Pre-print of the #COVIDSTEROID2 RCT comparing dexamethasone 6mg vs 12mg in hospitalized patients on high flow O2 or MV:
- no difference in survival or days free of MV with higher dose dex but…
- interesting “trend towards benefit” w/ higher dose dex
📄medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
1/



- no difference in survival or days free of MV with higher dose dex but…
- interesting “trend towards benefit” w/ higher dose dex
📄medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
1/




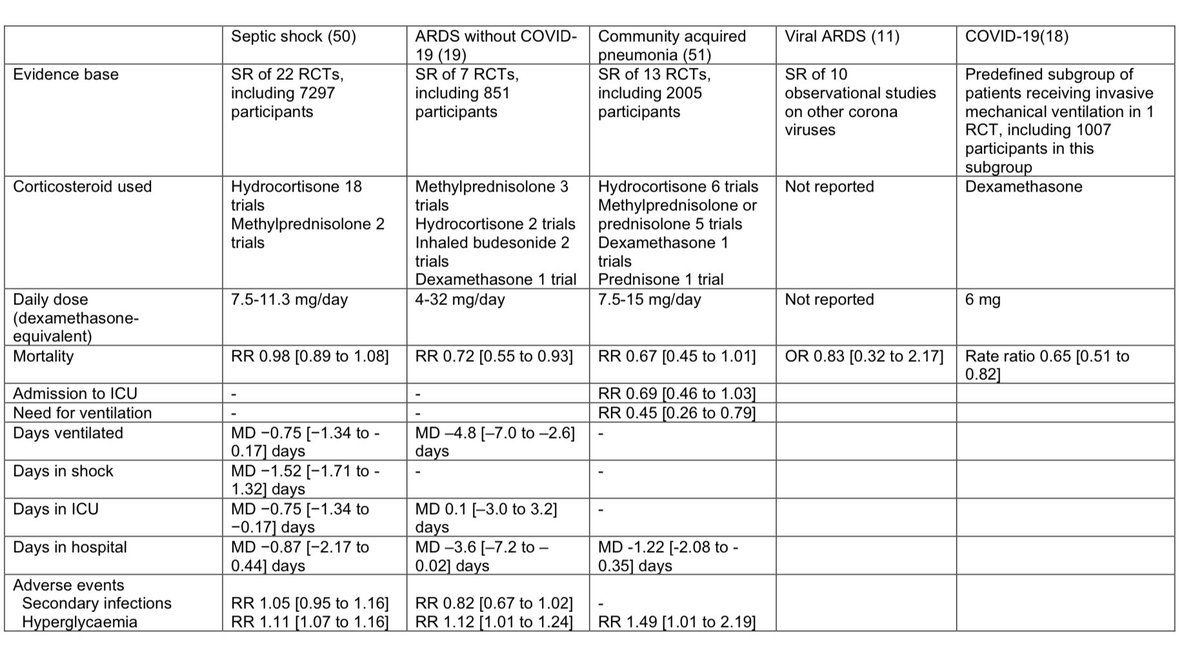
🔑 Question: we know from #RECOVERY that steroids are beneficial in severe COVID, but what’s the ideal dose?
#COVIDSTEROID2 was a large DB multi center RCT to answer this. It randomized patients on high flow O2 or MV to either 6mg or 12mg of dexamethasone for up to 10 days.
2/



#COVIDSTEROID2 was a large DB multi center RCT to answer this. It randomized patients on high flow O2 or MV to either 6mg or 12mg of dexamethasone for up to 10 days.
2/




The 1° endpoint was days alive free of lifesupport (MV, ECMO, RRT). 2° endpoints included 28 day mortality.
Based on prior studies, they powered for a 15% relative mortality reduction (ARR ~4.5%) combined w/ a 10% reduction in life support duration.
This is pretty ambitious.
3/

Based on prior studies, they powered for a 15% relative mortality reduction (ARR ~4.5%) combined w/ a 10% reduction in life support duration.
This is pretty ambitious.
3/

They randomized 1000 people (outcomes were available for 971). The two groups had similar baseline characteristics:
-mostly older (median 65), mostly male (~70%)
-comorbidities were frequent (DM, CHF, CAD, CHF)
~1/2 were on High flow O2, 1/4 on MV, & 1/4 on CPAP at enrollment
4/
-mostly older (median 65), mostly male (~70%)
-comorbidities were frequent (DM, CHF, CAD, CHF)
~1/2 were on High flow O2, 1/4 on MV, & 1/4 on CPAP at enrollment
4/

The results were interesting.
Compared to 6mg, 12mg of decadron was associated with:
-numerically lower mortality (27.1% vs 32.3%, ARR 5.2%)
-more days free of support (22 vs 20.5)
-lower rates of SAEs (11.3% vs 13.2%)
However NONE of these reached statistical significance
5/



Compared to 6mg, 12mg of decadron was associated with:
-numerically lower mortality (27.1% vs 32.3%, ARR 5.2%)
-more days free of support (22 vs 20.5)
-lower rates of SAEs (11.3% vs 13.2%)
However NONE of these reached statistical significance
5/




Slicing the data different ways yields similar findings: the higher dose of dexamethasone is numerically slightly better but doesn’t (quite) achieve statistical significance. 





What can we conclude?
It’s tempting to round “a trend towards benefit” up to “benefit” but this isn’t good science
If we round down a p=0.06 why not, for symmetry, dismiss a p=0.04 as “trending towards insignificant”?
Thresholds may be arbitrary but we shouldn’t just ignore
7/
It’s tempting to round “a trend towards benefit” up to “benefit” but this isn’t good science
If we round down a p=0.06 why not, for symmetry, dismiss a p=0.04 as “trending towards insignificant”?
Thresholds may be arbitrary but we shouldn’t just ignore
7/
Perhaps better to put this finding in context in two ways:
1) #RECOVERY demonstrated a huge mortality benefit by ICU standards (NNT 8); it’s hard to power a study to improve on this
2) prior studies (#DEXAARDS) had shown that a higher dose of dex (20mg/day) was safe/effective
8/
1) #RECOVERY demonstrated a huge mortality benefit by ICU standards (NNT 8); it’s hard to power a study to improve on this
2) prior studies (#DEXAARDS) had shown that a higher dose of dex (20mg/day) was safe/effective
8/
https://twitter.com/nickmmark/status/1275187455117848576
The differences b/w studies are germane:
#RECOVERY enrolled all hospitalized people w/ COVID & found a lower dose of 6mg dex was beneficial (but only in people with hypoxemia)
#COVIDSTEROID2 enrolled sicker people (all on O2) and found a “trend towards benefit” at 12 mg dex
9/
#RECOVERY enrolled all hospitalized people w/ COVID & found a lower dose of 6mg dex was beneficial (but only in people with hypoxemia)
#COVIDSTEROID2 enrolled sicker people (all on O2) and found a “trend towards benefit” at 12 mg dex
9/
#DEXAARDS enrolled people who were even sicker, those on MV who already met criteria for ARDS
This study was pre-COVID but I think we have enough data to say, uncontroversially, that COVID ARDS is ARDS
Thus it’s reasonable to conclude that sicker pts “need” more steroids🤯
10/
This study was pre-COVID but I think we have enough data to say, uncontroversially, that COVID ARDS is ARDS
Thus it’s reasonable to conclude that sicker pts “need” more steroids🤯
10/
Although #COVIDSTEROID2 doesn’t show a clear benefit for higher dose dex, it also demonstrates that 12mg isn’t worse than 6mg. In fact 12mg has numerically fewer serious side effects, including infxn
With diverging KM curves it’ll be interesting to see the 3 & 6 mo follow up
11/

With diverging KM curves it’ll be interesting to see the 3 & 6 mo follow up
11/


Clinical 🥡:
- this is a *NEGATIVE* study…
- yet there *IS* reason to think that a slightly higher dose dexamethasone (12mg instead of 6mg) may be safe & beneficial in sicker COVID patients (such as those with ARDS on MV)
- looking forward to reading the peer reviewed 📄
12/12
- this is a *NEGATIVE* study…
- yet there *IS* reason to think that a slightly higher dose dexamethasone (12mg instead of 6mg) may be safe & beneficial in sicker COVID patients (such as those with ARDS on MV)
- looking forward to reading the peer reviewed 📄
12/12
Things NOT to do:
-go above #DEXAARDS dosing; older studies found HARM w/ higher steroid doses in ARDS
-continue for longer than 10 days; NO studies demonstrate benefit for this
-substitute another steroid (unless you need to); no mineralocorticoid effects w/ dex may help
13/12
-go above #DEXAARDS dosing; older studies found HARM w/ higher steroid doses in ARDS
-continue for longer than 10 days; NO studies demonstrate benefit for this
-substitute another steroid (unless you need to); no mineralocorticoid effects w/ dex may help
13/12
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh