Replace your Dated 🐧Linux Command Line Utilities with These Modern Alternatives.
Thread🧵↓
Thread🧵↓
2. btop++
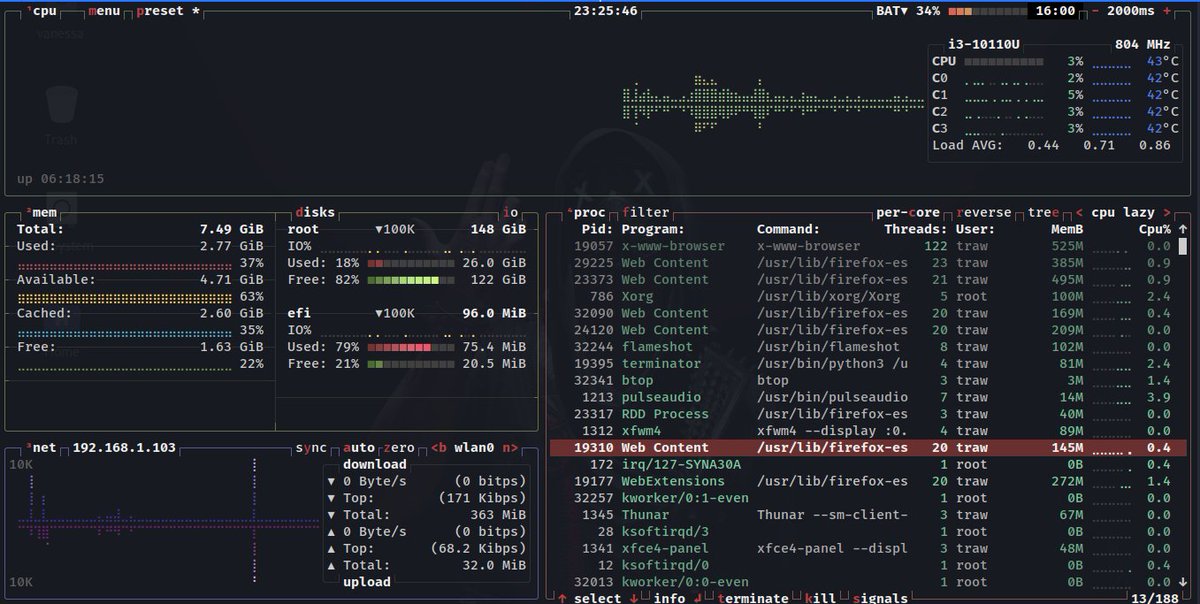
Modern replacement for top written in C+. Btop++ is a resource monitor that shows usage and stats for processor, memory, disks, network, and processes
github.com/aristocratos/b…

Modern replacement for top written in C+. Btop++ is a resource monitor that shows usage and stats for processor, memory, disks, network, and processes
github.com/aristocratos/b…

4. bat
A modern replacement for cat written in Rust. Unlike cat, this tool supports syntax highlighting for many programming languages out of the box.
github.com/sharkdp/bat
A modern replacement for cat written in Rust. Unlike cat, this tool supports syntax highlighting for many programming languages out of the box.
github.com/sharkdp/bat

6. fd
A simple, fast, and user-friendly alternative to the find command written in Rust.
github.com/sharkdp/fd
A simple, fast, and user-friendly alternative to the find command written in Rust.
github.com/sharkdp/fd

9. tldr
TL;DR stands for "Too Long; Didn't Read".
tldr is great when you just want to check a few common commands syntax without scrolling through a detailed manpage.
github.com/tldr-pages/tldr
TL;DR stands for "Too Long; Didn't Read".
tldr is great when you just want to check a few common commands syntax without scrolling through a detailed manpage.
github.com/tldr-pages/tldr

11. zoxide
Yet another tool written in Rust. Zoxide is a fast replacement for the cd command. It keeps track of the directories you visit and you can quickly navigate to them without specifying the complete path.
github.com/ajeetdsouza/zo…
Yet another tool written in Rust. Zoxide is a fast replacement for the cd command. It keeps track of the directories you visit and you can quickly navigate to them without specifying the complete path.
github.com/ajeetdsouza/zo…

14. fzf
Fzf is fast fuzz search tool Guess which language it is written in? Nope, not Rust. It's written in Go.
github.com/junegunn/fzf
Fzf is fast fuzz search tool Guess which language it is written in? Nope, not Rust. It's written in Go.
github.com/junegunn/fzf

15. broot
A new way to see and navigate directory trees. I'm beginning to think that Rust is now the god language😄😄.
github.com/Canop/broot
A new way to see and navigate directory trees. I'm beginning to think that Rust is now the god language😄😄.
github.com/Canop/broot

15. Glances
Glances an Eye on your system. A top/htop/btop alternative written in Python.
github.com/nicolargo/glan…
Glances an Eye on your system. A top/htop/btop alternative written in Python.
github.com/nicolargo/glan…

16. bottom
Yet another cross-platform graphical process/system monitor. Inspired by gtop, gotop, and htop. Guess which language it is written in? You might have guessed right. It's written in Rust.
github.com/ClementTsang/b…
Yet another cross-platform graphical process/system monitor. Inspired by gtop, gotop, and htop. Guess which language it is written in? You might have guessed right. It's written in Rust.
github.com/ClementTsang/b…

🎯That's all folks!
If you found this thread useful, please consider following @xtremepentest and retweeting the first tweet.
If you found this thread useful, please consider following @xtremepentest and retweeting the first tweet.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















