Reverse image search using Google Lens is often superior to Google Reverse Image Search. Officially, Google Lens is only available in iOS and Android apps, not on the desktop. How do you get it running on your PC or Mac? Next tweets! (1/....) 

For Linux and Windows users, download google.com/chrome/beta/ and click Experiments. Next to 'Search your screen, with Google Lens', select Right click and select 'Search Part of the Page with Google Lens' from the context menu. (2/....)
Follow the rest of the instructions here: bit.ly/3l25lXW . For Mac, it's more complicated. Download Android emulator first, via bluestacks.com/index.html and install Google App, click on Lens symbol (3/3) 

Forget what I just said! Found a way, by accident, that is way faster and works for Windows and Mac! Will post it in few minutes (4/4)
Yup, it works! Glad to announce a way to use Google Lens on desktop via a very simple method.
Step 1: type in straight into Chrome chrome://flags
(5/...)
Step 1: type in straight into Chrome chrome://flags
(5/...)

Oh, wow, now something else to share with you. In Chrome, the search will lead to a link. That link works in many browsers! Can y help me and tell me if it works? (8/..) lens.google.com/search?p=ASQ0R…
Found something else to share. Now you have Google Lens, you maybe notice you can't upload your own photos! Just from other webpages. How do you fix that? (9/...)
Voila! From now on, you can use any photo, also your own, to be scrutinised by Google Lens on your desktop. (11/11) 
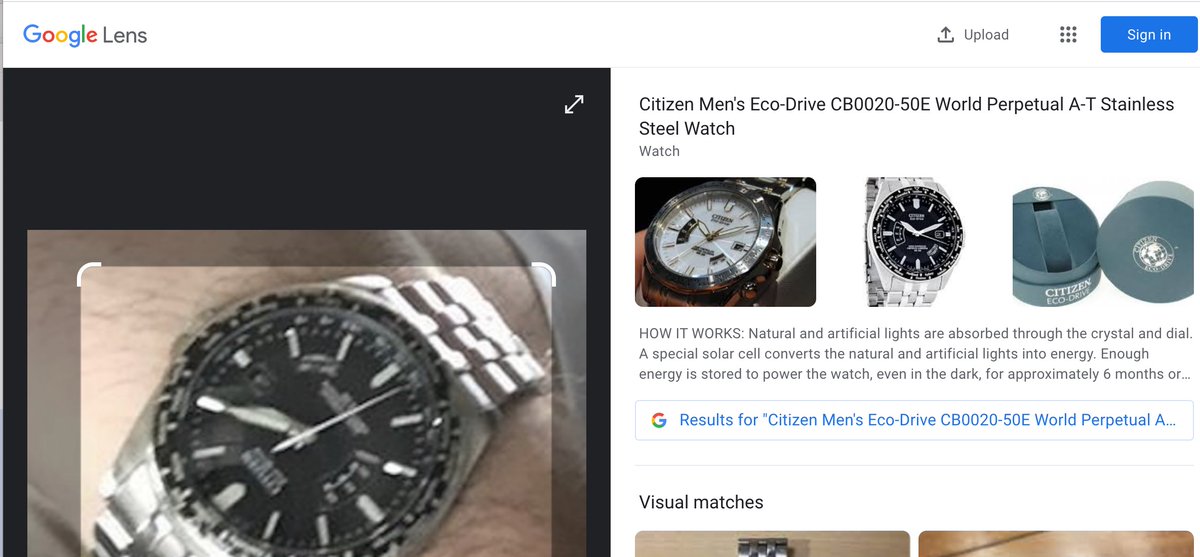
However, bear in mind that neither Google Lens nor Google Image Search are good in face recognition anymore as a result of GDPR. Use Lens for objects, landscapes, and any other type of geolocation. Have fun you all ! (12/12) 

Oh my, we can even improve the last tip (how to use Google Lens for your own photos) thanks to @StefanVoss, I adapted the tip slightly. Here is the shortcut. Type lens.google.com/search?p in your browser. Ignore the error. Just drag your image into the screen (13/13) 


Why bother? You can always ask me. This is why. Google reversed image search does not recognize this still from stream from state TV Syria (grainy, poor quality). However, Google lens correctly identifies the city: Rojava! (14/14) 

So the moment @StefanVoss pointed out that you can upload it via Computer, I tried some other stuff. And found the fastest way: you can just drag and drop your photo into the error screen.
The only downside is that Google Lens desktop doesn’t recognize text as good as Google Lens via the app on mobile or tablet does. So if you want to research text, go for the app. But for geolocation, it’s great in all platforms (15/15)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh