1/ Here is a comprehensive review of the data on whether we need COVID BOOSTER SHOTS.
THE MOST IMPORTANT TAKEAWAY:
IF YOU HAVEN'T YET GOTTEN A COVID VACCINE, NOW'S THE TIME!
I'll put a Threadreader unroll at the end for those of you who find that more convenient to read/share.
THE MOST IMPORTANT TAKEAWAY:
IF YOU HAVEN'T YET GOTTEN A COVID VACCINE, NOW'S THE TIME!
I'll put a Threadreader unroll at the end for those of you who find that more convenient to read/share.
2/ Will we need COVID vaccine boosters?
Firstly, is “booster” even the right terminology?
I would argue not.
I think what we’re talking about is refining the COVID vaccine dosing regimen.
Firstly, is “booster” even the right terminology?
I would argue not.
I think what we’re talking about is refining the COVID vaccine dosing regimen.
3/ When your doctor prescribes you medication for high blood pressure & then increases the dose, it doesn’t mean that the medication doesn’t work.
It’s that they didn’t know what dose would work for you or wanted to start lower rather than overshoot.
It’s that they didn’t know what dose would work for you or wanted to start lower rather than overshoot.
4/ Similarly with COVID, we’re still optimizing vaccine dosing regimens.
5/ With hepatitis B, we’ve learned that you need 3 doses. That 3rd dose isn’t a “booster.” It’s the 3rd dose in the series. We don’t give yearly boosters of hepatitis B vaccine. We just give a 3 dose series.
COVID may be similar.
COVID may be similar.
6/ For reasons we don’t entirely understand (though it makes a lot of sense), the immune system recognizes repeated exposures to a pathogen as a greater threat.
Hence the success of vaccine regimens split into 2 or 3 immunizations.
Hence the success of vaccine regimens split into 2 or 3 immunizations.
7/ Why might you need more than one dose of a vaccine?
- To extend the duration of an immune response (e.g. pertussis vaccine)
- To overcome immune-evasion (e.g. influenza vaccine)
- To extend the duration of an immune response (e.g. pertussis vaccine)
- To overcome immune-evasion (e.g. influenza vaccine)
8/ Our immune response to some infectious diseases lasts longer than for other infectious diseases.
Viruses and other pathogens mutate. The faster & more significant the mutations, the more quickly they’re able to evade our immune systems.
Pathogens mutate at different rates.
Viruses and other pathogens mutate. The faster & more significant the mutations, the more quickly they’re able to evade our immune systems.
Pathogens mutate at different rates.
9/ Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein can lead to immune evasion.
No SARS-CoV-2 variant fully evades our immune system.
The Beta variant &, to a lesser degree, the Gamma & Delta variants, partially evade our immune responses.
No SARS-CoV-2 variant fully evades our immune system.
The Beta variant &, to a lesser degree, the Gamma & Delta variants, partially evade our immune responses.
10/ But If we have a strong enough immune response, we can still overcome that partial immune-evasion.
11/ How will we know whether we’ll need to tweak COVID vaccine dosing regimens?
- Decreased vaccine effectiveness
-- But it’s important that we be clear about what we mean by vaccine effectiveness.
-- See Katherine Wu’s piece about this in The Atlantic:
theatlantic.com/science/archiv…
- Decreased vaccine effectiveness
-- But it’s important that we be clear about what we mean by vaccine effectiveness.
-- See Katherine Wu’s piece about this in The Atlantic:
theatlantic.com/science/archiv…
12/
-- Breakthrough infections are not the same thing as breakthrough disease.
-- We’re currently in the disease control phase of our public health response. We’re trying to reduce severe disease, hospitalization, & death. What matters most at this stage is breakthrough disease.
-- Breakthrough infections are not the same thing as breakthrough disease.
-- We’re currently in the disease control phase of our public health response. We’re trying to reduce severe disease, hospitalization, & death. What matters most at this stage is breakthrough disease.
13/
-- Thus far, breakthrough infections seem to cause no or mild symptoms.
-- But breakthrough infections would still be of concern if they lead to infection of others, especially unvaccinated people who may be at risk for severe COVID.
-- Thus far, breakthrough infections seem to cause no or mild symptoms.
-- But breakthrough infections would still be of concern if they lead to infection of others, especially unvaccinated people who may be at risk for severe COVID.
14/
- Correlates of immunity/protection
-- These are surrogate measures that should predict vaccine effectiveness.
-- These are measurable signs that someone is immune.
- Correlates of immunity/protection
-- These are surrogate measures that should predict vaccine effectiveness.
-- These are measurable signs that someone is immune.
15/
-- Correlates of immunity/protection are kind of like fasting cholesterol levels. They predict who’s at risk of a heart attack and who needs treatment.
nature.com/articles/s4159…
As of right now, neutralizing antibodies are our best correlate of immunity.
-- Correlates of immunity/protection are kind of like fasting cholesterol levels. They predict who’s at risk of a heart attack and who needs treatment.
nature.com/articles/s4159…
As of right now, neutralizing antibodies are our best correlate of immunity.
16/
This graph shows the correlation between neutralizing antibodies & vaccine effectiveness.
Neutralizing antibody titers predict vaccine effectiveness, at least WHEN nAbs were measured during phase 1, 2, & 3 trials, i.e. within a couple months, at most, after vaccination.
This graph shows the correlation between neutralizing antibodies & vaccine effectiveness.
Neutralizing antibody titers predict vaccine effectiveness, at least WHEN nAbs were measured during phase 1, 2, & 3 trials, i.e. within a couple months, at most, after vaccination.

17/ But how well do neutralizing antibody levels correlate with vaccine effectiveness the farther out you go from vaccination?
If neutralizing antibody titers wane, does that mean they’re gone for good?
If neutralizing antibody titers wane, does that mean they’re gone for good?
18/ It’s important to remember that there’s more to the immune system than antibodies.
Let’s review how the HUMORAL IMMUNE SYSTEM works.
Let’s review how the HUMORAL IMMUNE SYSTEM works.
19/ These pink curves represent antibody levels.
Early after infection or vaccination, antibody levels rise.
But eventually, these antibody levels fall.
But it doesn’t mean that you’re no longer immune to infection once your antibody levels drop.
Early after infection or vaccination, antibody levels rise.
But eventually, these antibody levels fall.
But it doesn’t mean that you’re no longer immune to infection once your antibody levels drop.

20/ You wouldn’t want your antibody levels to remain elevated indefinitely vs every pathogen that infects you or every vaccine you get because then your blood would turn to sludge. If your short-lived plasma cells lived forever, your lymph nodes would be the size of footballs.
21/ What are some of the other immune responses that protect you?
Initially after infection / vaccination, naïve B-cells weakly recognize protein antigen.
This leads to proliferation & differentiation of these naïve B-cells into short-lived plasma cells, which secrete antibodies.
Initially after infection / vaccination, naïve B-cells weakly recognize protein antigen.
This leads to proliferation & differentiation of these naïve B-cells into short-lived plasma cells, which secrete antibodies.

22/ Short-lived plasma cells are responsible for the primary antibody response.
When these short-lived plasma cells die off, the antibodies they produced also wane.
When these short-lived plasma cells die off, the antibodies they produced also wane.

23/ But the immune response doesn’t stop there.
B-cells & T-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, & other secondary lymphoid organs form GERMINAL CENTERS, which is like a finishing school for immune cells.
B-cells & T-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, & other secondary lymphoid organs form GERMINAL CENTERS, which is like a finishing school for immune cells.

24/ Through a process called SOMATIC HYPERMUTATION, activated B-cells undergo AFFINITY MATURATION, getting better and better at recognizing the antigen. 

25/ While the amount of antibody produced decreases over time, the quality of these antibodies increases.
Neutralizing antibody titers reflect both quantity & quality.
Neutralizing antibody titers reflect both quantity & quality.
26/ In the germinal centers, some of these B-cells become plasmablasts (precursors to plasma cells), migrate to the bone marrow, and differentiate into LONG-LIVED PLASMA CELLS. 
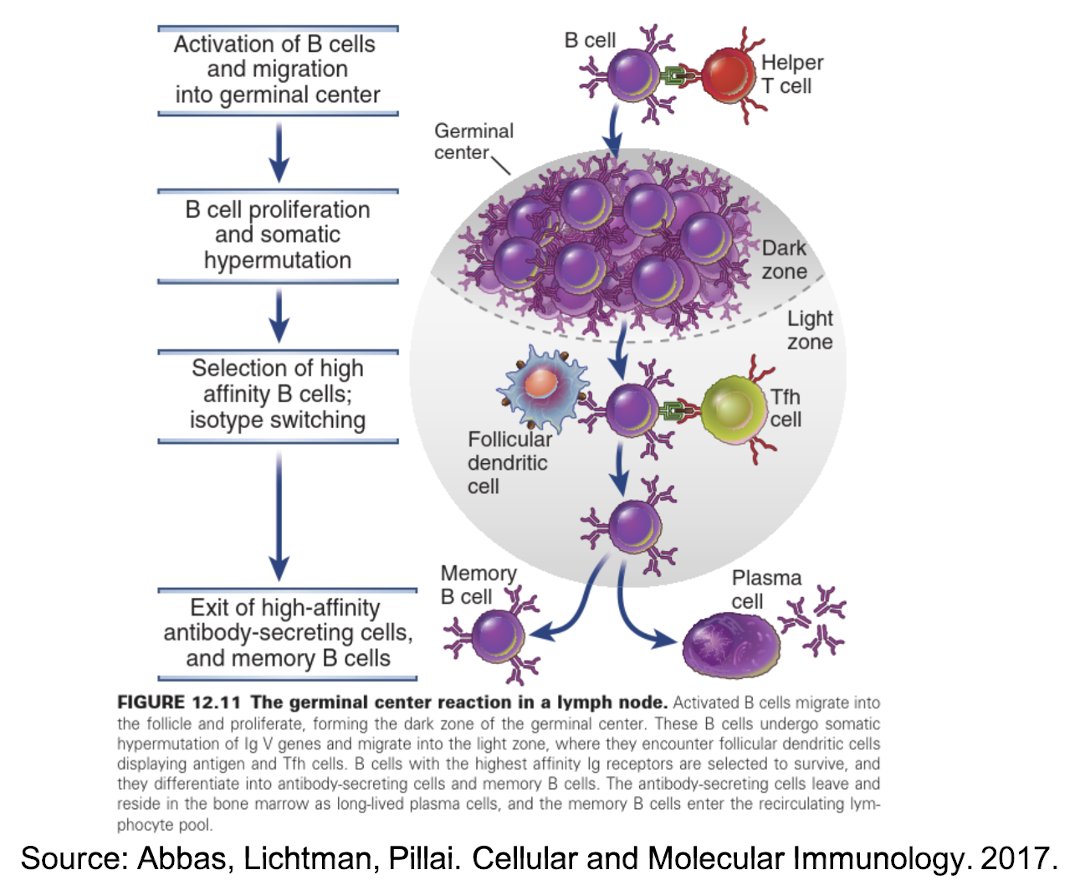
27/ It takes ~2-3 weeks after vaccination before the bone marrow becomes a major site of antibody production.
Long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow may continue to secrete antibodies for decades after infection/vaccination.
Long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow may continue to secrete antibodies for decades after infection/vaccination.

28/ Long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow secrete antibodies that provide immediate protection upon rechallenge.
About half of the antibodies in the blood of a healthy adult are produced by long-lived plasma cells.
About half of the antibodies in the blood of a healthy adult are produced by long-lived plasma cells.
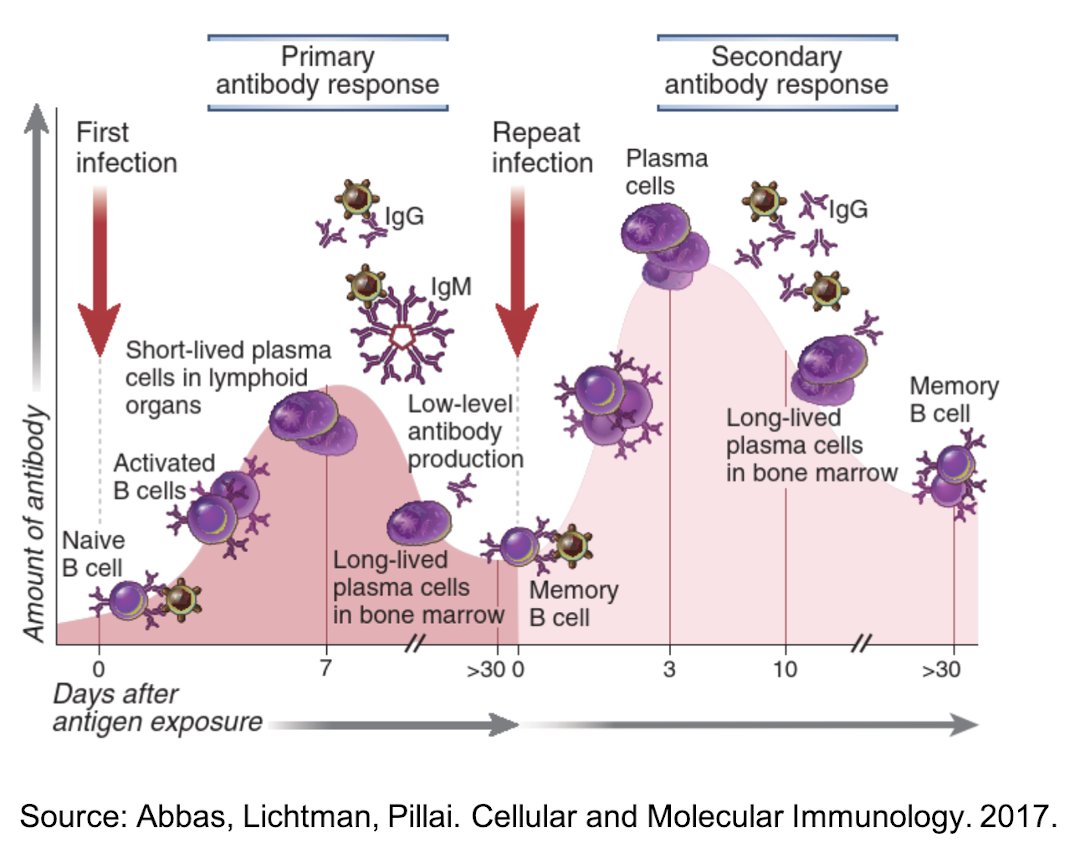
29/ Memory B-cells are also generated during the germinal center reaction and can rapidly respond to rechallenge.
Some memory B-cells remain in the lymphoid organs where they were generated, while others exit and recirculate between the blood and lymphoid organs.
Some memory B-cells remain in the lymphoid organs where they were generated, while others exit and recirculate between the blood and lymphoid organs.

30/ Long-lived memory B-cells do not secrete antibodies, but they survive for prolonged periods.
When they are rechallenged with an infectious pathogen, they proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells. These plasma cells then make antibody.
When they are rechallenged with an infectious pathogen, they proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells. These plasma cells then make antibody.

31/ Memory B-cells can proliferate & differentiate far more quickly than naïve B-cells, so the secondary immune response is faster and stronger (notice that the second pink curve of antibodies has a steeper slope and higher peak). 

32/ If neutralizing antibody titers drop after infection or vaccination, does that mean you’re no longer immune?
No. You’re still protected by long-lived plasma cells in your bone marrow and memory B-cells.
No. You’re still protected by long-lived plasma cells in your bone marrow and memory B-cells.

33/ In fact, memory B-cell responses continue to increase over many months after SARS-CoV-2 infection with progressive increases in somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation during that time.
34/ How we define correlates of protection/immunity matters. It’s not just WHAT, but what WHEN.
- Do neutralizing antibody titers measured soon after infection or vaccination predict vaccine effectiveness over the long term?
- Do neutralizing antibody titers measured soon after infection or vaccination predict vaccine effectiveness over the long term?
35/
- Can we think of the initial peak neutralizing antibody titer as a setpoint of sorts?
- Are neutralizing antibody titers analogous prognostic value to CD4+ T-cell count nadirs & HIV viral load peaks in patients with HIV?
- Can we think of the initial peak neutralizing antibody titer as a setpoint of sorts?
- Are neutralizing antibody titers analogous prognostic value to CD4+ T-cell count nadirs & HIV viral load peaks in patients with HIV?
36/
- Or do lower neutralizing antibody titers measured years later correlate with waning vaccine effectiveness?
- Or do lower neutralizing antibody titers measured years later correlate with waning vaccine effectiveness?
37/ It's important that we identify good correlates of immunity/protection.
We won't be able to conduct randomized, controlled trials of every vaccine dose/regimen/combo vs every new mutant variant.
We won't be able to conduct randomized, controlled trials of every vaccine dose/regimen/combo vs every new mutant variant.
38/ What about the innate immune response?
SARS-CoV-2 is very good at suppressing the innate immune response by preventing, for example, the release of type 1 interferons.
The innate immune response controls viral replication in the respiratory tract and lungs.
SARS-CoV-2 is very good at suppressing the innate immune response by preventing, for example, the release of type 1 interferons.
The innate immune response controls viral replication in the respiratory tract and lungs.
39/ The innate immune response also primes adaptive immune responses, like B- and T-cell responses.
cell.com/cell/fulltext/…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32887754/
cell.com/cell/fulltext/…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32887754/
40/ And what about T-cells?
CD4+ T cells are most strongly associated with lessened COVID disease severity.
T cell responses may be important for faster viral clearance and tissue repair.
CD4+ T cells are most strongly associated with lessened COVID disease severity.
T cell responses may be important for faster viral clearance and tissue repair.
41/ Where the T-cell response is deficient or absent, the innate immune response might continue (cytokine storm) & cause the hyperinflammatory state seen in patients with severe COVID.
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
science.sciencemag.org/content/371/65…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
science.sciencemag.org/content/371/65…
42/ So what are our best correlates of immunity/protection vs SARS-CoV-2?
Early? Neutralizing antibody titers?
Later? Neutralizing antibody titers and/or long-lived plasma cells in bone marrow & memory B-cells?
Early? Neutralizing antibody titers?
Later? Neutralizing antibody titers and/or long-lived plasma cells in bone marrow & memory B-cells?
43/ This graph shows what happens to antibody responses after 2 doses of Pfizer vaccine.
In red are people who didn’t get COVID before getting vaccinated.
In black are people who had COVID before getting vaccinated.
In red are people who didn’t get COVID before getting vaccinated.
In black are people who had COVID before getting vaccinated.
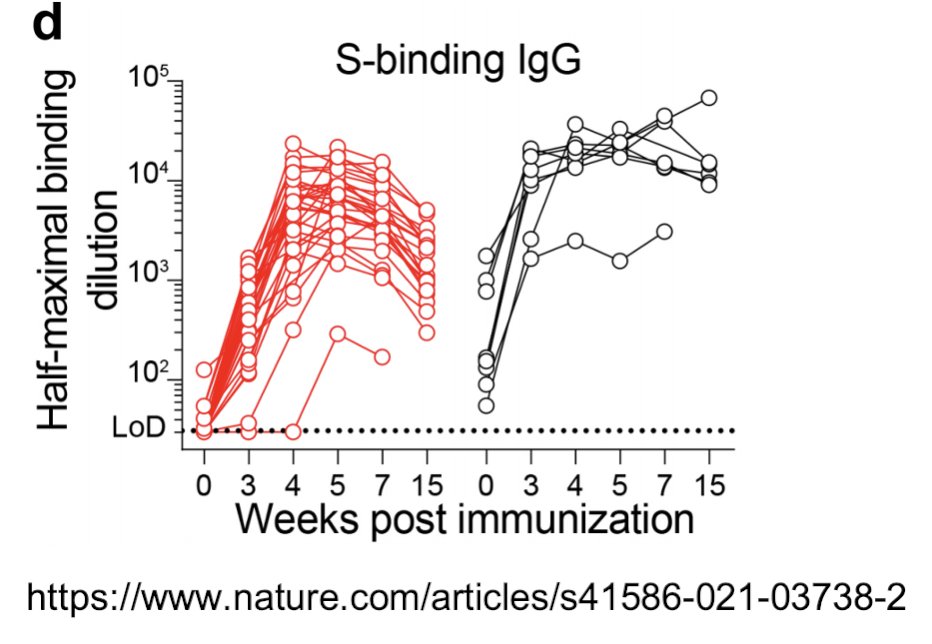
44/ In both cases, antibody titers peak about 4 weeks after the second dose of Pfizer vaccine & then decline.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
This is what we EXPECT to happen as per #19 above.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
This is what we EXPECT to happen as per #19 above.
45/ This graph shows what’s happening in the germinal centers (GC) in lymph nodes (LN) after vaccination.
Memory B-cells & plasma cells in the lymph nodes continue to mature & strengthen.
Memory B-cells & plasma cells in the lymph nodes continue to mature & strengthen.
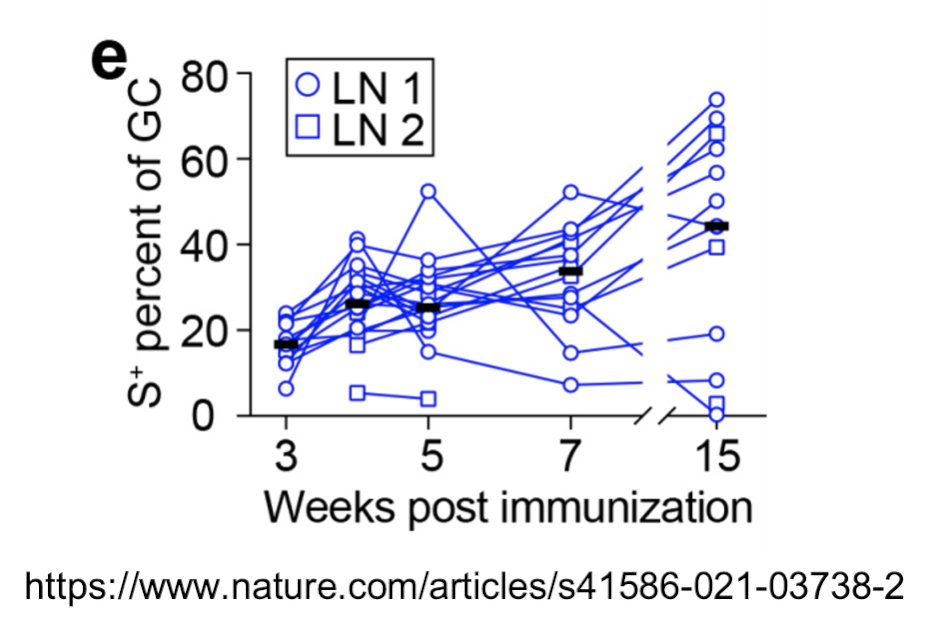
46/ Even though antibody levels may wane over time, long-lived plasma cells in bone marrow & memory B-cells still provide protection.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
nature.com/articles/s4158…
47/ If you’re also protected by long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow and memory B-cell responses, should we be looking at those, too?
Or are neutralizing antibody levels soon after infection/vaccination a good enough surrogate?
We're not sure.
Or are neutralizing antibody levels soon after infection/vaccination a good enough surrogate?
We're not sure.
48/ When might our immune responses—antibody, long-lived plasma cells in bone marrow, and memory B-cell responses—wane enough that we might need additional doses of COVID vaccine?
49/ Other Qs remain unanswered, too:
- We don’t know how neutralizing antibody titers will decline over time for people who got infected vs people who were vaccinated.
- Is rate of decay different for naturally infected vs vaccinated persons?
- We don’t know how neutralizing antibody titers will decline over time for people who got infected vs people who were vaccinated.
- Is rate of decay different for naturally infected vs vaccinated persons?
50/
- And is rate of decay predicted by initial neutralizing antibody titer?
- Does your initial neutralizing antibody titer predict the robustness and durability of your bone marrow plasma cell and memory B-cell responses?
- And is rate of decay predicted by initial neutralizing antibody titer?
- Does your initial neutralizing antibody titer predict the robustness and durability of your bone marrow plasma cell and memory B-cell responses?
51/
- How do age & immunosuppression impact on the duration & robustness of your immune response?
nature.com/articles/s4159…
- How do age & immunosuppression impact on the duration & robustness of your immune response?
nature.com/articles/s4159…
52/ As explained above, the need to tweak vaccine dosing regimens depends on whether you need more doses
- to extend the DURATION of an immune response
OR
- to overcome IMMUNE-EVASION (i.e. a mutating, evolving pathogen).
- to extend the DURATION of an immune response
OR
- to overcome IMMUNE-EVASION (i.e. a mutating, evolving pathogen).
53/ And this is where the SARS-CoV-2 variants come in.
Even if an immune response after vaccination is DURABLE, it may not be STRONG or TARGETED enough against new, emerging variants.
Even if an immune response after vaccination is DURABLE, it may not be STRONG or TARGETED enough against new, emerging variants.
54/ The Phase III Ensemble Study of the J&J vaccine provided us with an early signal that the immune response to vaccination could potentially be evaded by variants.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
55/ Remember that Phase III clinical trials of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines were conducted PRIOR to the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants.
The J&J vaccine had lower vaccine efficacy in Brazil and South Africa where variants of concern (VOC) had emerged.
The J&J vaccine had lower vaccine efficacy in Brazil and South Africa where variants of concern (VOC) had emerged.
56/ Phase III ENSEMBLE trial of J&J vaccine
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
Brazil: 70% of COVID during the study was due to the P.2 variant
South Africa: 95% of COVID during the study was due to the Beta variant.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
Brazil: 70% of COVID during the study was due to the P.2 variant
South Africa: 95% of COVID during the study was due to the Beta variant.

57/ Now let’s look at correlates of immunity/protection for the J&J COVID vaccine versus the variants.
This is data from a Phase I-IIA trial of the J&J vaccine given in one- and two-dose schedules and low-dose vs high-dose.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
This is data from a Phase I-IIA trial of the J&J vaccine given in one- and two-dose schedules and low-dose vs high-dose.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
58/ Note that the FDA authorized the single-dose, low-dose J&J regimen shown here (the filled triangles).
The horizontal bars represent the median neutralizing antibody response against each variant.
The horizontal bars represent the median neutralizing antibody response against each variant.

59/ The median antibody titers 71 days after vaccination were 5x & 3.3x lower for the Beta & Gamma variants than versus early strains.
But though we see a drop, neutralizing antibody titers remain well above the limits of detection.
But though we see a drop, neutralizing antibody titers remain well above the limits of detection.

60/ Here’s another study. J&J was again given as 1- & 2-dose regimens & in low versus high doses.
The x-axis shows strains of SARS-CoV-2: early (WA1/2020, D614G) versus variants of concern (Alpha, Delta, Gamma, Beta).
The y-axis shows neutralizing antibody titers.
The x-axis shows strains of SARS-CoV-2: early (WA1/2020, D614G) versus variants of concern (Alpha, Delta, Gamma, Beta).
The y-axis shows neutralizing antibody titers.

61/ The graph on the top shows neutralizing antibody titers a month after vaccination.
The graph on the bottom shows neutralizing antibody titers 8 months after vaccination.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
The graph on the bottom shows neutralizing antibody titers 8 months after vaccination.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…

62/ The horizontal red line represents median neutralizing antibody titers in each group.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…

63/ Neutralizing antibody titers to the variants were lower than for the early strains at both 1 months and 8 months after vaccination.
This was most pronounced vs Beta with a reduction of 13x at 1 month & 3x at 8 months versus the early strains.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
This was most pronounced vs Beta with a reduction of 13x at 1 month & 3x at 8 months versus the early strains.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…

64/ These data are consistent with ongoing affinity maturation and improved neutralizing activity against variants of concern with time.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
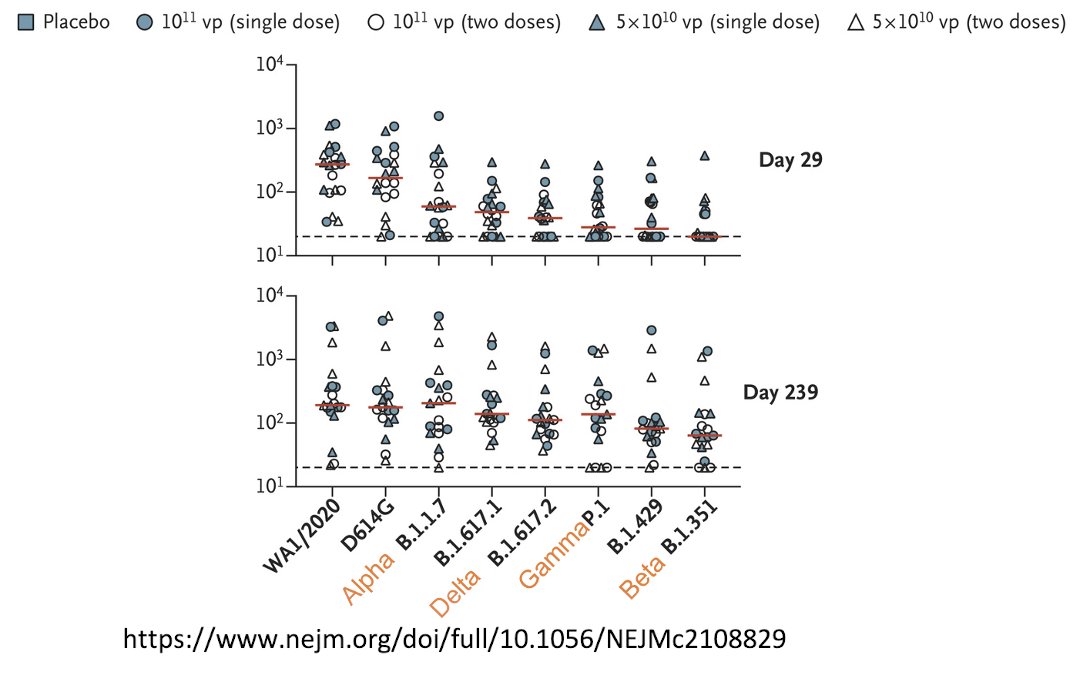
65/ Here’s more real-world evidence of the effectiveness of the J&J (& Pfizer & Moderna) vaccine vs the variants.
This is a cohort of healthcare workers at @nyuniversity @nyulangone (i.e. my coworkers).
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
This is a cohort of healthcare workers at @nyuniversity @nyulangone (i.e. my coworkers).
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
66/ This graph shows neutralizing antibody titers elicited by each vaccine (BNT162b2 = Pfizer, mRNA-1273 = Moderna, Ad26.COV2.S = J&J) against an early strain of the virus (D614G) versus variants of concern. 

67/ While the Pfizer & Moderna vaccines retain significant neutralizing antibody activity against the variants of concern 80-90 days after vaccination, the J&J vaccine does not.
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…

68/ Now let’s turn to the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. These are both mRNA vaccines with comparable vaccine effectiveness, so I’ll discuss both together.
69/ I’m going to focus on more recent studies of the Pfizer & Moderna vaccine effectiveness, which were conducted after the emergence of the Delta variant.
70/ Here’s real-world evidence of the effectiveness of the Pfizer & AZ vaccines vs the Delta & Alpha variants in the UK.
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
71/ In this case-control study, two doses of the Pfizer vaccine were 93% effective against the Alpha variant & 88% effective vs the Delta variant.
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

72/ Here is data from Public Health England (PHE).
Adjusted for age, co-morbidities, & other related factors, they found that 2 doses of the Pfizer vaccine was highly protective vs symptomatic disease from the Alpha & Delta variants (OR 0.06 and 0.12 respectively)...
Adjusted for age, co-morbidities, & other related factors, they found that 2 doses of the Pfizer vaccine was highly protective vs symptomatic disease from the Alpha & Delta variants (OR 0.06 and 0.12 respectively)...
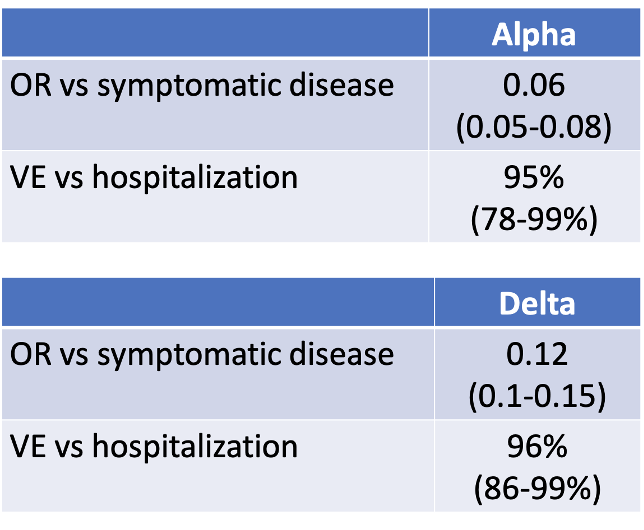
73/ ...and highly effective against hospitalization related to infection with the Alpha & Delta variants (VE 95% and 96% respectively).
khub.net/web/phe-nation…
khub.net/web/phe-nation…

74/ And now let’s have a look at correlates of immunity/protection, i.e. neutralizing antibody activity elicited by the Pfizer & Moderna vaccines.
75/ These are neutralizing antibody titers 35-51 days after people received 2 doses of the Moderna vaccine or 7-27 days after they received 2 doses of the Pfizer vaccine.
The horizontal dotted line represents the threshold for protective immunity.
The horizontal dotted line represents the threshold for protective immunity.
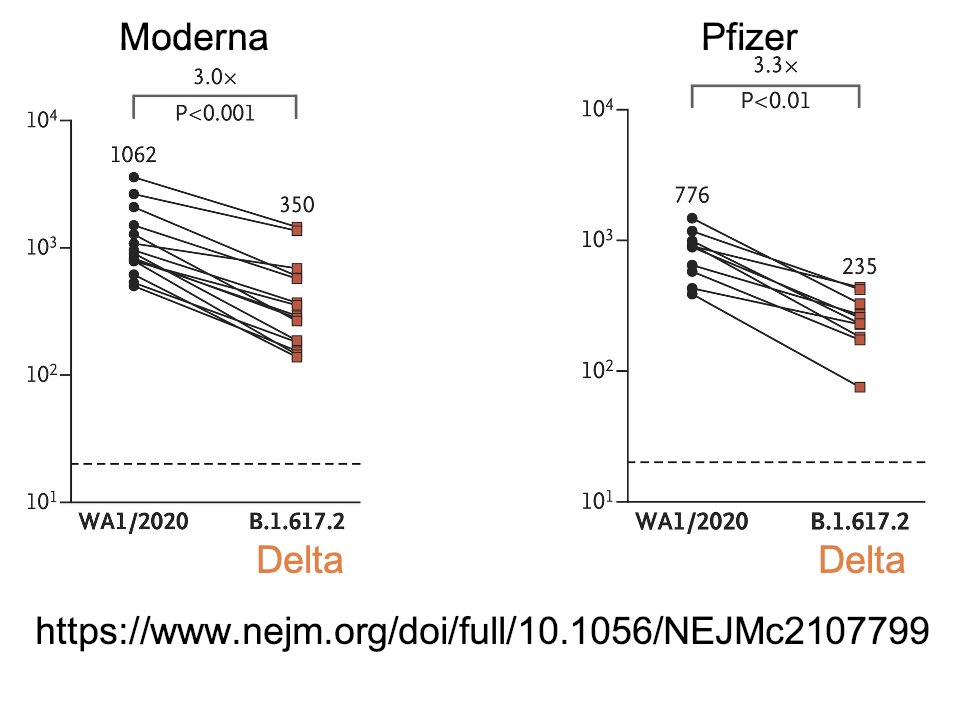
76/ While there is a drop in neutralizing antibody activity against Delta as compared with the early WA1/2020 strain, both the Pfizer & Moderna vaccines elicit protective immune responses against both.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…

77/ Here’s data from the Legacy Study in the UK.
2 doses of Pfizer elicited protected neutralizing antibody responses (>40) against all variants in almost all participants except 3% with Delta & 5% with Beta.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
2 doses of Pfizer elicited protected neutralizing antibody responses (>40) against all variants in almost all participants except 3% with Delta & 5% with Beta.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…

78/ The neutralizing antibody titers versus Beta & Delta were lower than for early strains & Alpha.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
thelancet.com/journals/lance…

79/ Here’s data from France.
This graph shows neutralizing antibody titers 5 weeks after a 2nd dose of Pfizer vaccine.
The dotted line represents limits of detection.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
This graph shows neutralizing antibody titers 5 weeks after a 2nd dose of Pfizer vaccine.
The dotted line represents limits of detection.
nature.com/articles/s4158…

80/ Neutralizing antibody titers are significantly lower vs Beta than the early D614G & Alpha variants.
Neutralizing antibody titers were slightly lower vs Delta than the early D614G and Alpha variants.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
Neutralizing antibody titers were slightly lower vs Delta than the early D614G and Alpha variants.
nature.com/articles/s4158…

81/ Why did Pfizer announce that a 3rd dose of its COVID vaccine might be needed?
cdn.pfizer.com/pfizercom/2021…
cdn.pfizer.com/pfizercom/2021…
82/ The data Pfizer shared with the WH COVID Response Team has not yet been shared publicly.
This data is based on Pfizer’s ongoing follow-up of phase III study participants.
nytimes.com/2021/07/12/us/…
This data must be made public.
This data is based on Pfizer’s ongoing follow-up of phase III study participants.
nytimes.com/2021/07/12/us/…
This data must be made public.
83/ The Pfizer press release said “data from a recent Nature paper demonstrate that immune sera obtained shortly after dose 2… have strong neutralization titers against the Delta variant in laboratory tests.” 

84/ Here’s the data from that Nature paper:
x-axis: original strain vs Delta variant
y-axis: neutralizing antibody titers
The dotted line is the limit of detection
Numbers above the bars = geometric mean titers
nature.com/articles/s4158…
x-axis: original strain vs Delta variant
y-axis: neutralizing antibody titers
The dotted line is the limit of detection
Numbers above the bars = geometric mean titers
nature.com/articles/s4158…

85/
Circles: two weeks after 2nd dose of Pfizer
Triangles: 4 weeks after 2nd dose of Pfizer
There’s a drop in neutralizing antibody titers against Delta versus the wildtype, but titers are still well above the limit of detection.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
Circles: two weeks after 2nd dose of Pfizer
Triangles: 4 weeks after 2nd dose of Pfizer
There’s a drop in neutralizing antibody titers against Delta versus the wildtype, but titers are still well above the limit of detection.
nature.com/articles/s4158…

86/
What does this mean for long-lived bone marrow plasma cell & memory B-cell responses?
What does this mean for vaccine effectiveness versus the Delta variant?
What does this mean for long-lived bone marrow plasma cell & memory B-cell responses?
What does this mean for vaccine effectiveness versus the Delta variant?
87/ Finally, how do age and immunosuppression impact on vaccine responses?
88/ Let’s start with age.
Older people have less robust immune responses because they’re less able to produce somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation (that B-cell finishing school is shutting down).
Older people have less robust immune responses because they’re less able to produce somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation (that B-cell finishing school is shutting down).
89/ Older people also have weaker T-cell cytokine responses.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26472076/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25157137/
nature.com/articles/s4158…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26472076/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25157137/
90/ This graph shows how people under 80 versus 80+ responded to two doses of Pfizer vaccine vs the variants.
You see a slight drop in neutralizing antibody titers among those 80+ vs each variant.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
You see a slight drop in neutralizing antibody titers among those 80+ vs each variant.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
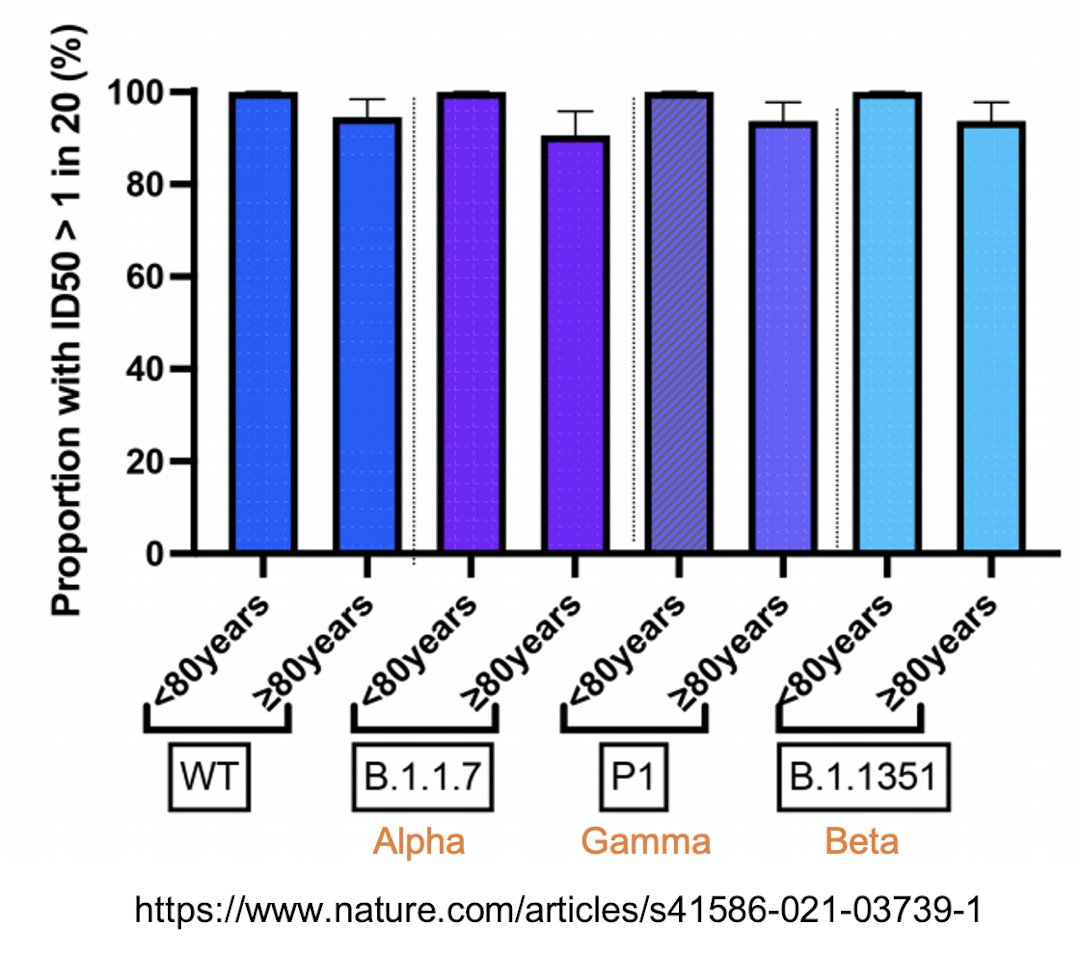
91/ But 2 doses of Pfizer vaccine remained potent against the variants, including among people over 80.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
nature.com/articles/s4158…

92/ Here’s data from the Legacy Study in the UK again.
These participants received 2 doses of Pfizer vaccine.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
These participants received 2 doses of Pfizer vaccine.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…

93/ There is not only a reduction in neutralizing antibody activity elicited vs the Beta & Delta variants as compared to the early strains & the Alpha variant, but also there’s a reduction in neutralizing antibody titer by age.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
thelancet.com/journals/lance…

94/ Next, let’s turn to immunosuppressed people.
~5% of the U.S. population is immunocompromised. This includes organ transplant recipients, dialysis patients, and patients on hefty immunosuppressive treatment for autoimmune disease or cancer.
~5% of the U.S. population is immunocompromised. This includes organ transplant recipients, dialysis patients, and patients on hefty immunosuppressive treatment for autoimmune disease or cancer.
95/ It’s important to note that patients with immunosuppression SHOULD STILL BE VACCINATED.
They may not respond as well to vaccination as other people, but THEY SHOULD STILL GET VACCINATED.
They may not respond as well to vaccination as other people, but THEY SHOULD STILL GET VACCINATED.
96/ We know that solid organ transplant recipients do not seem to respond as well to COVID vaccination.
acpjournals.org/doi/full/10.73…
Severe COVID cases have been observed among solid-organ transplant recipients who have received 2 doses of mRNA vaccine.
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/aj…
acpjournals.org/doi/full/10.73…
Severe COVID cases have been observed among solid-organ transplant recipients who have received 2 doses of mRNA vaccine.
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/aj…
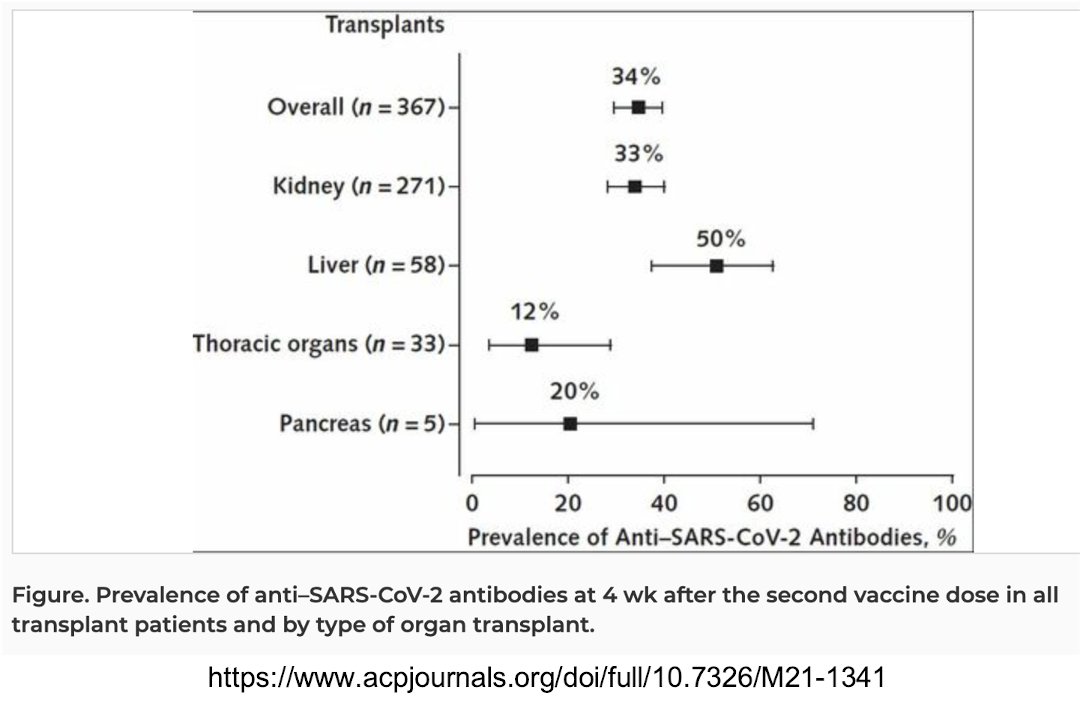
97/ This is a study looking at dialysis and kidney transplant patients.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
98/ We give solid organ transplant patients drugs to suppress their immune system (e.g. mycophenolate mofetil, steroids, calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus & cyclosporine) so that they don’t reject the transplanted organ.
99/ The healthy controls were mostly HCWs and were significantly younger than the other 2 groups.
The horizontal line is the median neutralizing antibody titer for each group.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
The horizontal line is the median neutralizing antibody titer for each group.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
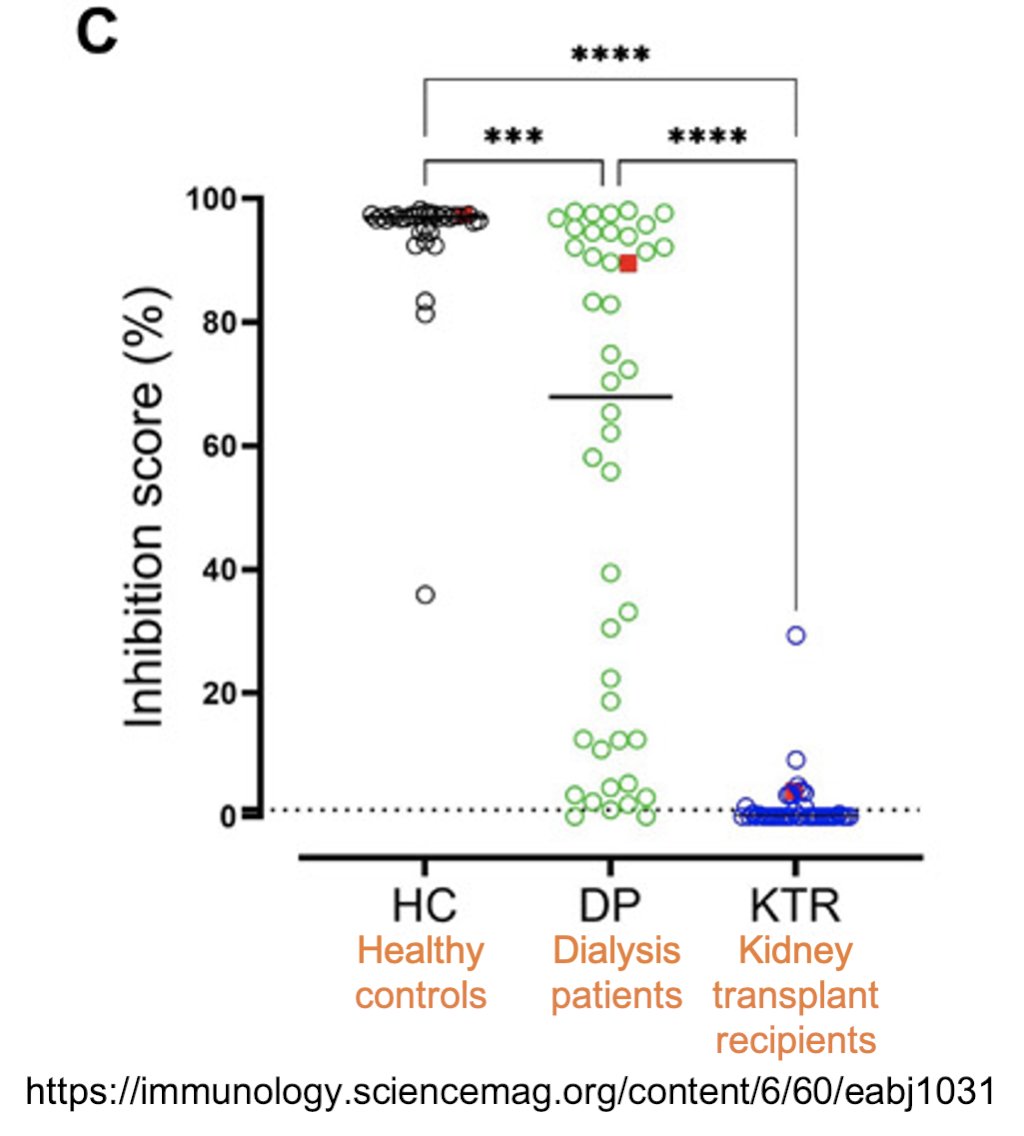
100/ Neutralizing antibody levels are lower for dialysis patients, but they’re almost nil in kidney transplant recipients.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…

101/ In addition, this study found no generation of long-lived plasma cells and memory B-cells among kidney transplant recipients. Multiple parts of the immune system were affected by immunosuppression.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
102/ We may need to increase the vaccine dose and/or give additional doses, & even that may not be enough to elicit a protective immune response in all patients who are highly immunosuppressed.
We need to remember that vaccines are one tool, but we'll need other tools, too.
We need to remember that vaccines are one tool, but we'll need other tools, too.
103/ Here’s another study looking at neutralizing antibody responses in chronic dialysis patients, who are mildly immunosuppressed, vs kidney transplant recipients, who are profoundly immunosuppressed.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…

104/ The black dots show titers one week after the 2nd dose of Pfizer vaccine and the red dots show titers 3 weeks after the 2nd dose of Pfizer vaccine.
Neutralizing antibody titers were significantly lower among kidney transplant recipients.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
Neutralizing antibody titers were significantly lower among kidney transplant recipients.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…

105/ In addition, these researchers found markedly diminished generation of SARS-CoV-2-specific plasmablasts & memory B cells among kidney transplant recipients & dialysis patients than among healthy controls.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…

106/ The black dots represent pre-vaccination and the red dots post-vaccination B-cell responses.
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…
immunology.sciencemag.org/content/6/60/e…

107/ This is a study looking at 658 solid organ (e.g. kidney, liver, heart, lung pancreas) transplant recipients who received mRNA vaccines.
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
108/ Their immunosuppressive regimens included mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, steroids, tacrolimus, sirolimus, everolimus, cyclosporine, &/or belatacept.
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
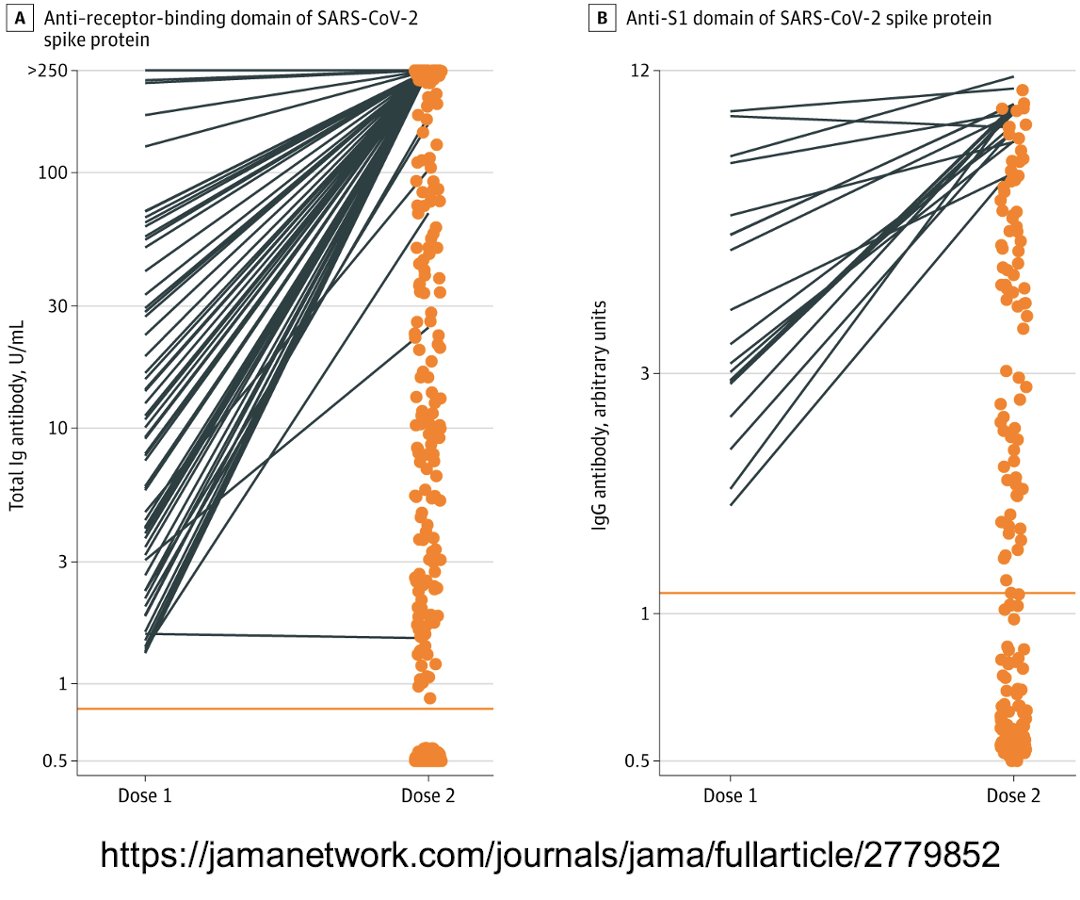
109/ The orange dots represent neutralizing antibody titers after 2 doses of Pfizer or Moderna vaccines.
46% had no Ab response after both doses.
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
46% had no Ab response after both doses.
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
110/ Here’s a study that looked at giving a THIRD dose of Pfizer vaccine to kidney, liver, lung, heart, & pancreas transplant recipients.
The horizontal bars are median antibody titers for each group.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
The horizontal bars are median antibody titers for each group.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
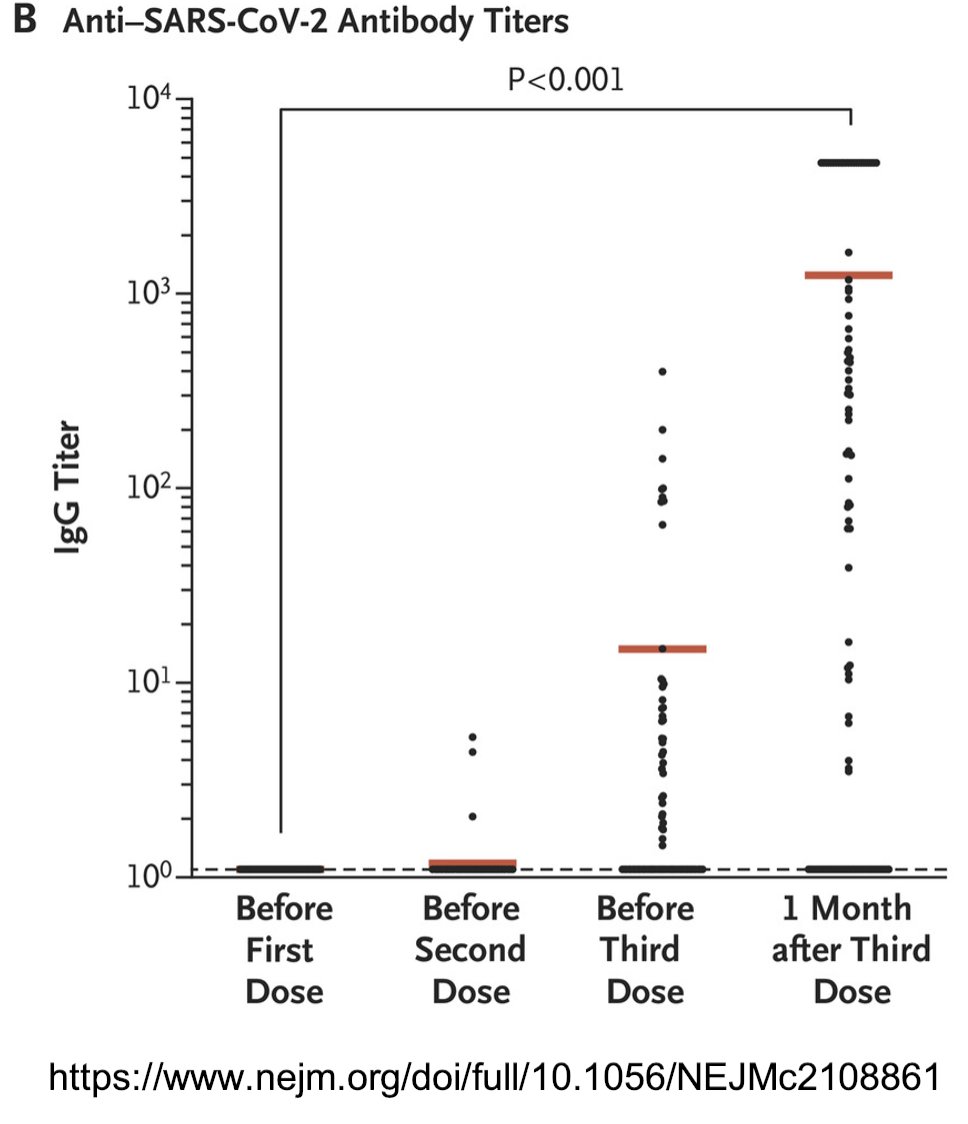
111/ The third dose of Pfizer vaccine elicited detectable neutralizing antibody titers.
With more doses & other dosing regimens, we may be able to overcome the dampening effects of immunosuppressive drugs.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
With more doses & other dosing regimens, we may be able to overcome the dampening effects of immunosuppressive drugs.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…

112/ What about stem cell transplant patients? Are their immune responses to vaccination impaired, too?
Based on this study in the Lancet, 2 doses of mRNA vaccine seem to provide adequate protection for stem cell transplant patients.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
Based on this study in the Lancet, 2 doses of mRNA vaccine seem to provide adequate protection for stem cell transplant patients.
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
113/ Other patients, like patients with autoimmune disease, are also given immunosuppressive drugs.
This study looked at patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking immunosuppressive drugs.
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
This study looked at patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking immunosuppressive drugs.
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
114/ Conventional synthetic DMARDs (30%): methotrexate, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, azathioprine
Biological DMARDs (47%): etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, certolizumab, Anakinra, tocilizumab, rituximab, abatacept
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
Biological DMARDs (47%): etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, certolizumab, Anakinra, tocilizumab, rituximab, abatacept
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
115/ Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors (tofacitinib, baricitinib, upadacitinib)
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
116/ y-axis: neutralizing antibody titers in response to 2 doses of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines
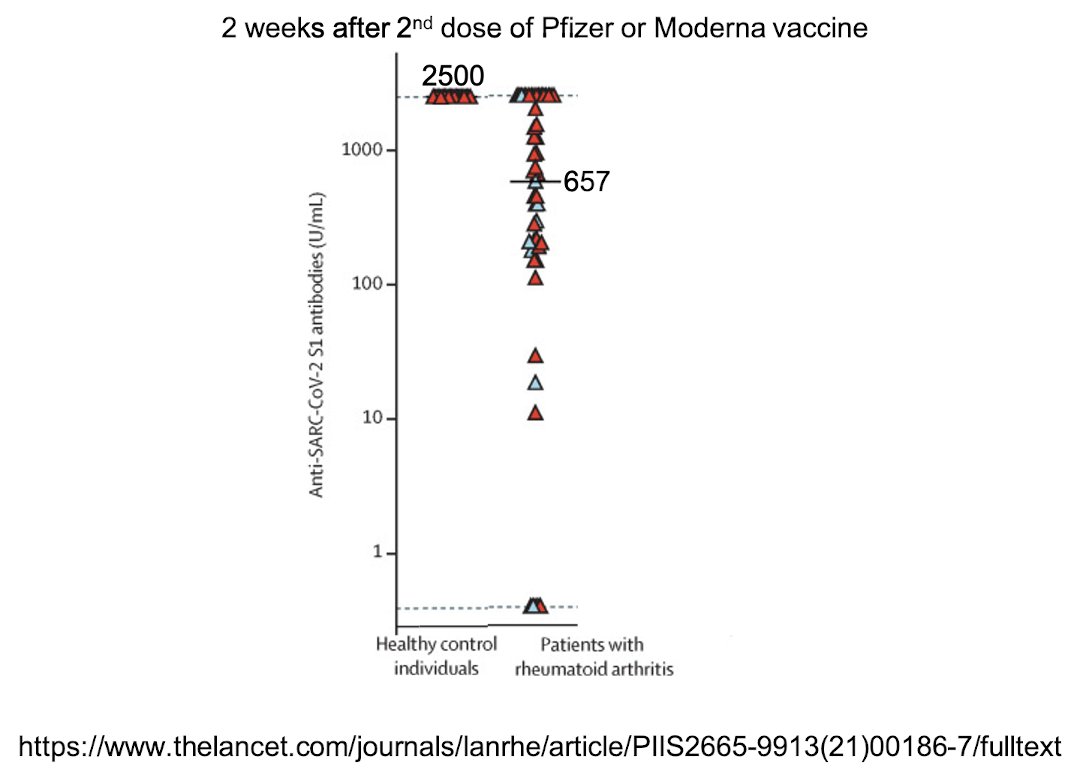
The horizontal bars represent median antibody titers: 2500 among healthy controls vs 657 among patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
The horizontal bars represent median antibody titers: 2500 among healthy controls vs 657 among patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…

117/ Neutralizing antibody titers were significantly lower in rheumatoid arthritis patients 2 weeks after 2nd dose than in the healthy control group.
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
118/ Patients with certain cancers may also be immunosuppressed.
This study looked at patients with cancer.
cell.com/cancer-cell/fu…
Y-axis: neutralizing antibodies
Horizontal line: mean antibody titers for each group
This study looked at patients with cancer.
cell.com/cancer-cell/fu…
Y-axis: neutralizing antibodies
Horizontal line: mean antibody titers for each group

119/ Patients with blood cancers (“hematologic malignancies) had lower neutralizing antibody titers after COVID vaccination than did patients with solid organ tumors (e.g. lung cancer, colon cancer).
cell.com/cancer-cell/fu…
cell.com/cancer-cell/fu…

120/ Immunosuppressive drugs are often used in the treatment of cancer.
121/ Certain drugs resulted in lower neutralizing antibody titers after vaccination—anti-CD38 antibody treatment, anti-CD20 antibody treatment, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T)—while stem cell transplant (SCT) did not.
cell.com/cancer-cell/fu…
cell.com/cancer-cell/fu…

122/ Here’s a study looking at patients
being treated for chronic lymphocytic leukemia & non-Hodgkin lymphoma
and who were given mRNA COVID vaccines.
Jurgens et al. Serologic response to mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in lymphoma patients. Am.J.Hematol. (in press)
being treated for chronic lymphocytic leukemia & non-Hodgkin lymphoma
and who were given mRNA COVID vaccines.
Jurgens et al. Serologic response to mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in lymphoma patients. Am.J.Hematol. (in press)
123/
BTKi = Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (e.g. ibrutinib), venetoclax, & anti-CD20 therapy (e.g. rituximab) are all immunosuppressive drugs used to treat cancer.
BTKi = Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (e.g. ibrutinib), venetoclax, & anti-CD20 therapy (e.g. rituximab) are all immunosuppressive drugs used to treat cancer.
124/ Patients receiving these drugs had significantly lower neutralizing antibody responses to vaccination than did healthy controls or cancer patients who hadn’t yet started treatment.
125/
Jurgens et al. Serologic response to mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in lymphoma patients. Am J Hematol. (in press)
Jurgens et al. Serologic response to mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in lymphoma patients. Am J Hematol. (in press)
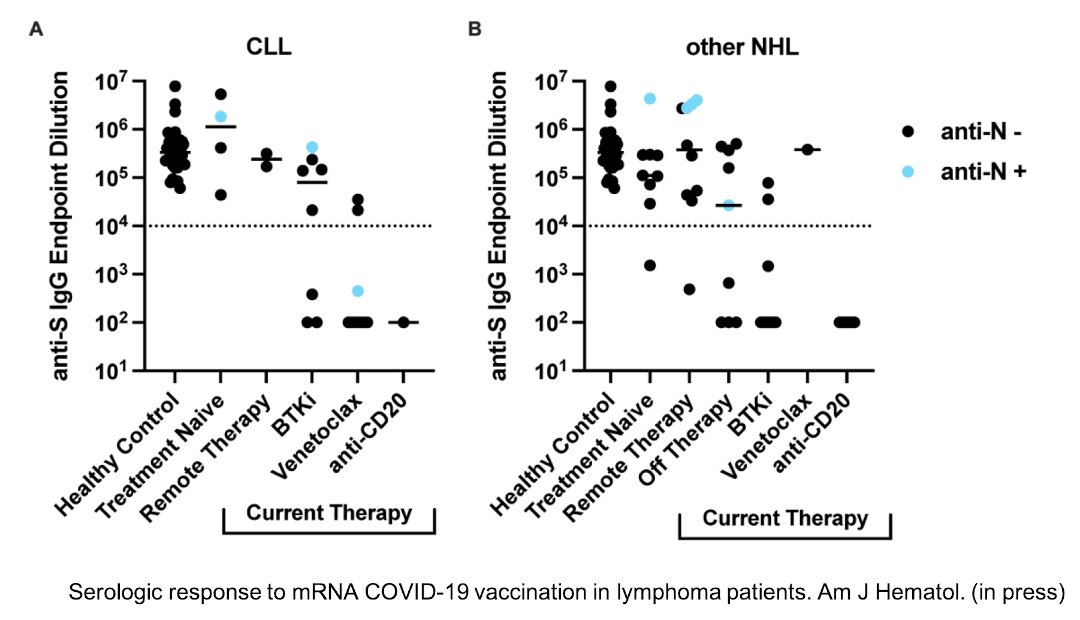
126/ What’s really striking is that patients receiving these immunosuppressive drugs for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia or non-Hodgkin lymphoma remained immunosuppressed with poor response to vaccination even 24 months after treatment. 

127/ France was the first to start giving 3rd doses of Pfizer/Moderna vaccine to immunosuppressed patients, including organ transplant recipients, recent bone marrow transplant patients, dialysis patients, ...
128/ ... & patients with autoimmune diseases undergoing strong immunosuppressive treatment (e.g. anti-CD20 or antimetabolites).
nytimes.com/2021/07/04/hea…
solidarites-sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/dgs_ur…
nytimes.com/2021/07/04/hea…
solidarites-sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/dgs_ur…
129/ Israel also recently announced it would give 3rd doses of Pfizer vaccine for immunosuppressed persons.
ft.com/content/79574d…
ft.com/content/79574d…
130/ Until the @CDCgov / ACIP &/or @US_FDA / VRBAC offer guidance, it will be difficult for immunosuppressed patients to get a 3rd dose of mRNA vaccine (or a dose of mRNA vaccine after 1st dose of J&J) in the U.S.
131/ In addition to giving additional or higher doses of vaccine to immunosuppressed persons, other options include pausing methotrexate, which has been shown to improve immunogenicity of influenza vaccination:
ard.bmj.com/content/77/6/8…
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
ard.bmj.com/content/77/6/8…
thelancet.com/journals/lanrh…
133/ How to summarize what this all means?
- We don’t yet have data to support additional or higher doses of COVID vaccine for the general public.
- We don’t yet have data to support additional or higher doses of COVID vaccine for the general public.
134/
- In making the case for a 3rd dose of its vaccine, Pfizer presented data from ongoing follow-up of phase III study participants to the White House COVID Response Team this week, but this data has yet to be shared publicly.
This data must be shared publicly.
- In making the case for a 3rd dose of its vaccine, Pfizer presented data from ongoing follow-up of phase III study participants to the White House COVID Response Team this week, but this data has yet to be shared publicly.
This data must be shared publicly.
135/ Based on the available data, some exceptions and groups in which I think an additional dose of COVID vaccine might be indicated include:
136/
- People who received the J&J vaccine, especially elderly persons who mount weaker immune responses to vaccination.
Why? The J&J vaccine offers less robust protection against the Beta & Delta variants.
- People who received the J&J vaccine, especially elderly persons who mount weaker immune responses to vaccination.
Why? The J&J vaccine offers less robust protection against the Beta & Delta variants.
137/
- Solid organ transplant recipients and other significantly immunosuppressed persons.
- Solid organ transplant recipients and other significantly immunosuppressed persons.
138/ We’re still studying heterologous prime-boost vaccine regimens.
This is when the 1st dose of a vaccine is one kind (e.g. J&J or AZ) followed by a 2nd type of vaccine (e.g. Pfizer or Moderna). Preliminary data suggests that mix-match regimens may be more potent.
This is when the 1st dose of a vaccine is one kind (e.g. J&J or AZ) followed by a 2nd type of vaccine (e.g. Pfizer or Moderna). Preliminary data suggests that mix-match regimens may be more potent.
139/ See:
nature.com/articles/s4159…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nature.com/articles/d4158…
doi.org/10.1101/2021.0…
doi.org/10.1101/2021.0…
dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3…
nature.com/articles/s4159…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nature.com/articles/d4158…
doi.org/10.1101/2021.0…
doi.org/10.1101/2021.0…
dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3…
140/ Does it make sense to get tested to see if you’re immune after vaccination?
The FDA recommends against it. This is completely unnecessary for most people.
However...
The FDA recommends against it. This is completely unnecessary for most people.
However...
141/ If you are in a high-risk group (e.g. solid organ transplant recipient), it may make sense to get tested in consultation with an infectious disease specialist or immunologist. It’s important that the right test be ordered and interpreted correctly.
142/ The right test is a quantitative, high-sensitivity Spike protein antibody test.
Many COVID antibody tests detect antibodies against nucleocapsid antigen. You will test negative on these tests if you were vaccinated, not infected.
Many COVID antibody tests detect antibodies against nucleocapsid antigen. You will test negative on these tests if you were vaccinated, not infected.
143/ Is COVID vaccination a treatment for long COVID?
Possibly.
Possibly.
144/ It’s hypothesized that symptoms of long COVID are the result of
- persistent SARS-CoV-2 replication (perhaps in immunoprivileged sites like the brain)
- viral fragments left over after infection
- autoimmune disease triggered by the infection
- persistent SARS-CoV-2 replication (perhaps in immunoprivileged sites like the brain)
- viral fragments left over after infection
- autoimmune disease triggered by the infection
145/ @Yale's Akiko Iwasaki @VirusesImmunity is leading the way on this research:
yalemedicine.org/news/vaccines-…
The idea for the study came from @Survivor_Corps, a grassroots COVID patient group.
yalemedicine.org/news/vaccines-…
The idea for the study came from @Survivor_Corps, a grassroots COVID patient group.
146/ In a poll @Survivor_Corps posted to their patient community about the effects of vaccination on long COVID, they found that about 40% of people reported mild to full resolution of their symptoms after they were vaccinated.
147/ Do you need EXTRA doses of vaccine to treat long COVID?
We don’t know.
We don’t know.
@threadreaderapp unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




