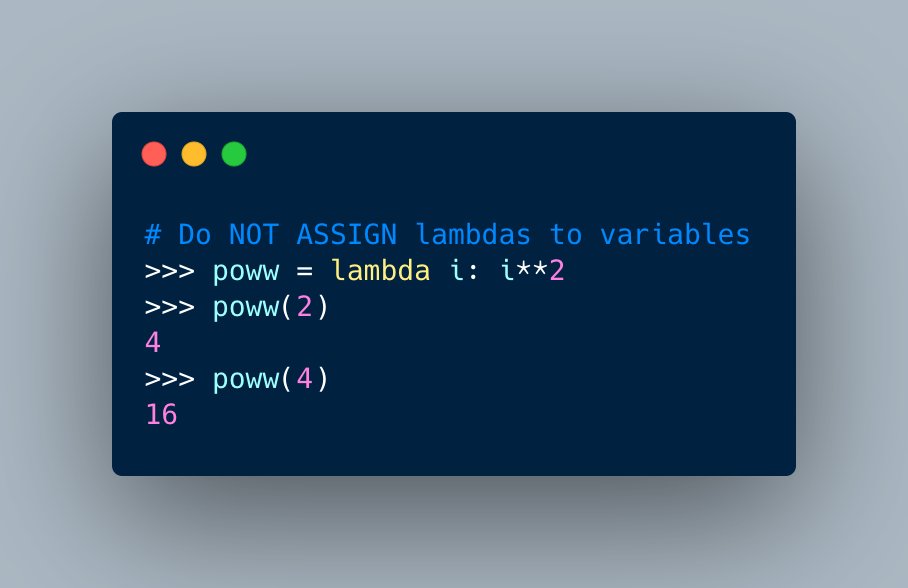
Logging in #Python is a popular topic and it's a really useful one to understand.
Today we are going to learn more about that!
🧵🐍👇
Today we are going to learn more about that!
🧵🐍👇
Python includes the `logging` module as a part of its standard library.
You can get started using it quite easily:
You can get started using it quite easily:

Python's `logging` module supports multiple logging levels:
🐍 notset
🐍 debug
🐍 info
🐍 warning
🐍 error
🐍 critical
🐍 notset
🐍 debug
🐍 info
🐍 warning
🐍 error
🐍 critical
You can set a logging level in #Python using `basicConfig()` 

Normally, when using Python's `logging` module, you would create a logger object instead of using `logging` directly.
If you do that, then you call the `setLevel()` method to set the logging level
If you do that, then you call the `setLevel()` method to set the logging level

Once you have a logger level set in your logging object, you need to choose where you wish to log.
You do that by creating a logging handler.
One of the most common logging handler to use is `StreamHandler` which logs to stdout by default
You do that by creating a logging handler.
One of the most common logging handler to use is `StreamHandler` which logs to stdout by default

Python's logging handler supports a lot of other logging handlers.
For example, you can log to an `SMTPHandler` which emails a log every time a log event happens.
Use this one with care!
For example, you can log to an `SMTPHandler` which emails a log every time a log event happens.
Use this one with care!

For a full list of logging handlers, check out the Python documentation here:
It supports platform specific handlers, like the Windows Log, sys log and much, much more more!
docs.python.org/3/library/logg…
It supports platform specific handlers, like the Windows Log, sys log and much, much more more!
docs.python.org/3/library/logg…
If you don't like the default logging format, you can change it with a `logging.Formatter()`
Here's an example of adding a formatter

Here's an example of adding a formatter


For a full listing of the formatting types, called LogRecords, look to the Python documentation here:
docs.python.org/3/library/logg…
docs.python.org/3/library/logg…
Python's logging module allows you to log to multiple handlers at once. For example, it's easy to log to a file and to stdout at the same time!
You can apply different formatters to different handlers too!
You can apply different formatters to different handlers too!

Some developers don't like coding up all that boilerplate code when working with the `logging` module
Fortunately, there are alternatives such as using a `dictConfig`:
Fortunately, there are alternatives such as using a `dictConfig`:

I created a video tutorial about logging with Python on my YouTube channel:
The code for these logging examples is up on my PyTips GitHub repo: github.com/driscollis/pyt…
I hope you enjoyed learning about logging in #Python with me.
Follow me for more great information on the Python programming language
Follow me for more great information on the Python programming language
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh