Thread with excerpts from “Taming the Wild Fields: Colonization and Empire on the Russian Steppe” by Willard Sunderland 

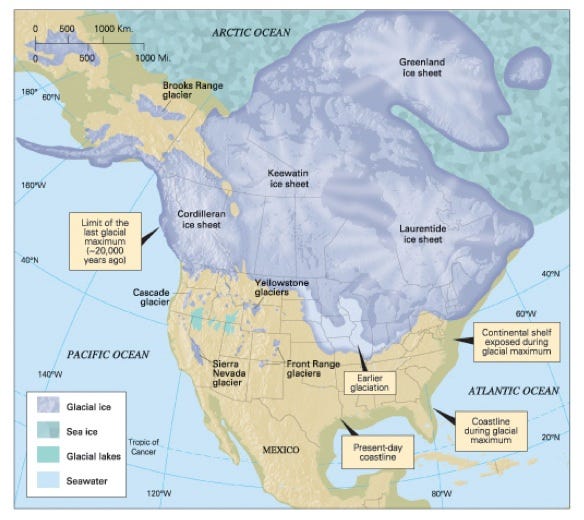
Ecologies of northern Eurasia. The steppe is a flat & grassy region that was ruled by pastoral nomads from Bronze Age through early modern period. 







Medieval Slavic farmers had a bloody relationship with their pastoral nomadic Cuman & Kipchak neighbors on the steppe. Despite mutual hatreds (biblically infused on Russian side) from raids, trade & military alliances kept Slavic & Cuman societies in mutual dependency. 





Slavs built long earthen & palisade walls on their southern frontier as early as late 10th century AD to shield their realm from the steppe tribes. 







Russia had few people living in the garrison towns of the Volga in late 16th century, so allowed for runaways to settle the region as Cossacks. Cossacks were very heterogeneous - included Poles, Tatars, & Ukrainians in addition to Russians. 



Muscovy’s defense line against steppe nomads was hundreds of miles long & built at immense cost. It was made of felled trees, ditches, blockposts, & fortified towns. Built gradually from 15th-17th centuries, the defense lines were successful & dramatically reduced steppe raids. 







Mid-17th century Kalmyks viewed their relationship with Russia as an alliance of equals, & used Russia in both internal conflicts as well as in their rivalries with their steppe rivals. 

500,000 settlers moved to the steppe in Catherine the Great’s reign. 56% went to southern & eastern Ukraine, 18% to the lower Volga, 16% to North Caucasus, 10% to southern Urals. 



Russian settlement of steppe was heavily male, so government deported women criminals to steppe & assigned them to men as wives. Some steppe settlers like the Greben Cossacks raided both their Caucasian neighbors & Russia proper for wives with government approval. 



Most 19th century colonists of the steppe were Orthodox Slavs. This was mostly because moving state peasants from overpopulated areas of core Russia was cheaper than moving the Uralic & Turkic peoples of the Volga. 







There was little immigration to Russia in mid-19th century. Existing foreign colonies had a great deal of autonomy until the 1870s. Russian bureaucrats liked German Mennonite settlers the most, Armenians the second most, & Balkans people least. 



By mid-19th century, settled people were 5x more efficient even in raising animals than the pastoral nomads were. Settled Christian converts from the steppe tribes as well as Slavic land squatters were increasingly favored by Russian government in land disputes as result. 





Late 19th southern Russia developed rapidly - telegraphs, railroads, stock exchanges, banks, opera houses, steam-powered mills, & hotels were built by the thousands. Kalmyks were freed from their obligations to their nobles in 1892. The Bashkirs too were finally settling down. 





Russian conscripts from the steppe averaged 1-3 cm taller than their countrymen from the mid-Volga in 1889. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh