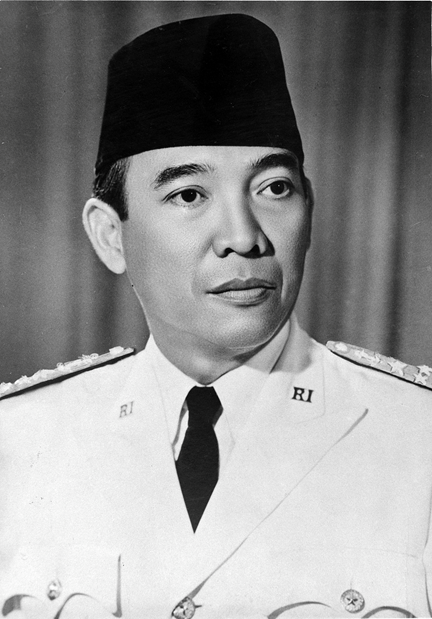

1973. Salvadore Allende, the progressive, democratically elected leader of Chile, was deposed and assassinated in a US-backed coup that installed the right-wing dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet. 
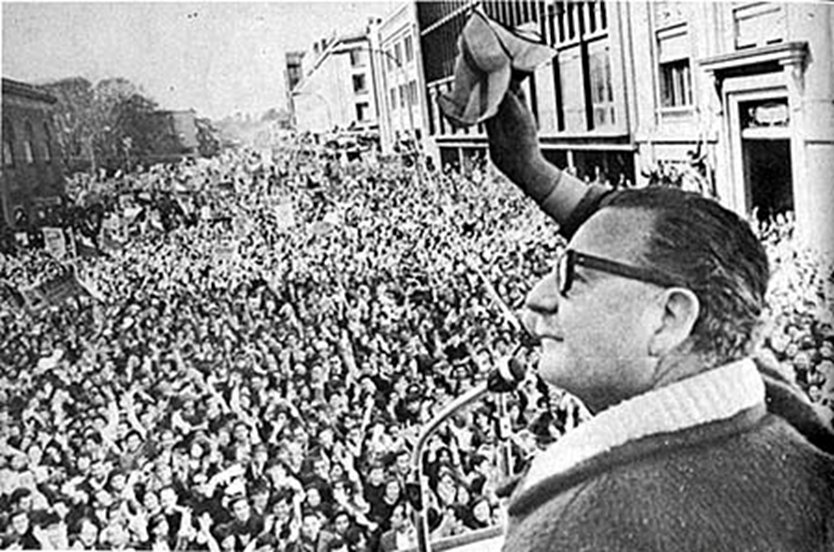

This is not distant history. The US has been involved in coups and attempted coups against elected governments in the South well into the 21st century. US legislators are lining up to defend the "sacredness" of democracy, but unfortunately this standard is selectively applied.
If you want to know more about this story, I cover it in a chapter titled "From colonialism to the coup" in The Divide, looking not just at interventions by the US but also by Britain and France. penguin.co.uk/books/111/1113…
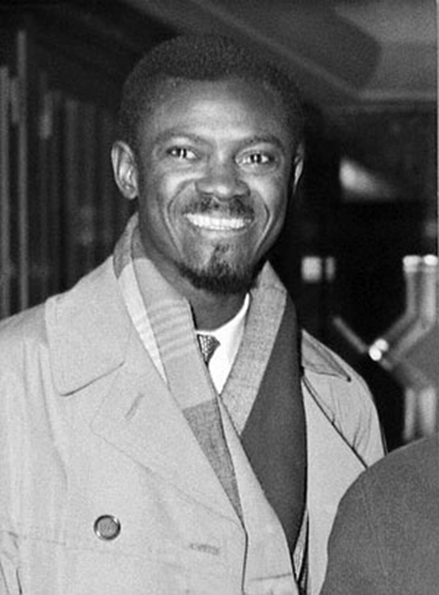
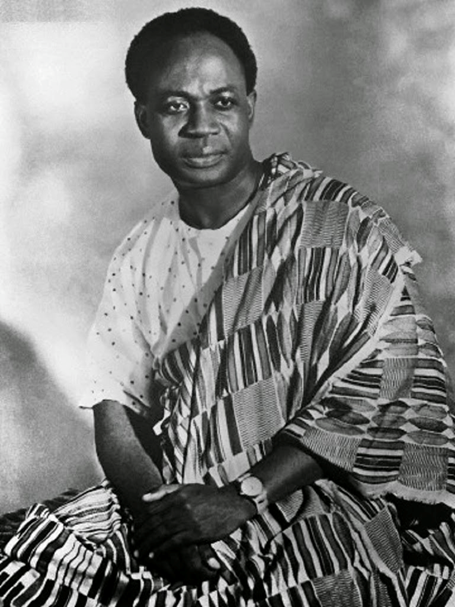
Another one I want to include: 1966. Kwame Nkrumah, the first leader of independent Ghana, co-founder of the Non-Aligned Movement and author of the book "Neocolonialism", was deposed in a coup backed by the US and Britain. 

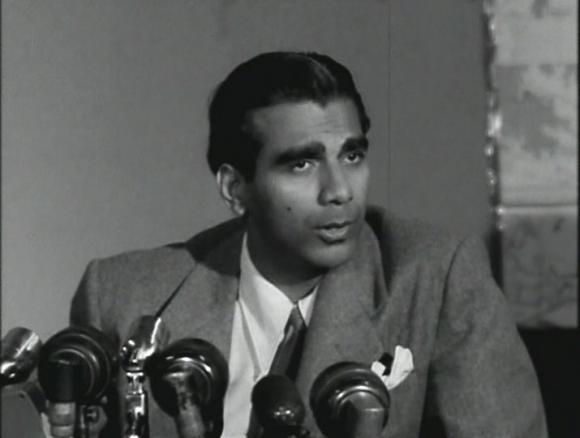
1964. Cheddi Jagan, the popular progressive leader of British Guiana, was removed from power by the US and UK. This was the second time Jagan was deposed; the first was in 1953, days after he won the election, in a coup orchestrated by Winston Churchill. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh