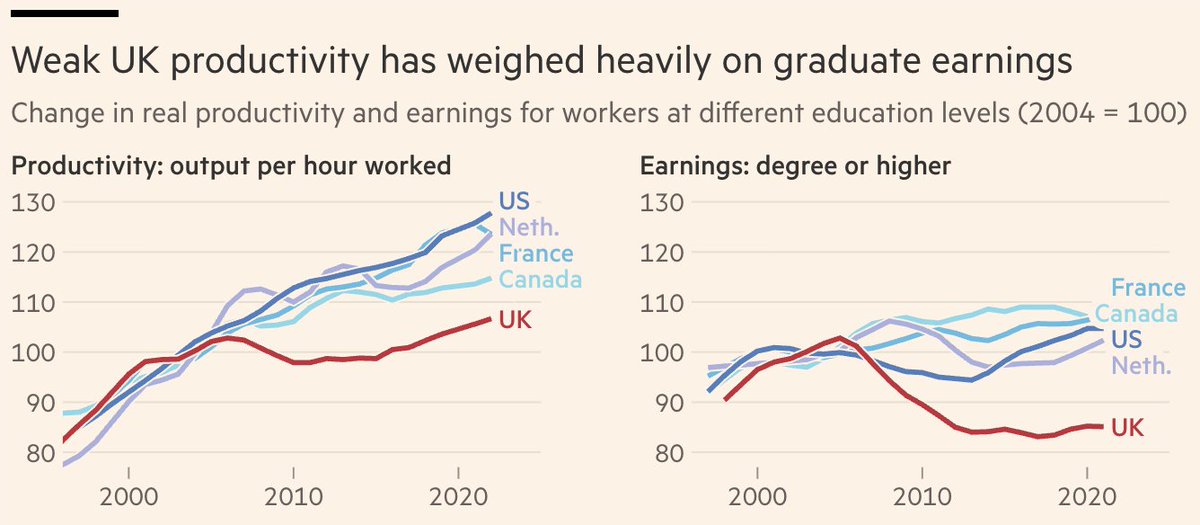
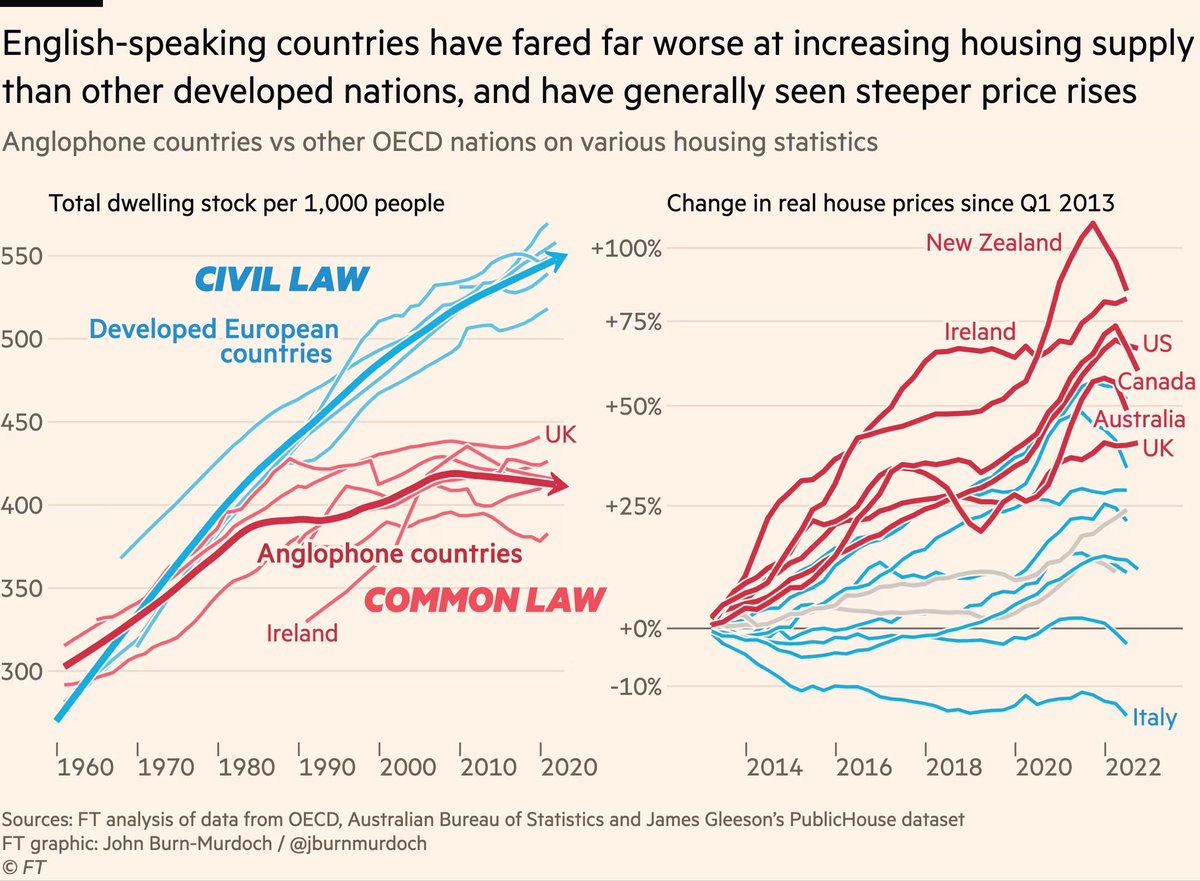
NEW: people worry when they hear "40% of hospitalisations are fully vaxxed", but this chart shows that's actually good news.
The more people you vaccinate, the higher their share of hospitalisations, but the *total* number in hospital is a fraction of what it would otherwise be
The more people you vaccinate, the higher their share of hospitalisations, but the *total* number in hospital is a fraction of what it would otherwise be
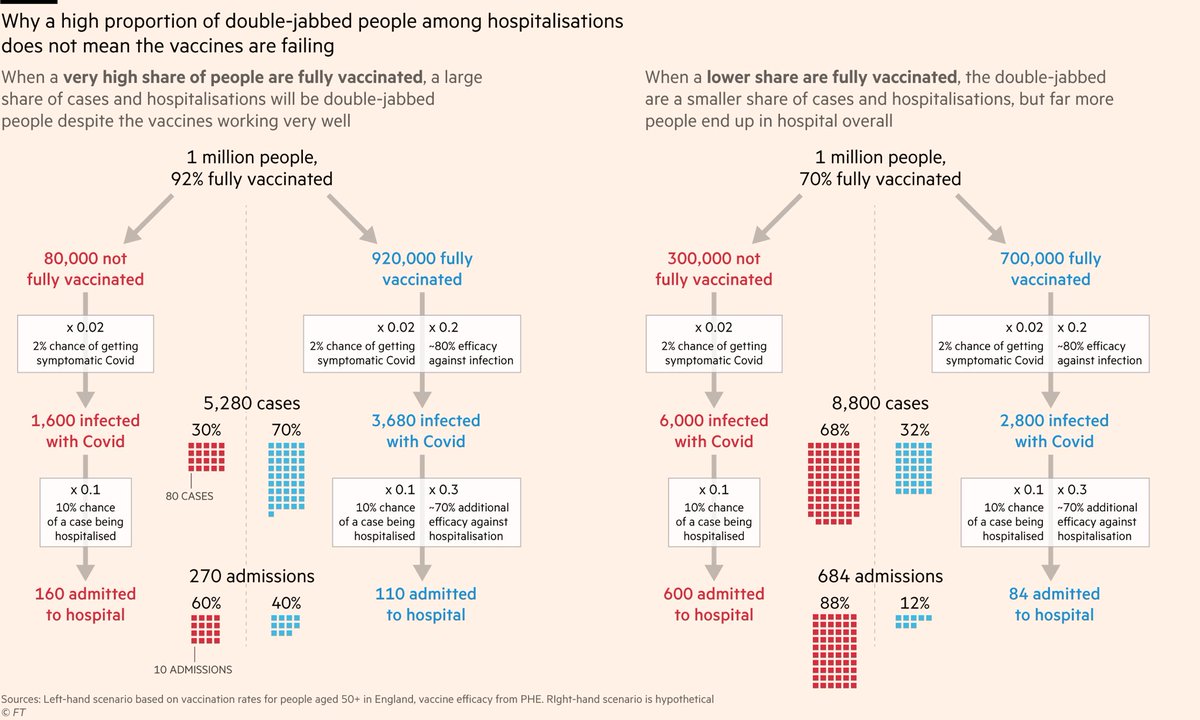
If fewer people are fully vaccinated, a smaller share of hospitalisations will be fully-vaxxed too, but this is not a good thing:
Overall there will be a lot more people in hospital because far more of the population is unprotected.
Overall there will be a lot more people in hospital because far more of the population is unprotected.
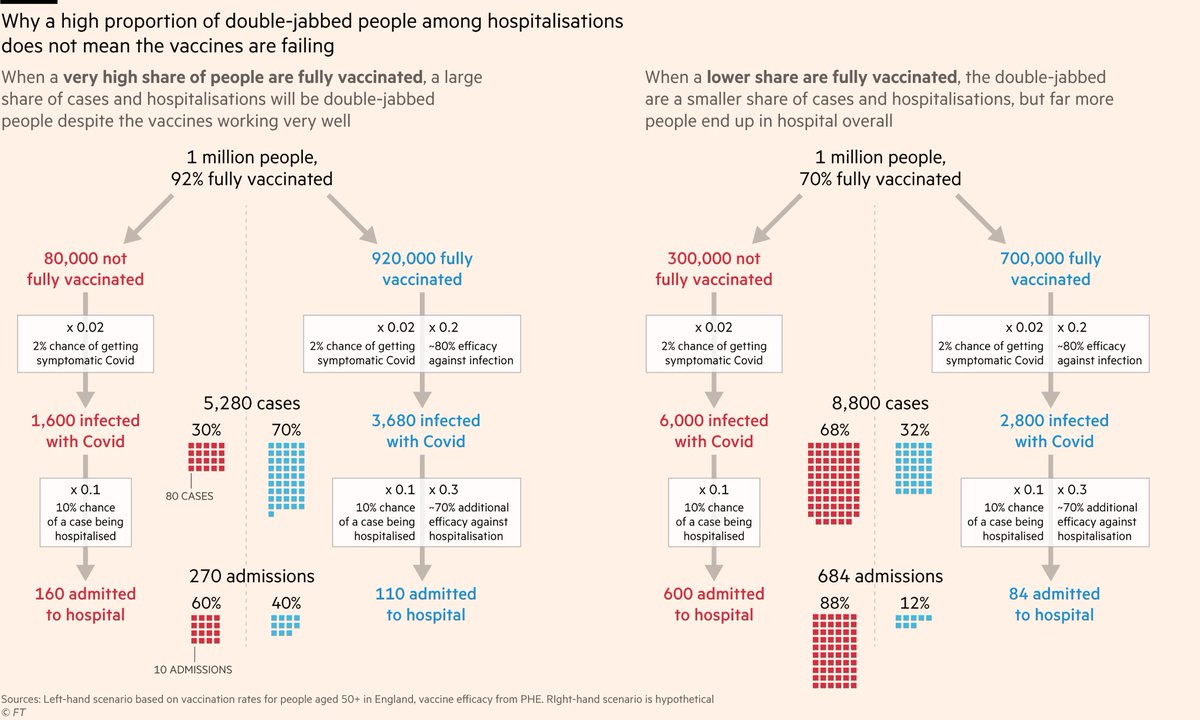
In other words: if you want to know whether the vaccination program is working, don't focus on whether the fully vaxxed make up 40% or 12% of hospitalisations.
Focus on whether the hospitalisation rate is 270 per million or 684 per million.
Focus on whether the hospitalisation rate is 270 per million or 684 per million.
But back to charts:
All the data we have suggests vaccines are working remarkably well. Far beyond what had been hoped for a year ago.
For example, a fully-vaxxed 80-year-old now has the same risk of dying from Covid as an unvaxxxed 50-year-old. That's an enormous drop in risk!
All the data we have suggests vaccines are working remarkably well. Far beyond what had been hoped for a year ago.
For example, a fully-vaxxed 80-year-old now has the same risk of dying from Covid as an unvaxxxed 50-year-old. That's an enormous drop in risk!

And we can see the game-changing impact of vaccinations clearly in the English hospitalisation data.
If it weren't for vaccines, more Covid patients would have been admitted to hospital yesterday than at the height of the winter peak. Instead we're 75% below it.
If it weren't for vaccines, more Covid patients would have been admitted to hospital yesterday than at the height of the winter peak. Instead we're 75% below it.

Here's the full story from @mroliverbarnes and me ft.com/content/0f11b2…
...which features other excellent lines like this from @anthonybmasters, who has a brilliant seatbelt analogy for vaccines 

And finally you should also read @TimHarford's latest, which discusses the "fully vaxxed share of hospitalisations" paradox alongside other features of the pandemic which defy our intuition ft.com/content/0f11b2…
As always, if you have any questions, comments etc please leave them here or DM, and I'll do my best to answer as many as possible 🙏
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh