One in every four cowboys was believed to be a Black man released from slavery despite the stories told in popular books and movies although the most famous cowboys of the old west were white.
Many of the slaves were familiar with cattle herding from Africa.
(THREAD)

Many of the slaves were familiar with cattle herding from Africa.
(THREAD)


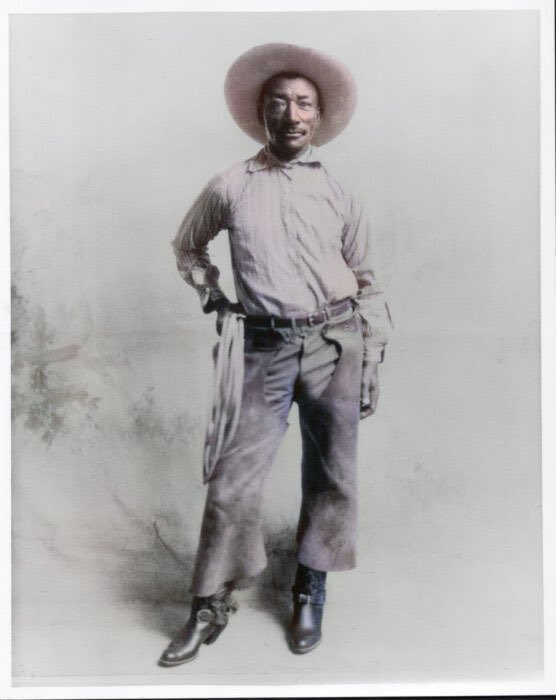
Bill Pickett (1871-1932), rodeo performer.
World famous black cowboy Bill Pickett "Dusky Demon" invented the rodeo sport, bulldogging (steer wrestling).

World famous black cowboy Bill Pickett "Dusky Demon" invented the rodeo sport, bulldogging (steer wrestling).


This is the actual man on which the movie D'Jango Unchained is loosely based.
His name is Dangerfield Newby, and he was a member of the John Brown raiders. He joined the gang to save his wife, Harriet and children from slavery.

His name is Dangerfield Newby, and he was a member of the John Brown raiders. He joined the gang to save his wife, Harriet and children from slavery.


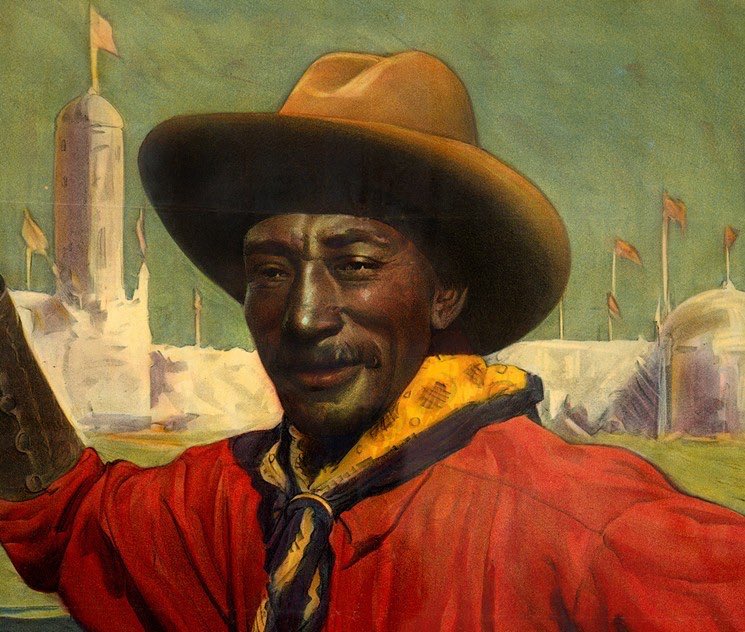
Jesse Stahl (1879-1935), cowboy and rodeo star.
Jesse is considered the greatest of all bronco riders by many rodeo enthusiasts.
In a time when a bronc rider rode a horse until it stood still, Jesse became a legend and set the bar for bronc-riding during the 1912 Salinas Rodeo.

Jesse is considered the greatest of all bronco riders by many rodeo enthusiasts.
In a time when a bronc rider rode a horse until it stood still, Jesse became a legend and set the bar for bronc-riding during the 1912 Salinas Rodeo.


Isom Dart, originally known as Ned Huddleston, gained a reputation as a late 19th Century Wyoming Territory outlaw. He had many aliases including "Black Fox," "Tan Mex," and "Calico Cowboy". 

Nat Love, aka Deadwood Dick (1854-1921), cowboy and saddler
Nate earned the nickname "Deadwood Dick" after winning a rodeo in South Dakota. As he tells it, he could hit anything within range of his Colt .45 revolvers or Winchester Model rifle, but killed only out of self-defense

Nate earned the nickname "Deadwood Dick" after winning a rodeo in South Dakota. As he tells it, he could hit anything within range of his Colt .45 revolvers or Winchester Model rifle, but killed only out of self-defense


Bass Reeves (1838-1910), lawman and deputy U.S. marshal.
Bass Reeves was the first African American commissioned to serve as a deputy marshal west of the Mississippi River. He brought to justice over 3,000 criminals and killed fourteen outlaws during his years as a marshal.

Bass Reeves was the first African American commissioned to serve as a deputy marshal west of the Mississippi River. He brought to justice over 3,000 criminals and killed fourteen outlaws during his years as a marshal.


George Fletcher (1890-1973), rodeo star and cowboy.
George Fletcher was the first Black cowboy to compete for a world championship in bronco riding at the 1911 Pendleton Round-Up, Oregon's largest rodeo.

George Fletcher was the first Black cowboy to compete for a world championship in bronco riding at the 1911 Pendleton Round-Up, Oregon's largest rodeo.


Texas cowboy Robert Lemmons was one of the greatest mustangers of all time. He became a legend in his day by perfecting his unique method of catching wild mustang horses. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh