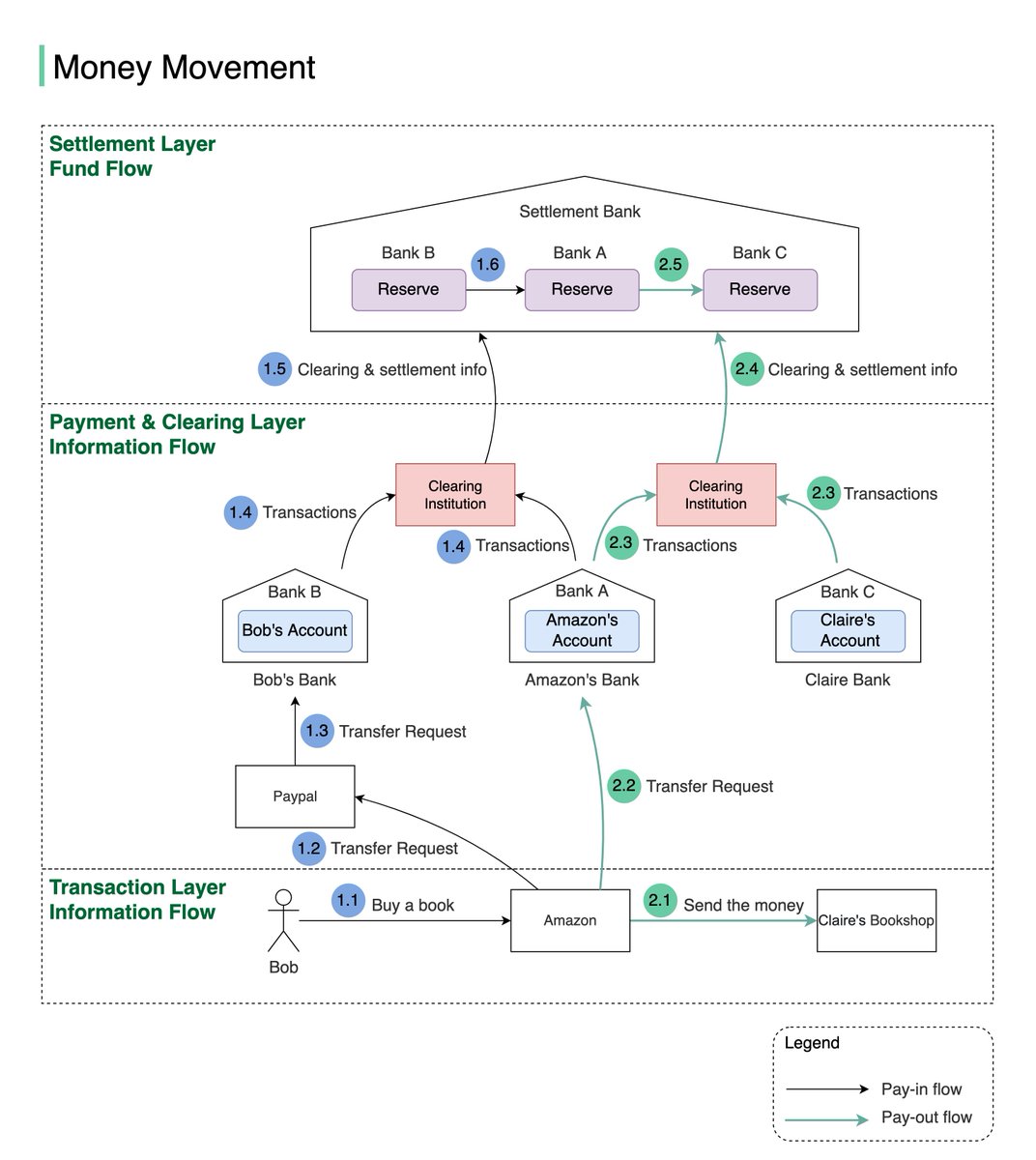
One picture is worth more than a thousand words. This is what happens when you buy a product using Paypal/bank card under the hood.1/8 
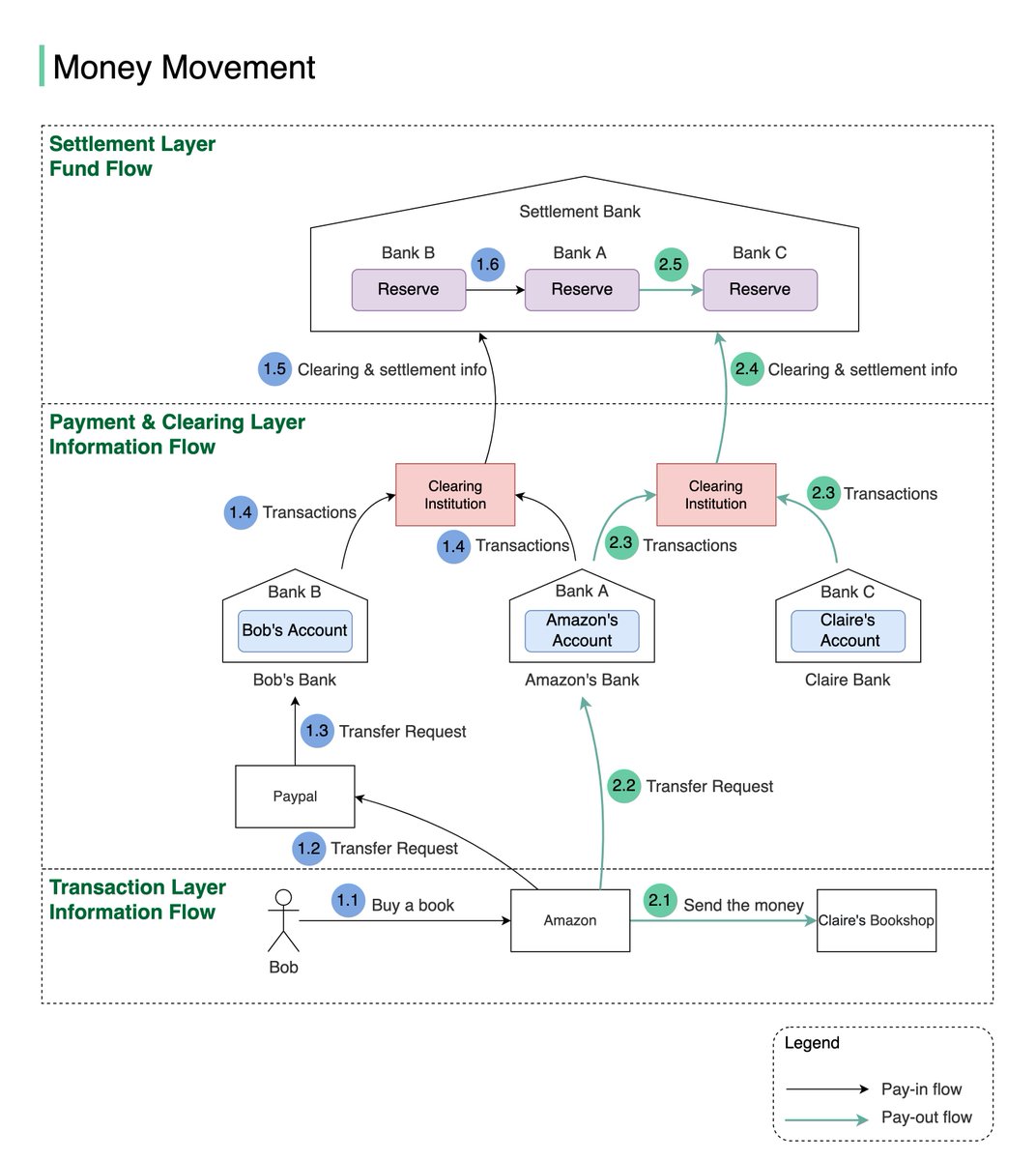
To understand this, we need to digest two concepts: 𝐜𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 & 𝐬𝐞𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭. Clearing is a process that calculates who should pay whom with how much money; while settlement is a process where real money moves between reserves in the settlement bank. 2/8 
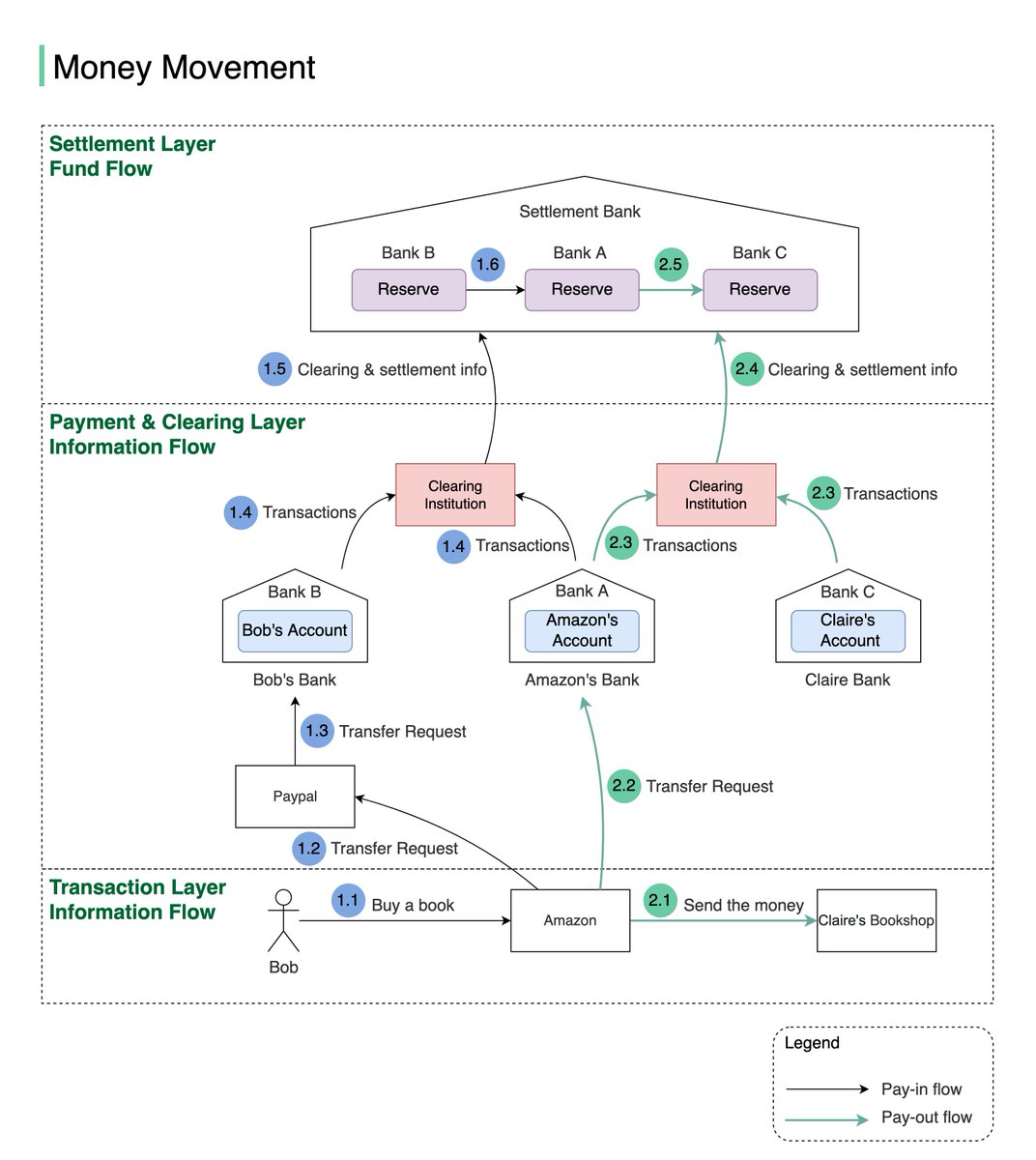
Let’s say Bob wants to buy an SDI book from Claire’s shop on Amazon.
- Pay-in flow (Bob pays Amazon money):
1.1 Bob buys a book on Amazon using Paypal.
1.2 Amazon issues a money transfer request to Paypal.3/8
- Pay-in flow (Bob pays Amazon money):
1.1 Bob buys a book on Amazon using Paypal.
1.2 Amazon issues a money transfer request to Paypal.3/8
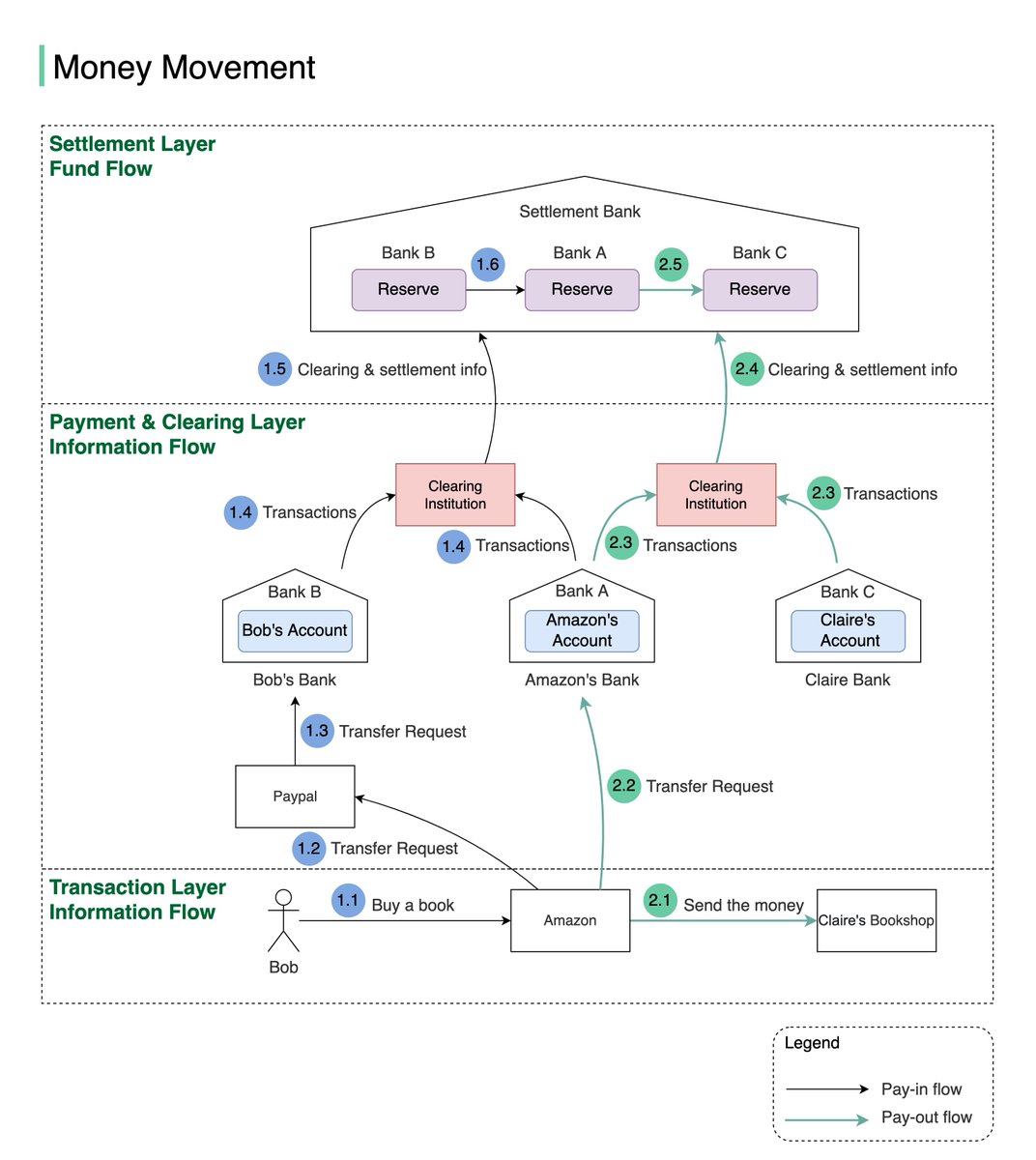
1.3 Since the payment token of Bob’s debit card is stored in Paypal, Paypal can transfer money, on Bob’s behalf, to Amazon’s bank account in Bank A.4/8 
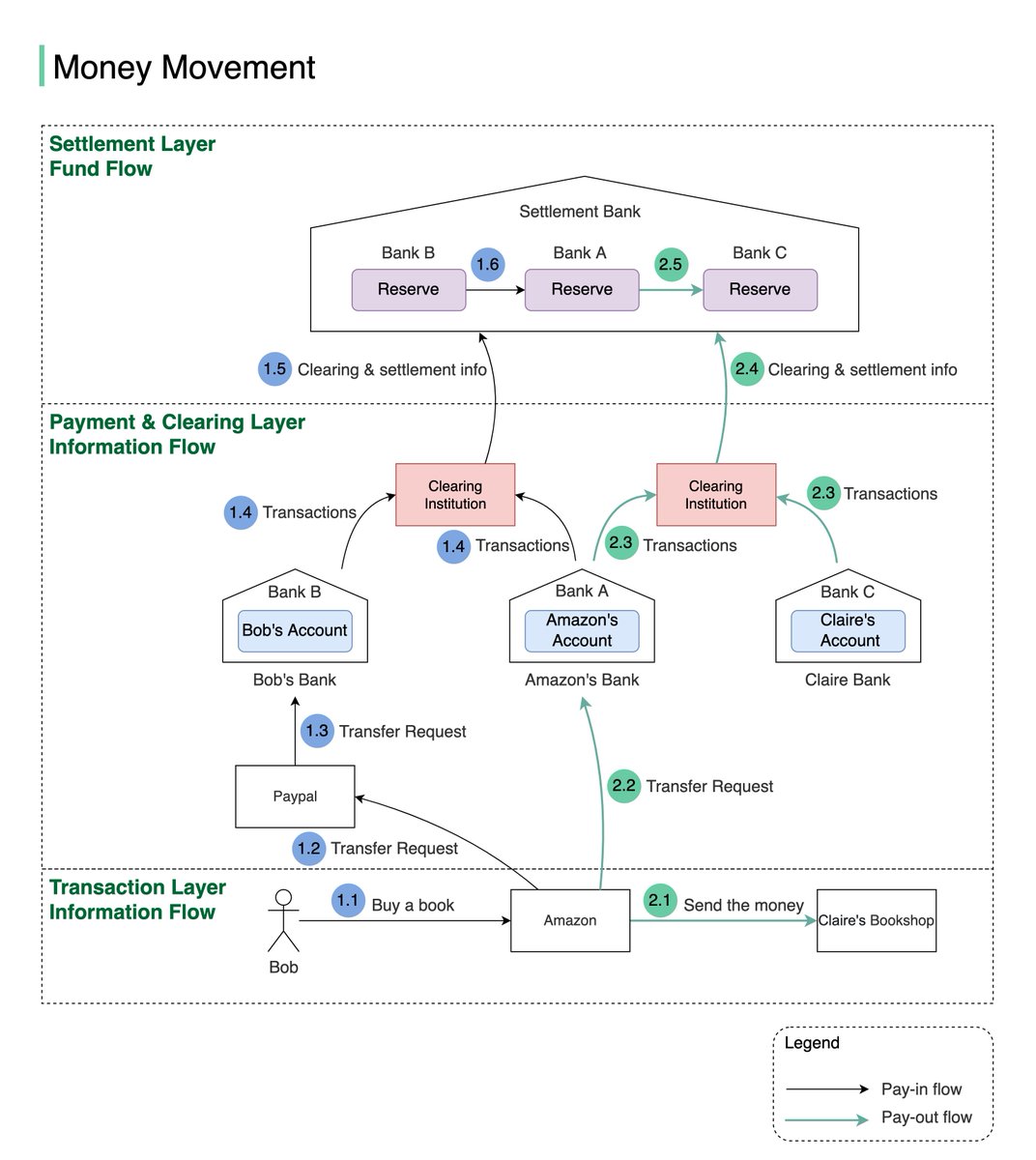
1.4 Both Bank A and Bank B send transaction statements to the clearing institution. It reduces the transactions that need to be settled. 5/8 
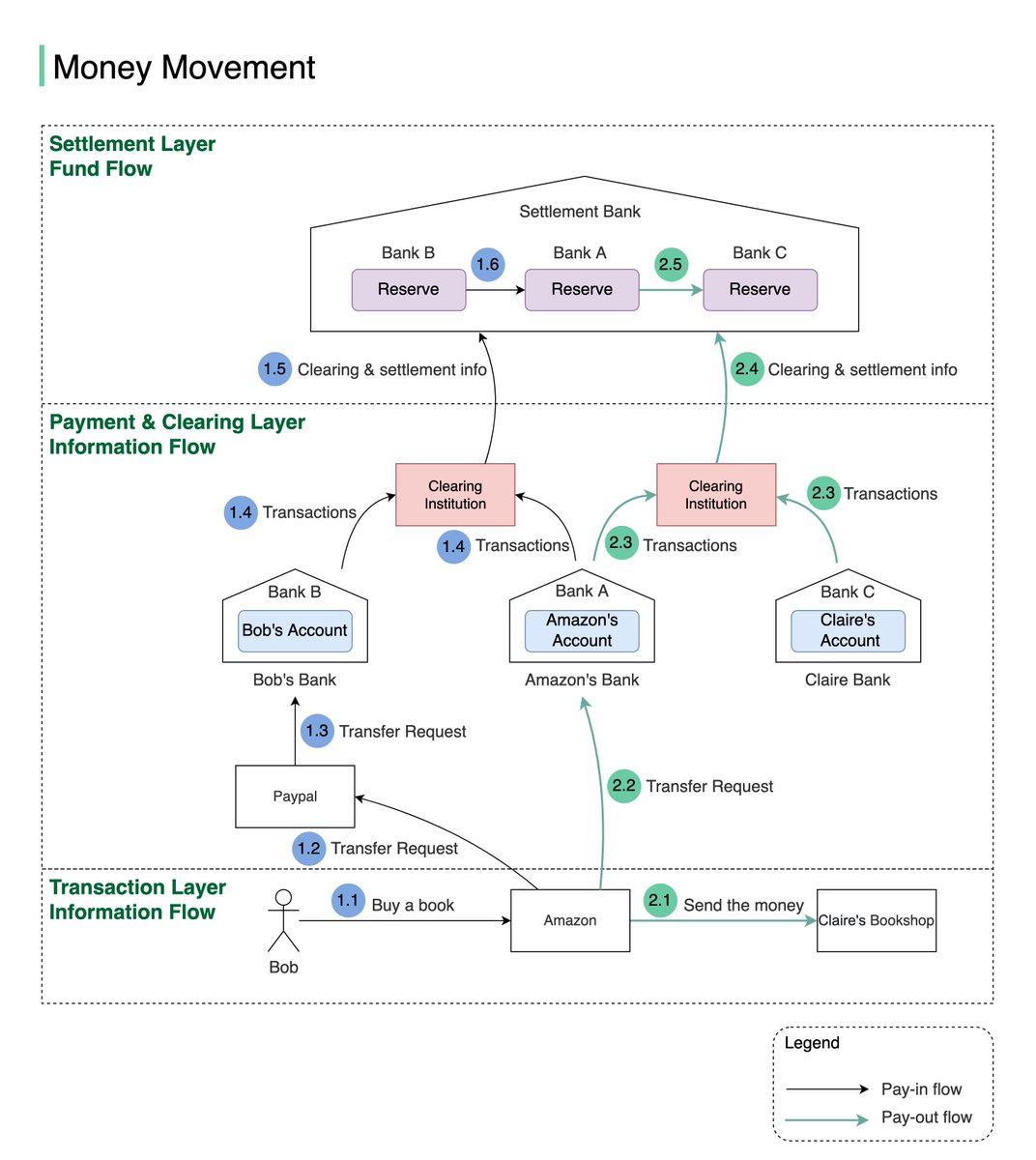
1.5 & 1.6 The clearing institution sends clearing and settlement information to the settlement bank. Both Bank A and Bank B have pre-deposited funds in the settlement bank as money reserves, so actual money movement happens between two reserve accounts in the settlement bank6/8 

- Pay-out flow (Amazon pays the money to the seller: Claire):
2.1 Amazon informs the seller (Claire) that she will get paid soon
2.2 Amazon issues a money transfer request from its own bank to the seller bank (bank C). Both banks record the transactions, but no money is moved7/8
2.1 Amazon informs the seller (Claire) that she will get paid soon
2.2 Amazon issues a money transfer request from its own bank to the seller bank (bank C). Both banks record the transactions, but no money is moved7/8
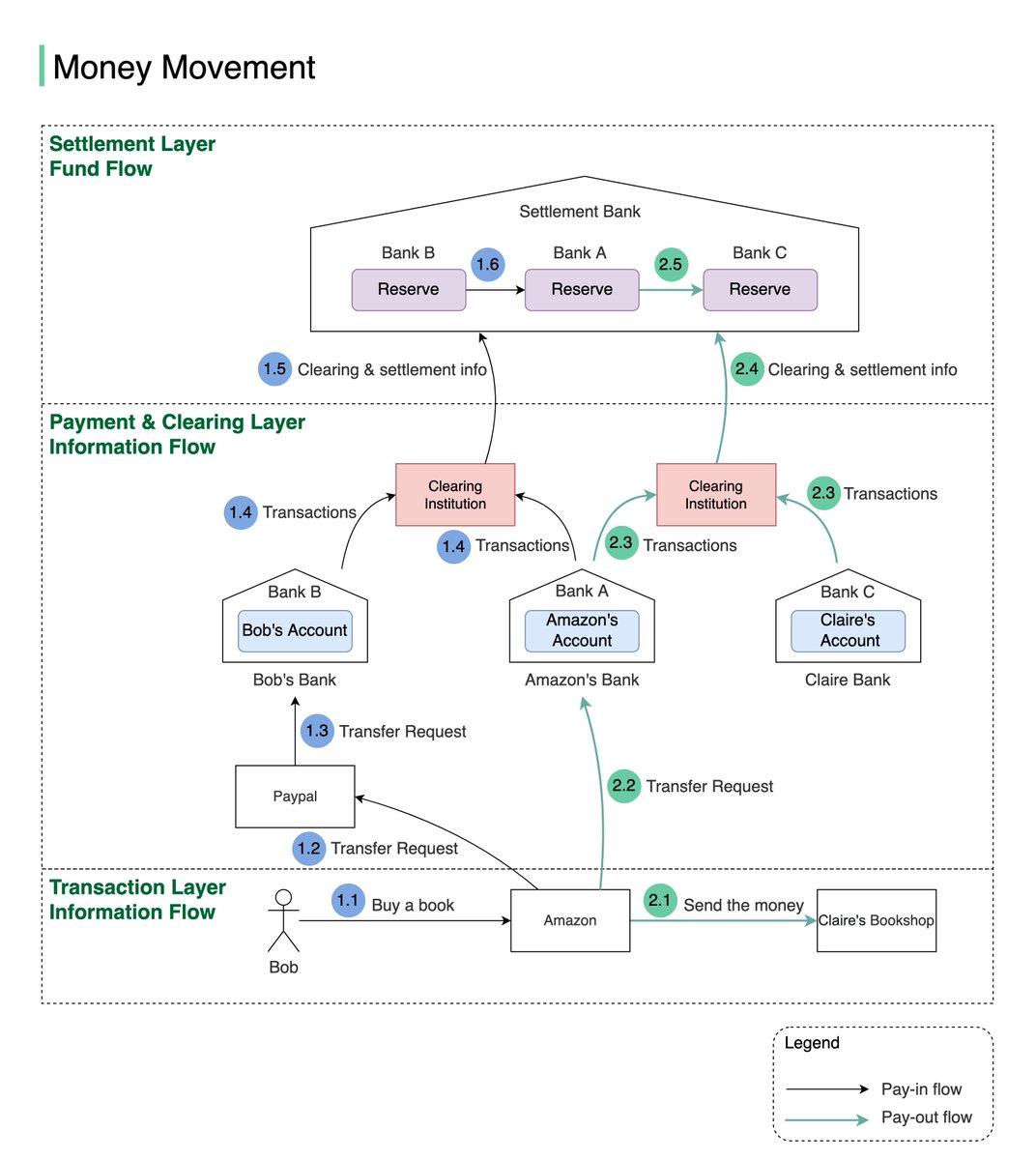
2.3 Both Bank A and Bank C send transaction statements to the clearing institution.
2.4 & 2.5 The clearing institution sends clearing and settlement information to the settlement bank. Money is transferred from Bank A’s reserve to Bank C’s reserve. 8/8
2.4 & 2.5 The clearing institution sends clearing and settlement information to the settlement bank. Money is transferred from Bank A’s reserve to Bank C’s reserve. 8/8
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh