It's a great day to look at a retweet botnet that uses GAN-generated profile pics and likes cymbals. #ThisCymbalDoesNotExist #MondayShenaniGANs
(GAN = "generative adversarial network", the AI technique used by thispersondoesnotexist.com to generate fake faces)
cc: @ZellaQuixote
(GAN = "generative adversarial network", the AI technique used by thispersondoesnotexist.com to generate fake faces)
cc: @ZellaQuixote

This botnet consists of (at least) 1301 accounts created between November 2020 and May 2021. Although most have tweeted dozens of times, none has liked more than two tweets. Thus far, they have (allegedly) sent all of their tweets via the Twitter Web App. 




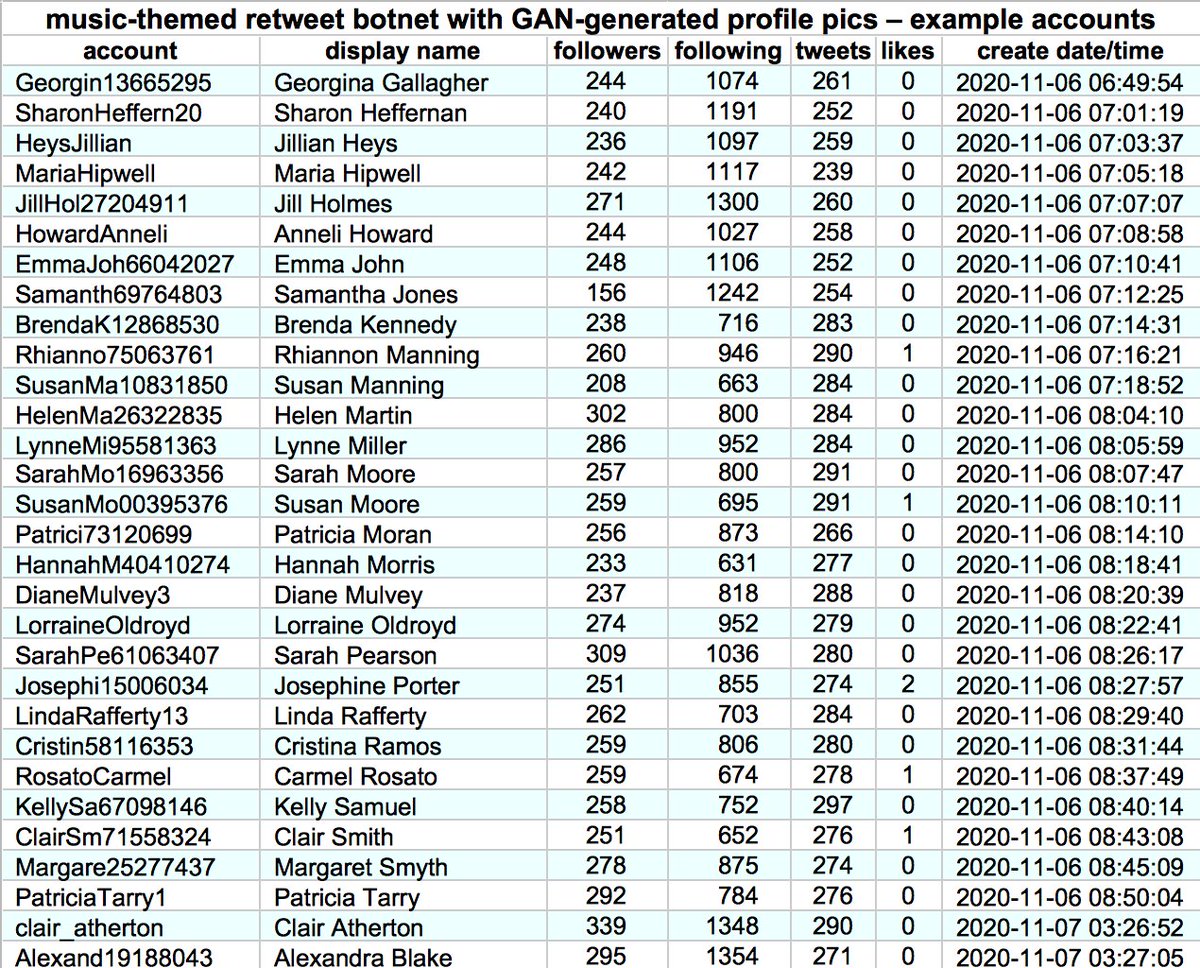
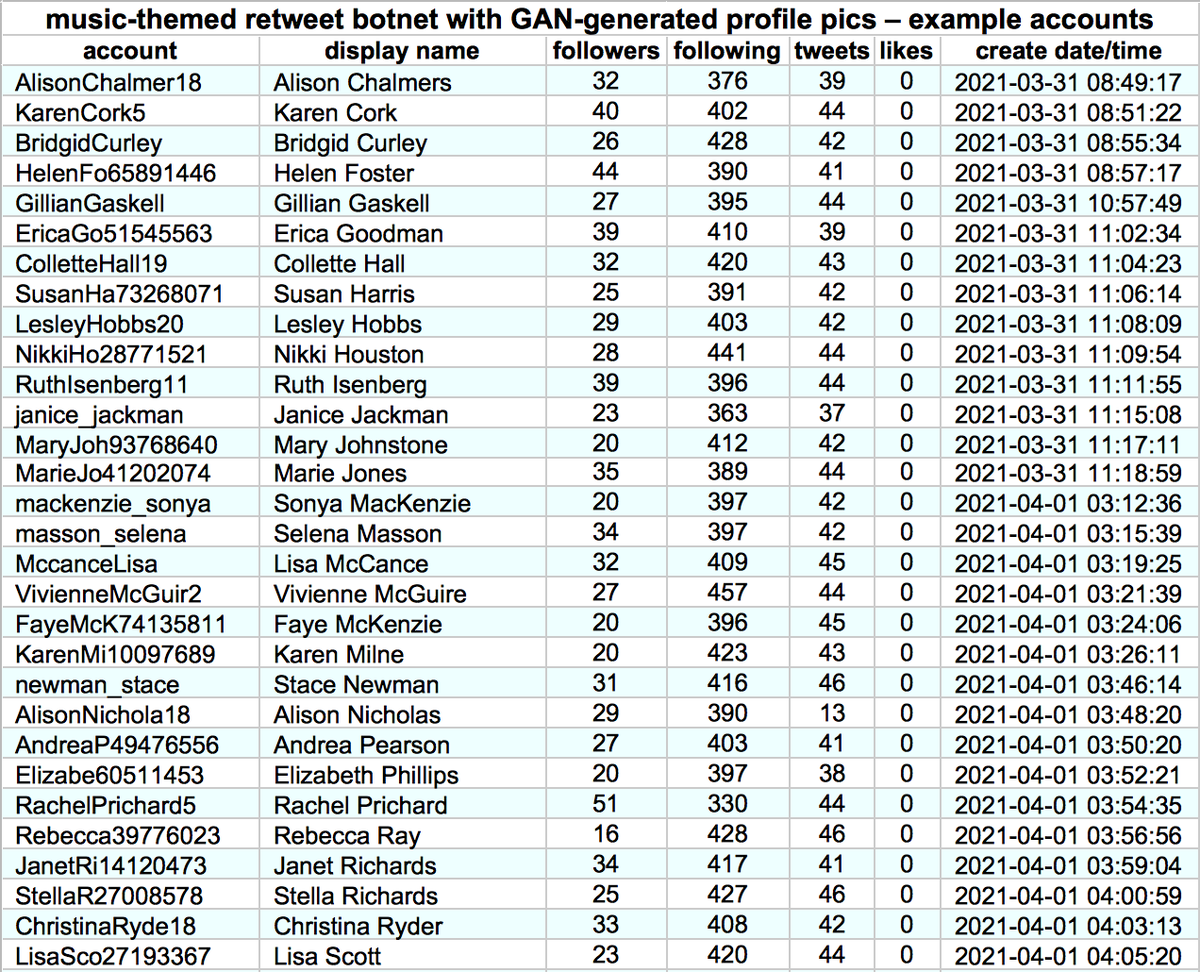

All 1301 accounts in this botnet uses GAN-generated face images as their profile pics, similar to those generated by thispersondoesnotexist.com. Almost all of the bots' profile pics are female. 

Unmodified GAN-generated face pics have the fingerprint that the major facial features (especially eyes) are always in the same pixel position on each image. This becomes apparent when one blends the images together.
Despite the fact that one can generate GAN face pics to one's heart's content, the operators of this botnet reused them across accounts. 216 of the 1301 accounts bear the same AI-generated face as other accounts in the network. 

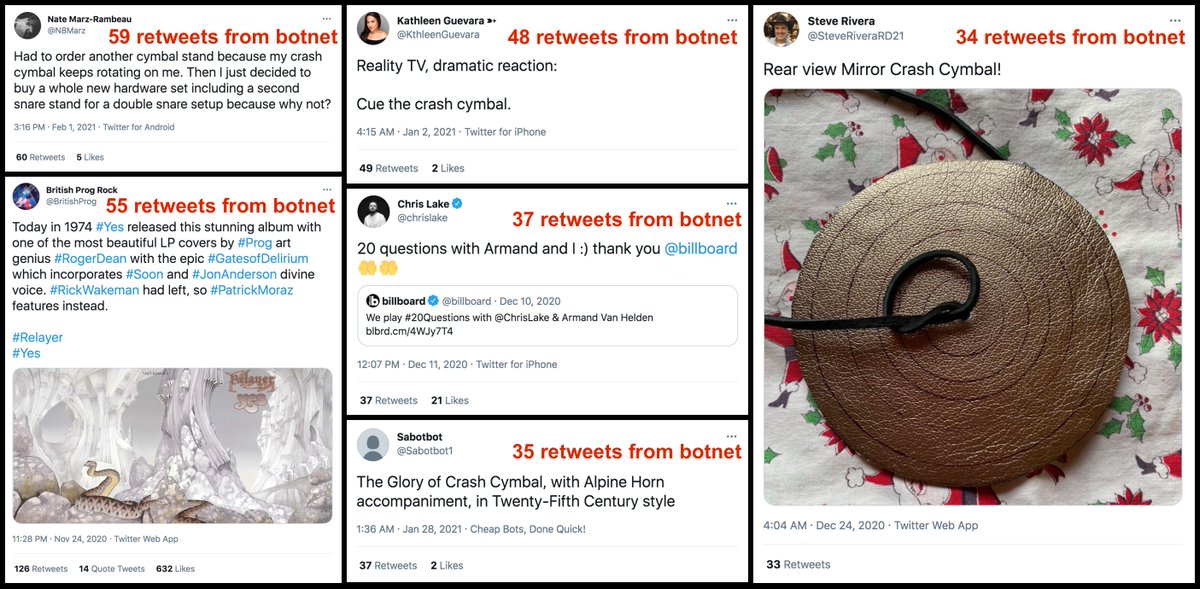
What does this botnet actually tweet? The vast majority of its content is retweets (183391 of 183925 tweets, 99.7%). The few non-retweets are mostly "thank you for following me tweets" accompanied by promotion of assorted musicians and bands. 



Who/what does this botnet retweet? Music-related accounts and tweets about bands/musicians/instuments/etc. Cymbals are a frequent theme of the most-retweeted tweets. Since these bots almost never like tweets, many of the tweets it amplifies end up with more retweets than likes. 




• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh































