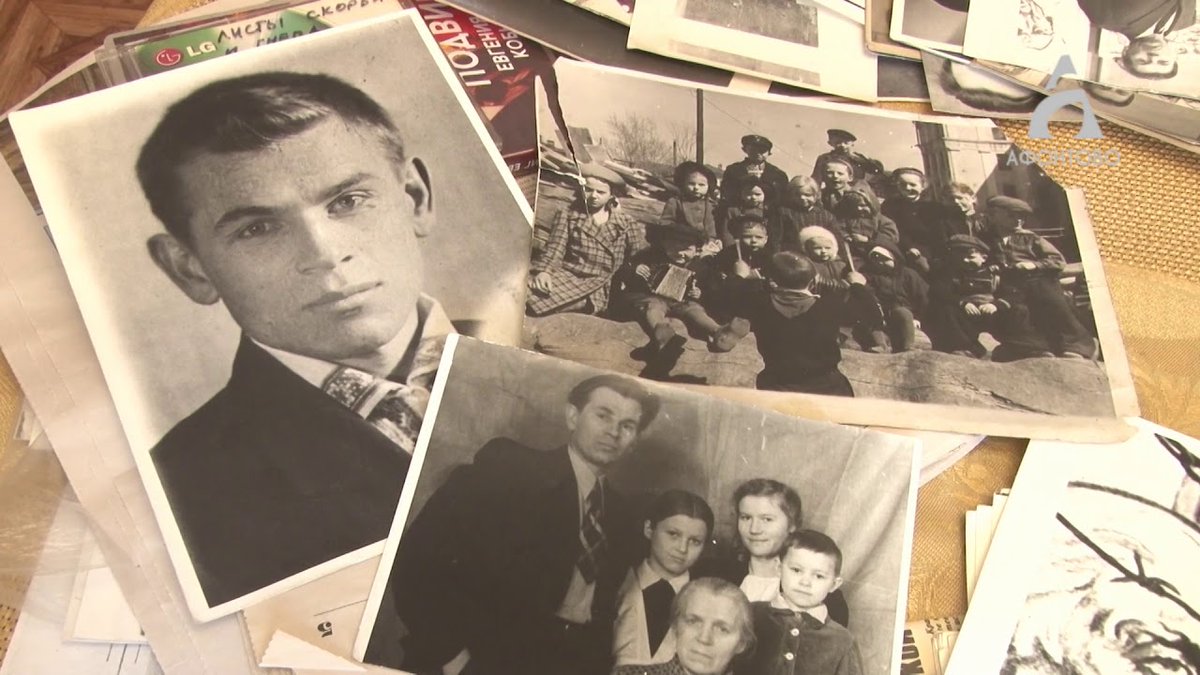
I'm getting a lot of questions about these photos, so here's what I've found;
The photos show Евгений Степанович Кобытев (Evgeny Stepanovich Kobytev) and yes, it's the same man in both photos and yes, before and after his experiences during WW2.
But there's more.
Thread;
The photos show Евгений Степанович Кобытев (Evgeny Stepanovich Kobytev) and yes, it's the same man in both photos and yes, before and after his experiences during WW2.
But there's more.
Thread;

Kobytev was an artist, writer and teacher, when the Nazis invaded the Soviet Union he became a private gunner of the 821st artillery regiment.
Wounded in battle he became a POW in the Khorol concentration camp where 90.000 POWs and civilians, often Jews, were murdered.
Wounded in battle he became a POW in the Khorol concentration camp where 90.000 POWs and civilians, often Jews, were murdered.

Danylo Lavrentiyovych Shumuk described the German POW camp as a 'pit of death with prisoners dying like flies from hunger, exposure and epidemics.'
Shumuk spend over 40 years imprisoned by several regimes, another story worth reading;
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Danylo_Sh…



Shumuk spend over 40 years imprisoned by several regimes, another story worth reading;
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Danylo_Sh…




The camp was little more than a pit, literally.
It was a quarry with just a few buildings that the prisoners weren't allowed to use so they spend most of their time outside, in the cold and hunter.
The only way Kobytev managed to survive was by distracting himself with art.



It was a quarry with just a few buildings that the prisoners weren't allowed to use so they spend most of their time outside, in the cold and hunter.
The only way Kobytev managed to survive was by distracting himself with art.




He made notes and sketches of what he saw, it distracted him.
When guards found out what he was doing the guards started ordering him to draw their portraits.
He was paid in food, terrible quality food, but food.
Of course those portraits were more flattering than these he made;



When guards found out what he was doing the guards started ordering him to draw their portraits.
He was paid in food, terrible quality food, but food.
Of course those portraits were more flattering than these he made;




He managed to escape in 1943 and returned straight to the front lines, fighting all the way to Germany, earning the Order of the Red Star and the Hero of the Soviet Union medal, but was refused the Victory over Germany medal because he had been a prisoner. 







After the war he became an art teacher again.
Like for most who suffered as he did, the rest of his life was impacted by the war.
He had nightmares, waking up screaming in the night.
But his art helped him and he eventually made a book about his experiences.
Like for most who suffered as he did, the rest of his life was impacted by the war.
He had nightmares, waking up screaming in the night.
But his art helped him and he eventually made a book about his experiences.

He also made exhibits of his work, especially in the places where he was once a prisoner, escapee and soldier, allowing locals to recognise themselves but also their tormentors in his pictures. 

So when his photos are shared and we're told they show the face of a soldier before and during the war, it's a bit of an understatement.
It's the face of a soldier before and after war but also after the unimaginable horrors of a concentration camp.
It's the face of a soldier before and after war but also after the unimaginable horrors of a concentration camp.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh