Convolutions! 1D! 2D! 3D!🔲
I've had a lot of trouble understanding different convolutions
What do different convolutions do anyway❓
Without the correct intuition, I found defining any CNN architecture very unenjoyable.
So, here's my little understanding (with pictures)🖼👇
I've had a lot of trouble understanding different convolutions
What do different convolutions do anyway❓
Without the correct intuition, I found defining any CNN architecture very unenjoyable.
So, here's my little understanding (with pictures)🖼👇
The Number associated with the Convolution signifies two things:
🔸The number of directions the filter moves in and,
🔸The dimensions of the output
Each convolution expects different shapes of inputs and results in output equal to the dimensions it allows the filter to move in.
🔸The number of directions the filter moves in and,
🔸The dimensions of the output
Each convolution expects different shapes of inputs and results in output equal to the dimensions it allows the filter to move in.
In 1⃣D-Conv, the kernel moves along a single axis.
It is generally applied over the inputs that also vary along a single dimension, ex: electric signal.
The input could be a 1D array and a small 1D kernel can be applied over it to get another 1D array as output.
It is generally applied over the inputs that also vary along a single dimension, ex: electric signal.
The input could be a 1D array and a small 1D kernel can be applied over it to get another 1D array as output.

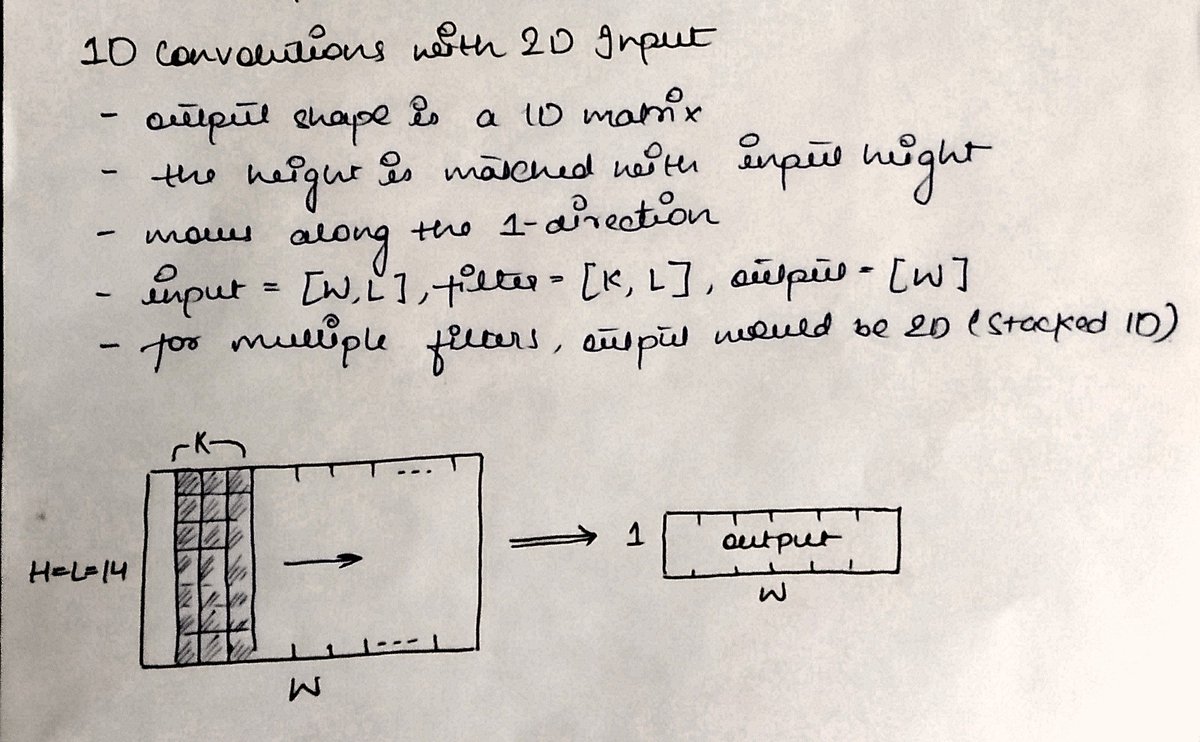
And... it can also be applied on two-dimensional inputs. How?
Remember, 1D convolution does not mean the kernel has to be 1D.
We can match the additional dimension of the input to that of the kernel.
If we have 20x8 image we can make a kernel of 3 to 3x8, output is still 1D.
Remember, 1D convolution does not mean the kernel has to be 1D.
We can match the additional dimension of the input to that of the kernel.
If we have 20x8 image we can make a kernel of 3 to 3x8, output is still 1D.
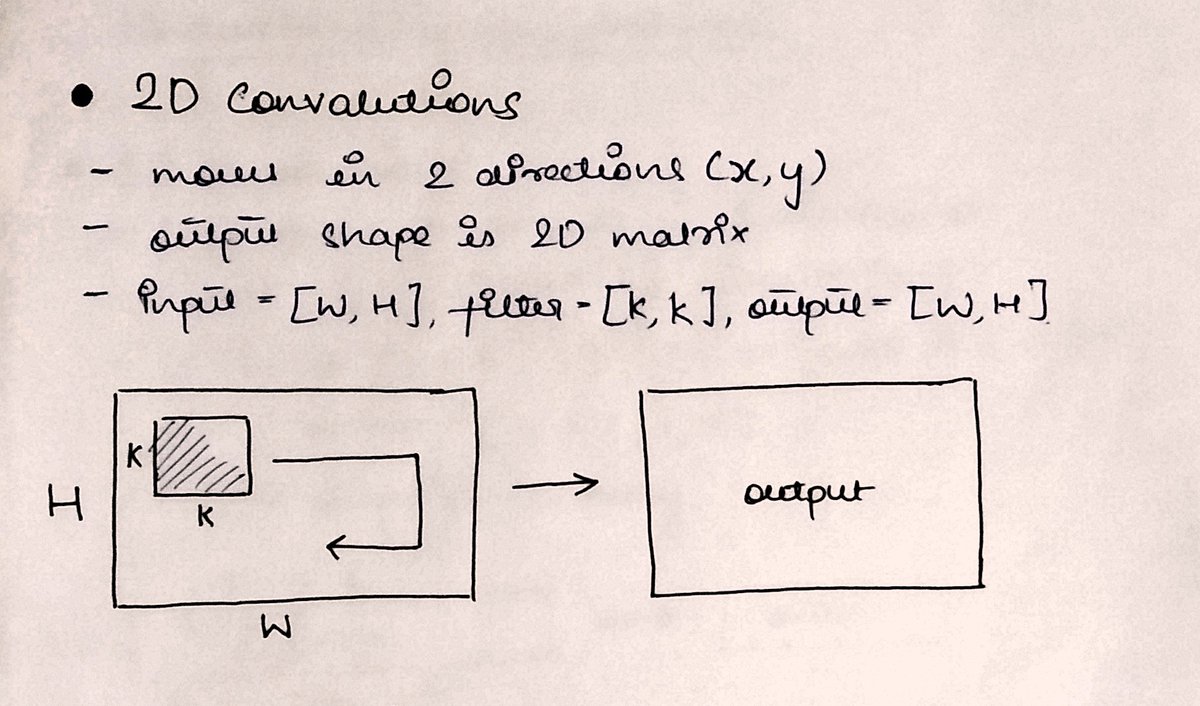
In 2⃣D-Conv, the kernel moves along two axes (x,y).
It is generally applied over the inputs which are also 2 dimensional, like a grayscale image (single channel)
The input is a 2D array and a 2D kernel is applied to get another 2D matrix as output.
It is generally applied over the inputs which are also 2 dimensional, like a grayscale image (single channel)
The input is a 2D array and a 2D kernel is applied to get another 2D matrix as output.
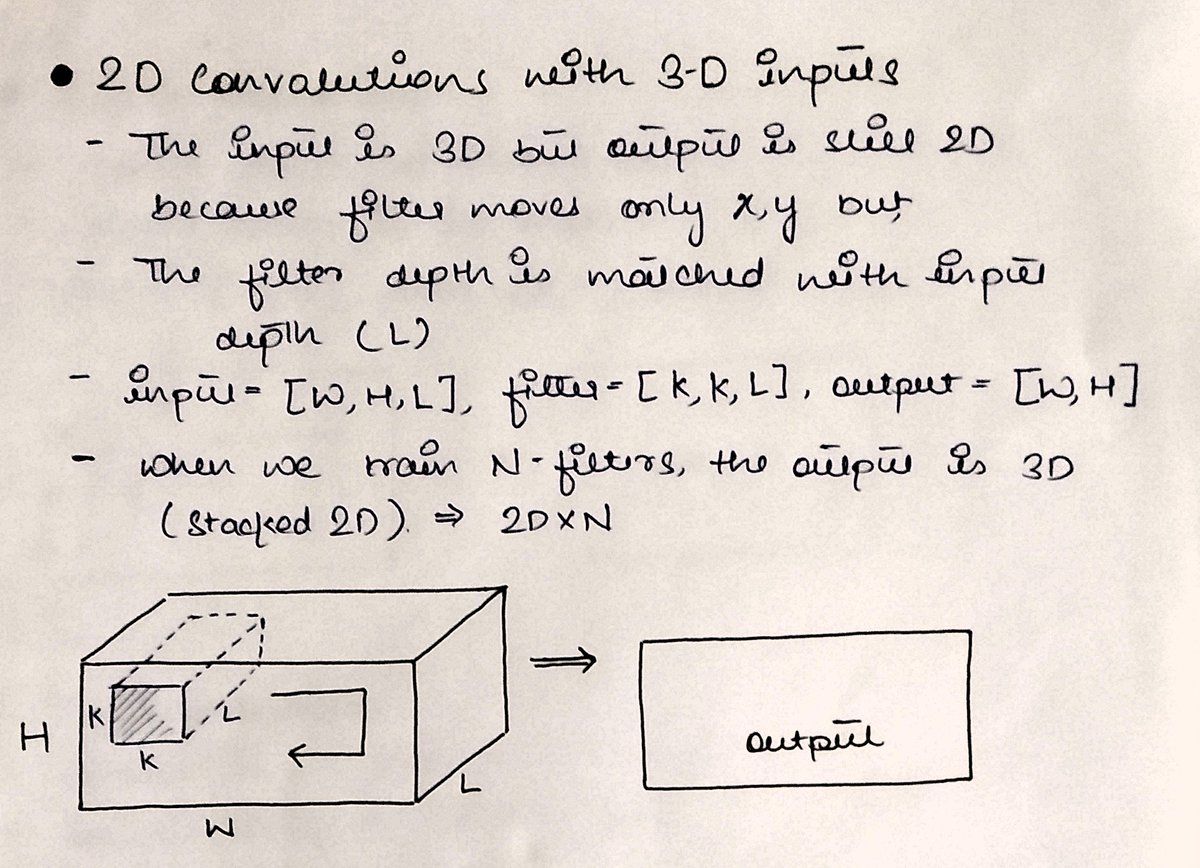
And yes, 2D convolutions can also be applied to a higher dimensional input like 3D.
The principle remains the same of matching the additional dimension with kernel depth.
an input of 28x28x6 can be slid over by a 3x3 kernel by making it 3x3x6.
The principle remains the same of matching the additional dimension with kernel depth.
an input of 28x28x6 can be slid over by a 3x3 kernel by making it 3x3x6.
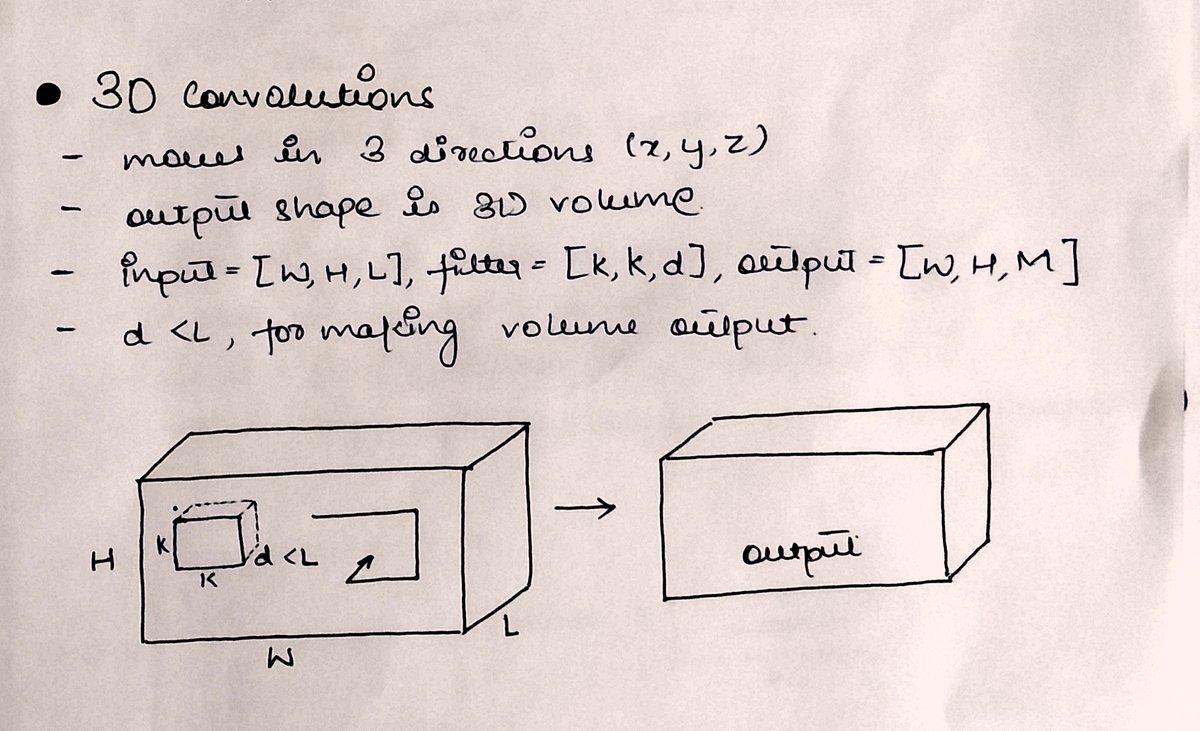
In 3⃣D-Conv, the kernel moves along three axes (x,y,z).
It is applied over 3-dimensional inputs
The input is a 3D array and a 3D kernel is applied to get another 3D cuboid-like output.
But the kernel depth must be less than the input depth to make sure we get 3D output.
It is applied over 3-dimensional inputs
The input is a 3D array and a 3D kernel is applied to get another 3D cuboid-like output.
But the kernel depth must be less than the input depth to make sure we get 3D output.
These points helped me build my intuitions of convolutions.
This definitely helps in understanding how to add or remove layers from a convolutional architecture properly.
This definitely helps in understanding how to add or remove layers from a convolutional architecture properly.
In the next thread, we will try to understand the shapes and calculating them correctly.
And maybe with little Keras code snippets as well!
Hope this helps! 👍
And maybe with little Keras code snippets as well!
Hope this helps! 👍
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh