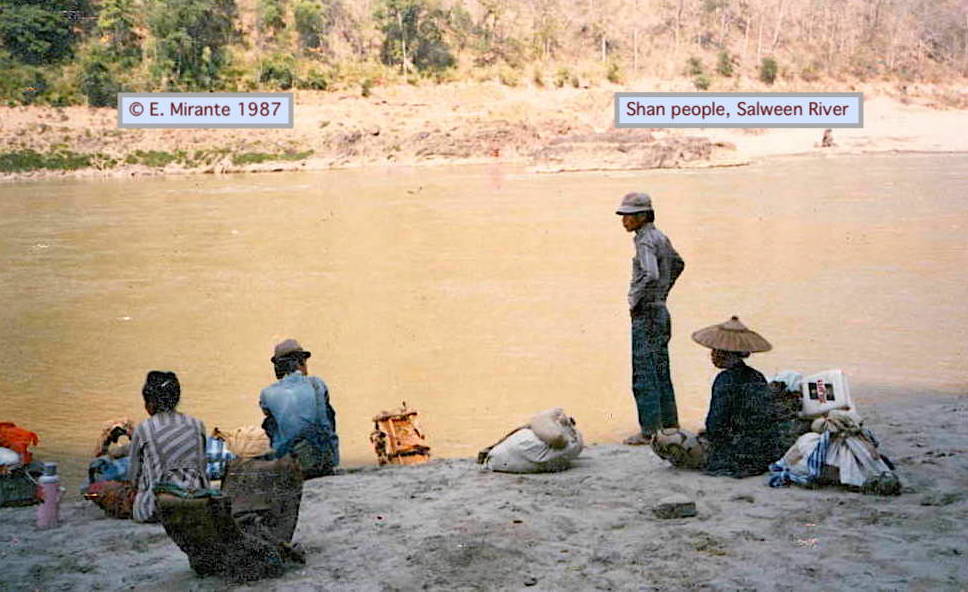
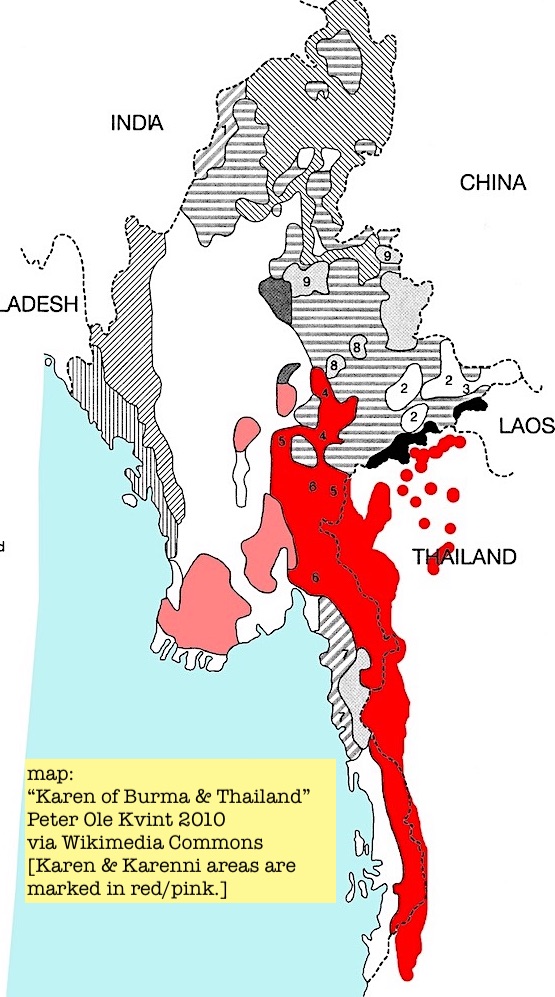
1. This History Thread is about sabotage in Burma (Myanmar) from cutting British colonial telegraph lines to hacking websites. Sabotage as a tactic is: destroying or damaging infrastructure or other property (not people) to prevent use by an opponent.
#WhatsHappeningInMyanmar 🌿
#WhatsHappeningInMyanmar 🌿

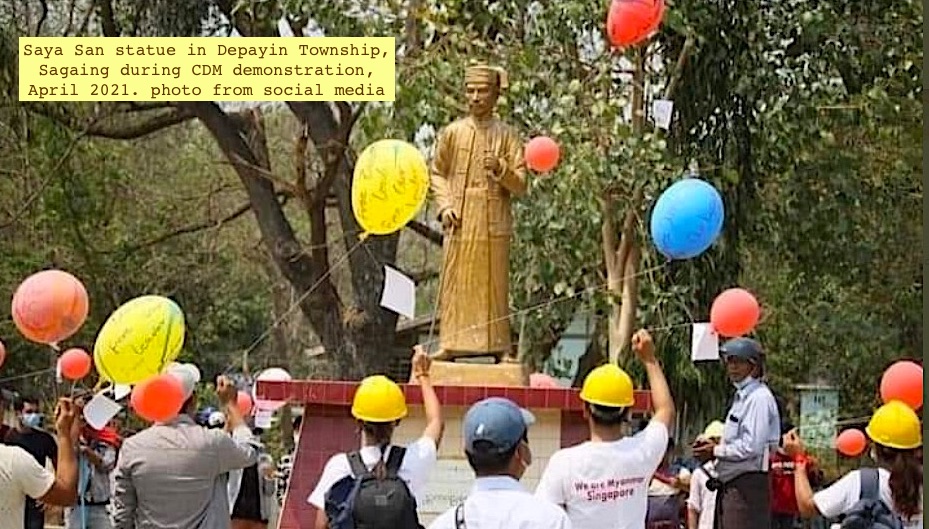
2. From 1880s through 1930s there were rebellions against British colonial rule in Burma. Saya San rebellion 1930-32 challenged British control w. tactics including destroying cutting telegraph lines & destroying telegraph stations, timber industry facilities & railway bridges. 

3. World War 2, as Japanese forces invaded Burma 1942, British 17th Indian Infantry Div. attempted to halt Japanese advance on Rangoon in battle at Sittang River. British destroyed Sittang bridge but that stranded 17th & other units in a major defeat. thisworldrocks.com/war-history/un…
4. WW2, March 1942 as Japanese forces were about to occupy Rangoon, British destroyed docks & oil depot so Japanese couldn’t use them. April ‘42 when British & Chinese troops lost Yenanyaung oil fields to Japanese, they set fire to the oil wells and refinery before they withdrew. 

5. Japanese occupation troops used logs, landmines to block/damage roads. Allied units like British Special Operations Executive, Chindits & US Det. 101 (included Kachins, Karens & others from Burma) conducted sabotage missions blowing up Japanese ammo storage, railways, bridges. 

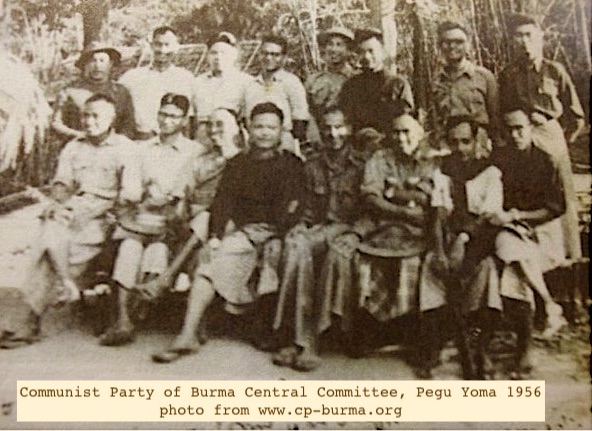
6. Post WW2 in independent Burma, 1950s-60s Communists (CPB) & Ethnic Armed Organizations (EAOs) incl. Karen National Union (KNU) & Karen National United Party conducted wide-ranging sabotage raids, sometimes jointly, severing roads, railways, bridges in Delta, Pegu Yoma, Arakan. 

7. 1970s New Mon State Party + U Nu’s Patriotic Liberation Army (PLA) sabotaged railway lines & KNU + PLA blew up power lines from Karenni St. hydroelectric Lawpita to Rangoon. Much later, in 2005 Karenni National Progressive Party (KNPP) destroyed Lawpita electric supply pylon. 

8. 1990s in partnership w. Myanmar (Burma) military junta, Total (France) PTT (Thailand) & Unocal (US later Chevron) built gas pipeline across SE Myanmar to Thailand despite sabotage threats. In 2003 Karen National Union sabotaged a domestic gas pipeline. ogj.com/pipelines-tran… 

9. Myanmar domestic Kanbauk-Myaingkalay gas pipeline (offshore to cement factories) exploded 2006. Locals were arrested for sabotaging it incl. a New Mon State Party (NMSP) member. But numerous ruptures before & since happened due to faulty construction. bnionline.net/en/independent… 

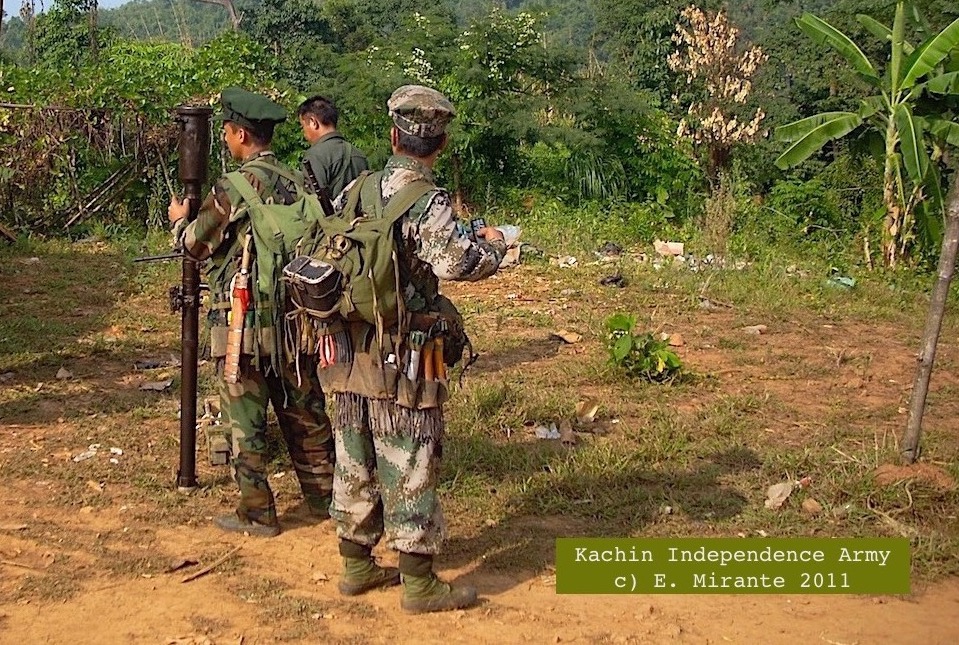
10. When Myanmar military broke 17 yr ceasefire w. Kachin Independence Army in 2011, KIA strategy immediately included sabotaging bridges, roads, railway. By 2012 Myanmar military claimed airstrikes were "necessary" because of KIA damaging infrastructure. newmandala.org/bridges-bombed… 

11. In August 2019 Northern Alliance EAOs including Ta’ang National Liberation Army (TNLA) damaged/destroyed 4 bridges during their coordinated Shan State raids. asiatimes.com/2019/08/myanma…
12. In 2019 Northern Alliance member Arakan Army (AA) used improvised explosive devices to damage Yangon-Sittway highway & bridge in Rakhine State. Also in 2019 AA destroyed construction materials being shipped for Paletwa Bridge (Chin State) construction. 

13. While Myanmar to China gas & oil pipelines were being built in 2014, conflicts between Chinese employees of China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) & workers from Myanmar led to burning of a CNPC building & oil storage in Rakhine State. irrawaddy.com/news/burma/bur…
14. When a police guard killed a Hpakant jade miner in 2017 other workers burned company’s equipment. In 2018 jade miners protesting wage delays destroyed a Hpakant company’s equipment & burned buildings. irrawaddy.com/news/burma/doz…
15. With echoes of 18th C. Ned Ludd, in 2017 Myanmar garment workers who had been struggling for decent conditions & benefits destroyed production line machinery & other equipment at a Chinese-owned Yangon factory. mmtimes.com/national-news/…
16. Myanmar military has used tech sabotage like DDoS attacks vs opponents or media and some racist Myanmar hackers launched attacks in support of Rohingya genocide. Since Feb. 1, 2021 coup, activist hackers have targeted several official Myanmar websites. voi.id/en/news/33758/…
17/17. Note: historically, sabotage could be highly effective tactic (or utterly counterproductive.) Careful planning & intelligence was key. Important to assess potential effects on noncombatants, environment.
My previous History Threads & reports are at projectmaje.org
My previous History Threads & reports are at projectmaje.org

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh