
12 November: FLAURA, intro to power
For Lung Cancer Awareness Month #LCAM I’m going to summarize 30 important lung cancer trials over 30 days. These posts are directed at non-medical professionals, with descriptions of the results and of what makes a good trial. #lcsm 1/15
For Lung Cancer Awareness Month #LCAM I’m going to summarize 30 important lung cancer trials over 30 days. These posts are directed at non-medical professionals, with descriptions of the results and of what makes a good trial. #lcsm 1/15

Today we are back to looking at EGFR-mutated lung cancer, with the FLAURA trial comparing osimertinib to either gefitinib or erlotinib in the first-line setting. Today’s discussion is from two papers, one looking at Progression Free Survival, the other at Overall Survival 2/15 

You may recall from the IPASS study (7 November) that gefitinib improved PFS compared to chemo, with fewer side effects.
Erlotinib was another drug similar to gefitinib.
Osimertinib was the next-generation of EGFR drugs, with several potential improvements. 3/15
Erlotinib was another drug similar to gefitinib.
Osimertinib was the next-generation of EGFR drugs, with several potential improvements. 3/15
Osimertinib:
1. Inhibits usual mutations, as well as the T790M mutation, which conveys resistance to other EGFR drugs
2. Gets into the brain well to either treat, or prevent, brain metastases
3. Had already been shown to be better than chemo if patients had T790M mutation 4/15
1. Inhibits usual mutations, as well as the T790M mutation, which conveys resistance to other EGFR drugs
2. Gets into the brain well to either treat, or prevent, brain metastases
3. Had already been shown to be better than chemo if patients had T790M mutation 4/15
The trial enrolled 530 people with the two commonest EGFR mutations, who had had no prior cancer treatment. They were randomized to either osimertinib or either of erlotinib/gefitinib. The primary outcome was time to cancer worsening (PFS). 5/15
Median progression-free survival was improved with osimertinib (18.9 vs 10.2 months p<0.001). This benefit was seen in patients with or without brain metastases. 6/15 

Overall survival was also improved with osimertinib, (38.6 months vs 31.8 months p=0.046). The trial was designed with a “power of 72% to determine...a longer duration of median overall survival from 25 to 33 months”. More on power, below. 7/15 
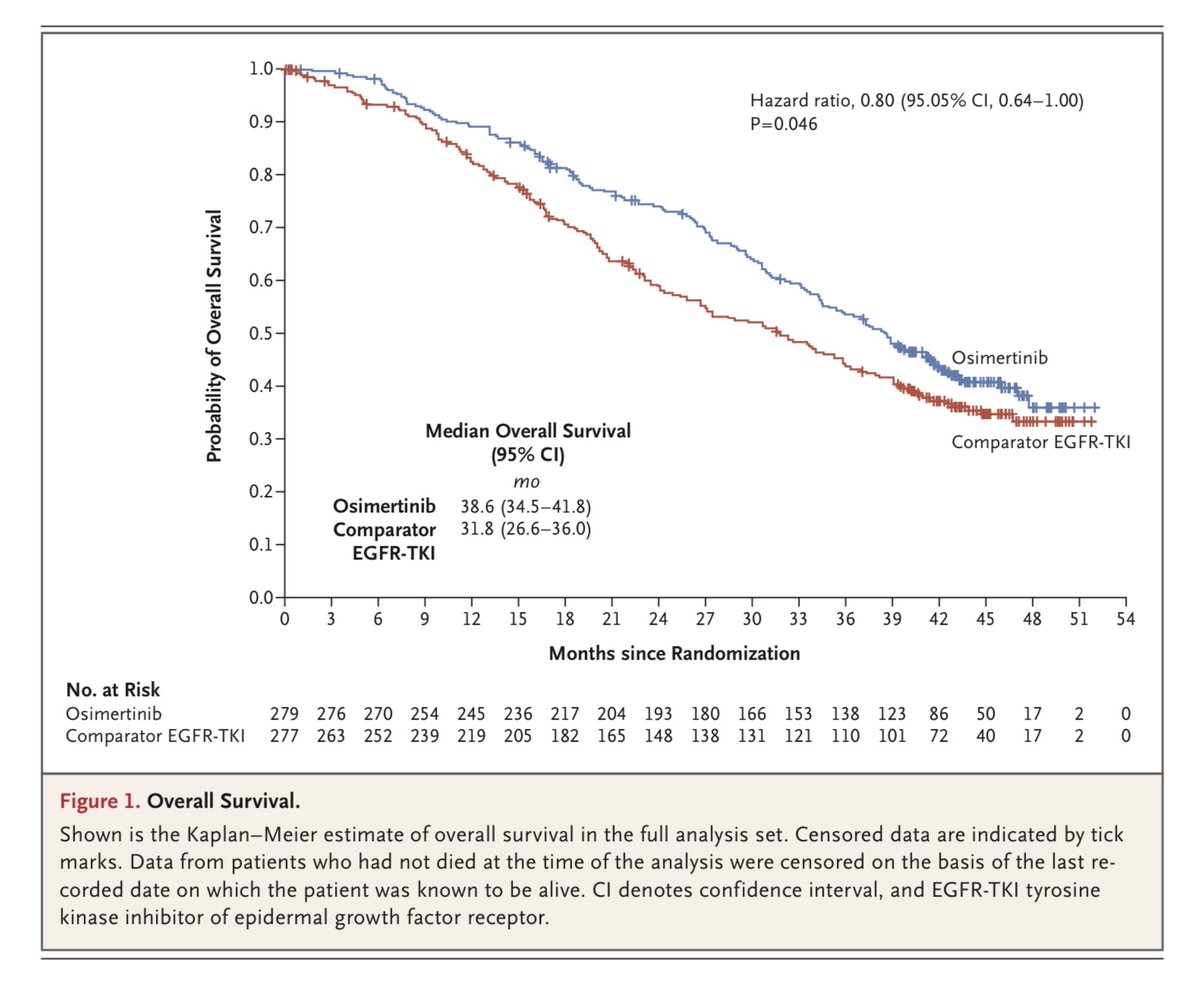
Crossover was allowed in this trial, and 31% of those in the control arm crossed over to osimertinib on progression. This sounds low, but osimertinib on progression is only indicated for people whose tumours develop T790M mutation. 8/15
This trial established osimertinib as the preferred first line EGFR drug, at least for people whose tumours have Exon 19 or L858R mutations. Some insurers dispute this, however, arguing that the degree of improvement does not warrant the 5-fold increase in cost with osimertinib.
We have discussed statistical significance, which helps us decide if an observed difference is true or due to chance.
Statistical power is in some ways the mirror image: it relates to the chance of missing a true difference if it is present. 10/15
Statistical power is in some ways the mirror image: it relates to the chance of missing a true difference if it is present. 10/15
A study might not detect a true difference between the arms if the difference is too small, if the estimates are too imprecise (confidence intervals too wide), or due to random fluctuations of chance.
In statistics, failing to find a true difference is also called a Type 2 error.
In statistics, failing to find a true difference is also called a Type 2 error.
If the probability of type 2 error is 20%, then we say that the power of the study is (1-0.2)=80%. A study has a particular power to detect a certain magnitude of difference (in the example above, a 72% power to detect an 8 month survival advantage). 12/15 

A smaller difference could be detected, but the power is lower, so the chance of missing it is higher. Studies are usually powered to either 80% or 90% for the primary endpoint. (Today’s study had 90% power for the primary end point, PFS). 13/15
A study’s power can be most easily increased by increasing the number of enrolled patients. Indeed, the need for statistical power is the primary determinant of the number of people enrolled in a trial (also called the sample size). 14/15
Tomorrow will see our first foray into the world of immunotherapy. We’ll also wrestle with the question of what, exactly, is a hazard ratio? 15/15 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









