how to avoid (panic about) declining market value of wind and solar
OR
how I learned to stop worrying about market value & love shadow prices
a DUAL perspective on a primal problem
new paper by @ReichenbergLina and me:
doi.org/10.1016/j.enec…
OR
how I learned to stop worrying about market value & love shadow prices
a DUAL perspective on a primal problem
new paper by @ReichenbergLina and me:
doi.org/10.1016/j.enec…

summary:
traditional "primal" view says low-marginal-cost wind and solar push down market prices when they produce a lot, suppressing revenue
we present another "dual" point of view: it is subsidies that suppress revenue, not variability
both are correct, but framing matters!
traditional "primal" view says low-marginal-cost wind and solar push down market prices when they produce a lot, suppressing revenue
we present another "dual" point of view: it is subsidies that suppress revenue, not variability
both are correct, but framing matters!

since market value decline is flip side of pushing in VRE with quotas/subsidies, it is a result of policy choice
we can also fix the problem by changing policy: by drawing in VRE (and other low-C gens) with carbon pricing instead
this avoids market value decline even at 100%
we can also fix the problem by changing policy: by drawing in VRE (and other low-C gens) with carbon pricing instead
this avoids market value decline even at 100%

since pricing of externalities is not possible in many markets, market value will naturally decline when VRE are pushed in via subsidies
system can still be close to cost-optimal for CO2 reduction (depends on available tech), so it's not necessarily anything to worry about
system can still be close to cost-optimal for CO2 reduction (depends on available tech), so it's not necessarily anything to worry about
saying "VRE market value should stay above VRE costs without externalities priced in" is the same as expecting low-carbon solutions to compete with subsidised fossil generators - an unreasonable task
exactly the same logic applies to non-variable nuclear.
if nuclear is forced to compete with subsidised fossils, its market value will be lower than the level required for cost recovery, and decline further at higher penetrations due to mismatch with demand variability
if nuclear is forced to compete with subsidised fossils, its market value will be lower than the level required for cost recovery, and decline further at higher penetrations due to mismatch with demand variability

in this dual perspective, policy is the ultimate mechanism determining whether market value can cover generator costs; variability (of supply or demand) is only a secondary characteristic which determines the speed of decline
we're not saying CO2 pricing fixes all, or that it's a substitute for VRE support - there is still a strong case for reducing investor risk to accelerate the energy transition with revenue guarantees. Hybrid schemes (combining support and CO2 prices) can give best of both worlds
the "primal" perspective has its place to explain the mechanism, but it leads to moral panic and has too often been used as a discourse of delay for sceptics of renewables (I could list so many more examples...)
https://twitter.com/nworbmot/status/1229451020834570241
a different dual perspective on market value can help us
a) focus on the problem at hand - reducing emissions ASAP (with ALL available technologies)
b) design an effective market structure for the day after tomorrow
a) focus on the problem at hand - reducing emissions ASAP (with ALL available technologies)
b) design an effective market structure for the day after tomorrow
read the paper by @ReichenbergLina and me just published in "Energy Economics":
doi.org/10.1016/j.enec…
research talk slides here:
nworbmot.org/energy/brown-i…
here's an old thread - a bit punchy - this time I'll try to be more conciliatory
doi.org/10.1016/j.enec…
research talk slides here:
nworbmot.org/energy/brown-i…
here's an old thread - a bit punchy - this time I'll try to be more conciliatory
https://twitter.com/nworbmot/status/1229450993768837120
so let's go: what is market value decline?
the traditional "primal" explanation goes:
prices are set by the intersection of demand and supply curves
wind and solar have zero marginal cost, so push the supply curve rightwards, suppressing prices
the traditional "primal" explanation goes:
prices are set by the intersection of demand and supply curves
wind and solar have zero marginal cost, so push the supply curve rightwards, suppressing prices

market value is the average price (lambda_t) seen by a generator (labelled s) for its dispatched energy (g_s,t) averaged over time (t) 

as larger shares of wind and solar (variable renewable energy = VRE) enter, their correlated generation suppresses prices exactly when they produce a lot, thereby "cannibalising" their own revenue
market value decline has been observed in many markets and modelling exercises
market value decline has been observed in many markets and modelling exercises

this appears to doom any attempts to integrate large shares of VRE into electricity markets
if they can't live from the market (i.e. with revenue > costs), aren't they destined to shrivel once state support withdraws?
if they can't live from the market (i.e. with revenue > costs), aren't they destined to shrivel once state support withdraws?
and how does this square with the hundreds (thousands?) of studies showing how high shares of renewables in power systems can be cost-effective?
this is where we get technical (sorry). in a long-term equilibrium where capacities of all assets are co-optimized, the "zero-profit rule" holds for all generators (and storage and transmission), i.e. on a per MWh basis:
levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) = market value (MV)
levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) = market value (MV)

each generator adjusts its capacity to find its niche where its costs are covered by the market, depending on the ratio of capex to opex, the availability profile, where it is located, etc.
this is a cost-based equilibrium without any policy intervention at all.
to disturb this equilibrium, we need to change something.
the implicit assumption in market value studies is to force in a given penetration of wind and solar into the equilibrium solution
to disturb this equilibrium, we need to change something.
the implicit assumption in market value studies is to force in a given penetration of wind and solar into the equilibrium solution
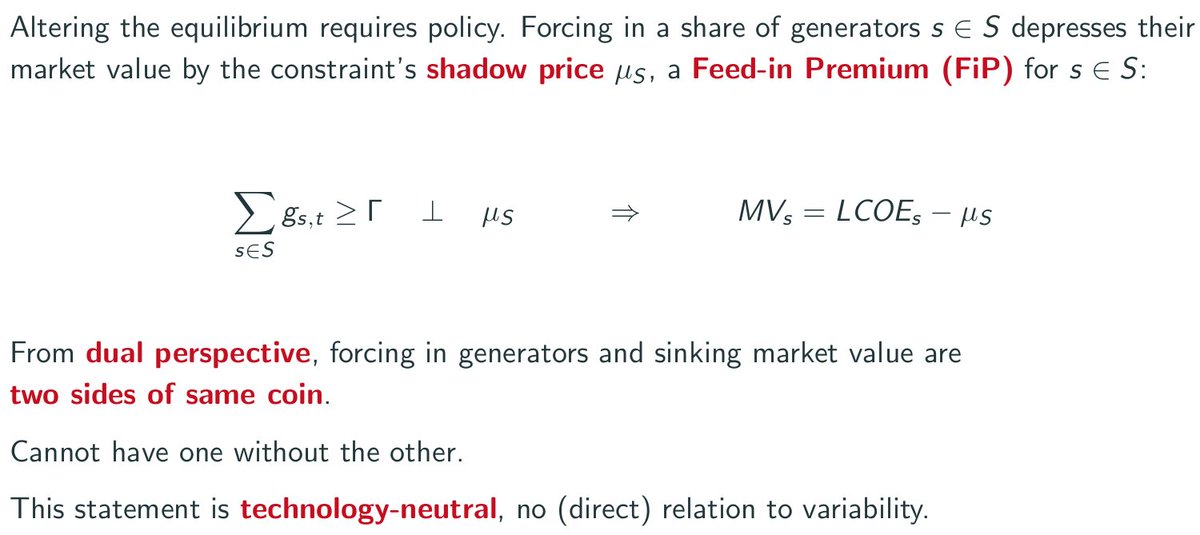
but this *automatically* lowers the market value. Assuming the LCOE stays roughly the same, it forces down the market value by a corresponding "feed-in premium", the shadow price mu_S of the constraint.
this choice of policy is directly responsible for reducing the market value
this choice of policy is directly responsible for reducing the market value

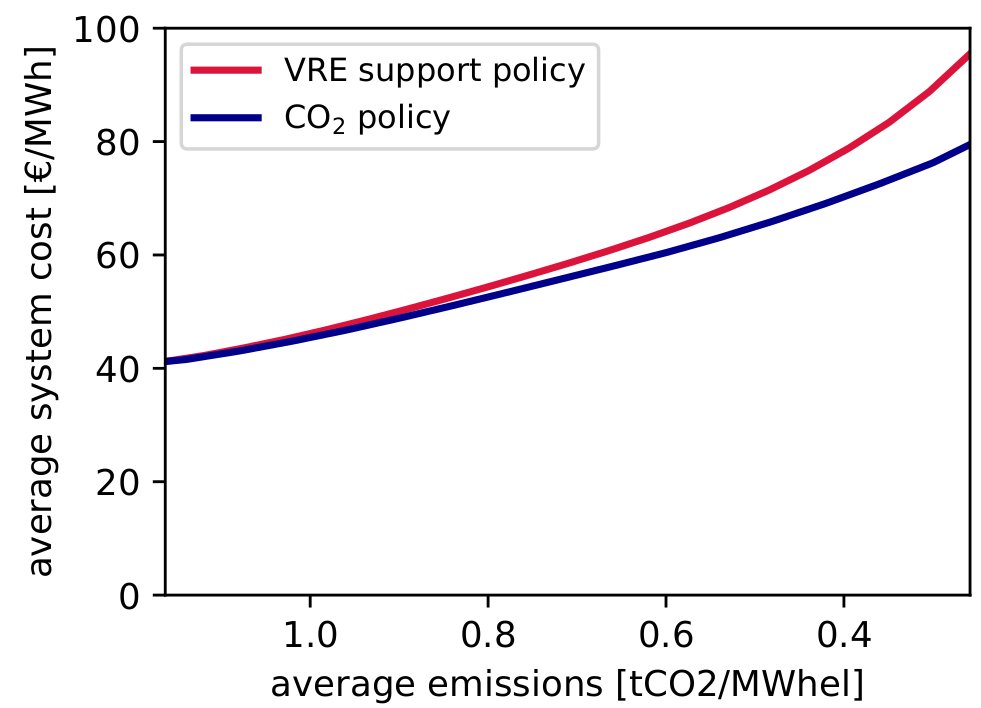
if we choose instead to limit carbon emissions, e.g. by imposing a CO2 tax, then the MV of VRE and other low-C generation remains equal to the LCOE, MV = LCOE, but now it the MV of fossil generators that is affected (pushed up so they can cover externalities of emissions) 

now we don't have any MV decline at all for VRE, even if we go all the way up to 100% VRE with sufficient flexibility from storage and transmission (in this graphic penetration is measured against demand, so it goes above 100% to cover storage losses) 
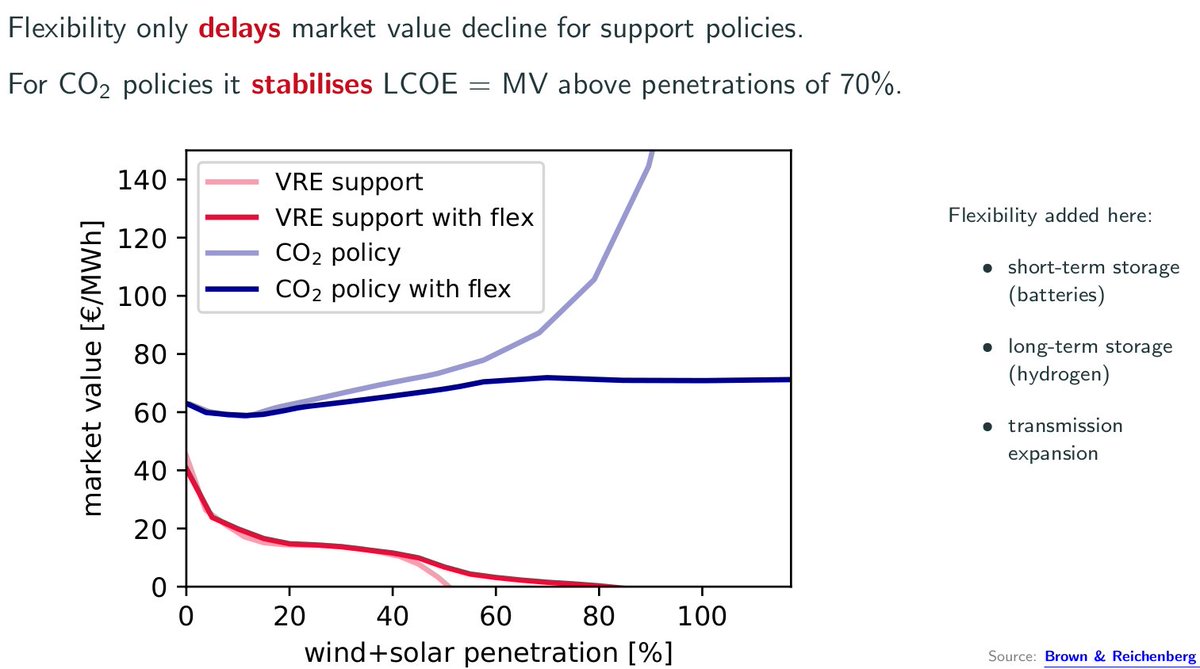
(note that without pricing externalities, the red curve, no amount of flexibility will save the market value at high shares - this is a sisyphean task)
this is the "dual" perspective because it focuses on the interactions of the shadow prices. from this perspective MV = LCOE is natural.
from the "primal" perspective the depression of prices by VRE is counter-acted by higher prices from CO2 pricing on the shoulders:
from the "primal" perspective the depression of prices by VRE is counter-acted by higher prices from CO2 pricing on the shoulders:

both perspectives are correct, but we argue the "dual" perspective is more useful from the perspective of policy making: both to understand to what extent MV decline is a problem (depends - system cost is a better measure of efficiency) and for avoiding it 

a few final twetes on price structure.
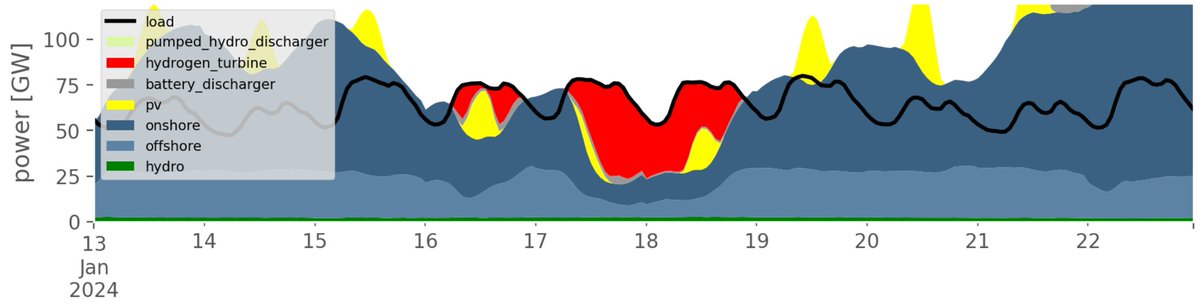
doesn't the system get very volatile with high shares of VRE, i.e. lots of hours of zero prices and lots of hours of very high prices?
short answer: not so much. storage and transmission remove big prices differences by arbitrage
doesn't the system get very volatile with high shares of VRE, i.e. lots of hours of zero prices and lots of hours of very high prices?
short answer: not so much. storage and transmission remove big prices differences by arbitrage

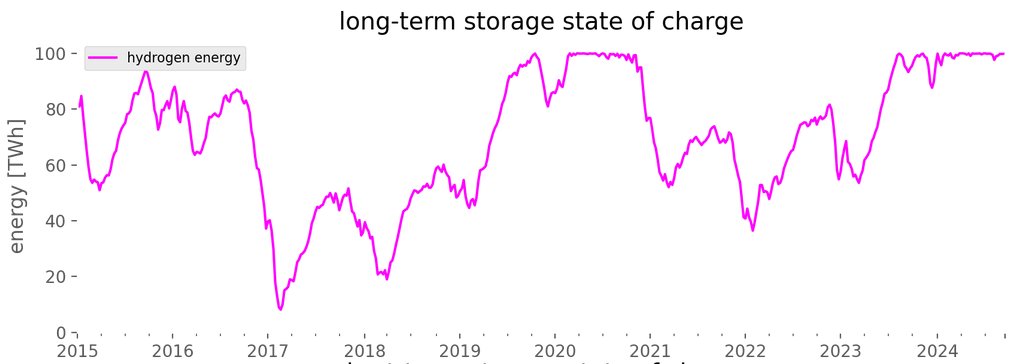
particularly the power-hydrogen-power storage discharging bids prevent prices going too high, while non-zero charging bids prevent them from going too low. here's the price duration curve showing this. 

other recent studies have found similar curves, particularly when other sectors (heating, transport) are included:
doi.org/10.1016/j.enec…
arxiv.org/abs/2105.01127
doi.org/10.3390/en1206…
doi.org/10.1016/j.apen…
arxiv.org/abs/2012.15371
dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/…
doi.org/10.1016/j.enec…
arxiv.org/abs/2105.01127
doi.org/10.3390/en1206…
doi.org/10.1016/j.apen…
arxiv.org/abs/2012.15371
dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/…
if you look at the distribution of hours when VRE make their revenue (measured in euros per capacity for each hour of the year), it barely budges (a result which surprised me quite a lot) 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh