🔥Every #Laravel Eloquent Recipes You’ll Ever Need
I’ve collected my 35 best performing Eloquent-related tweets and put them together in one huge thread. You’ll also find a downloadable PDF below.
🧵Terra-Thread is coming!
I’ve collected my 35 best performing Eloquent-related tweets and put them together in one huge thread. You’ll also find a downloadable PDF below.
🧵Terra-Thread is coming!
2/37
whereRelation
This example: give every Holding where the Stock relation's ticker column is equal to AAPL:
whereRelation
This example: give every Holding where the Stock relation's ticker column is equal to AAPL:

4/37
Invisible Database Columns
It’s a new concept in MySQL 8. What it does: when you run a select * query it won't retrieve any invisible column. If you need an invisible column's value you have to specify it explicitly in the select statement.
And now, Laravel supports this:
Invisible Database Columns
It’s a new concept in MySQL 8. What it does: when you run a select * query it won't retrieve any invisible column. If you need an invisible column's value you have to specify it explicitly in the select statement.
And now, Laravel supports this:

5/37
saveQuietly
If you ever need to save a model but you don't want to trigger any model events, you can use this method:
saveQuietly
If you ever need to save a model but you don't want to trigger any model events, you can use this method:

6/37
oldestOfMany
There's a special relationship called oldestOfMany. You can use it if you constantly need the oldest model from a hasMany relationship:
oldestOfMany
There's a special relationship called oldestOfMany. You can use it if you constantly need the oldest model from a hasMany relationship:

7/37
Default Attribute Values
You can specify default attribute values in migrations and in the Model as well:
Default Attribute Values
You can specify default attribute values in migrations and in the Model as well:

8/37
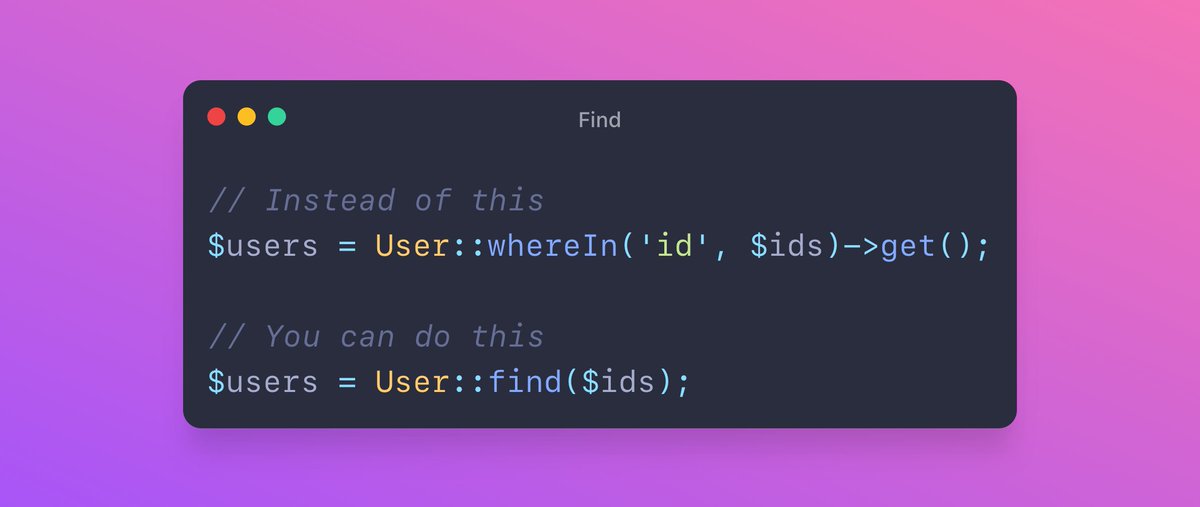
Find with an array of IDs
Everyone knows about the find method, but did you know that it accepts an array of IDs?
Find with an array of IDs
Everyone knows about the find method, but did you know that it accepts an array of IDs?
9/37
Get Dirty
In Eloquent you can check if a model is "dirty" or not. Dirty means it has some changes that are not persisted yet:
Get Dirty
In Eloquent you can check if a model is "dirty" or not. Dirty means it has some changes that are not persisted yet:

10/37
withDefault
If you have a nullable relationship you can easily end up checking for null values all over the place. Fortunately, the withDefault method solves this problem:
withDefault
If you have a nullable relationship you can easily end up checking for null values all over the place. Fortunately, the withDefault method solves this problem:

11/37
❗Stop bookmarking
I've put together a 34 pages PDF from these tips. You can download it here (free):
martinjoo.gumroad.com/l/laravel-eloq…
❗Stop bookmarking
I've put together a 34 pages PDF from these tips. You can download it here (free):
martinjoo.gumroad.com/l/laravel-eloq…
12/37
Boot Eloquent Traits
We all write traits that are being used by Eloquent models. If you need to initialize something in your trait when an event happened in the model, you can boot your trait:
Boot Eloquent Traits
We all write traits that are being used by Eloquent models. If you need to initialize something in your trait when an event happened in the model, you can boot your trait:

13/37
updateOrCreate
Creating and updating a model often use the same logic. Fortunately Eloquent provides a very convenient method called updateOrCreate.
It will run an update query if the model exists and an insert query if it does not exist:
updateOrCreate
Creating and updating a model often use the same logic. Fortunately Eloquent provides a very convenient method called updateOrCreate.
It will run an update query if the model exists and an insert query if it does not exist:

15/37
when
We often need to append a where clause to a query based on some conditional, for example, a Request parameter. Instead of if statements you can use the when method:
when
We often need to append a where clause to a query based on some conditional, for example, a Request parameter. Instead of if statements you can use the when method:

16/37
appends
If you have an attribute accessor and you often need it when the model is converted into JSON you can use the $appends property.
It’s useful when you’re working with Blade:
appends
If you have an attribute accessor and you often need it when the model is converted into JSON you can use the $appends property.
It’s useful when you’re working with Blade:

19/37
hasManyThrough
Consider this: Department → has many → Employee → has many → Paycheck
You can define a hasManyThrough relationship on the Department model that will return Paychecks through the Employee model:
hasManyThrough
Consider this: Department → has many → Employee → has many → Paycheck
You can define a hasManyThrough relationship on the Department model that will return Paychecks through the Employee model:

20/37
hasManyDeep
Okay, this is clickbait, because there is no hasManyDeep relationship in Laravel but there is an excellent package called eloquent-has-many-deep.
Consider the following relationships:
Country -> has many -> User -> has many -> Post -> has many -> Comment
hasManyDeep
Okay, this is clickbait, because there is no hasManyDeep relationship in Laravel but there is an excellent package called eloquent-has-many-deep.
Consider the following relationships:
Country -> has many -> User -> has many -> Post -> has many -> Comment

21/37
Push
Sometimes you need to save a model and its relationship as well. In this case, you can use the push method:
Push
Sometimes you need to save a model and its relationship as well. In this case, you can use the push method:

22/37
withAvg
In this example, we have a Book and a Rating model. A book has many ratings. Let's say we need to order the books by the average rating.
We can use the withAvg method:
withAvg
In this example, we have a Book and a Rating model. A book has many ratings. Let's say we need to order the books by the average rating.
We can use the withAvg method:

23/37
Eager Loading Specific Columns
select * queries can be slow and memory-consuming. If you want to eager a relationship but you don't need every column, you can specify which ones you want to load:
Eager Loading Specific Columns
select * queries can be slow and memory-consuming. If you want to eager a relationship but you don't need every column, you can specify which ones you want to load:

24/37
saveMany
With the saveMany function, you can save multiple related models in one function call.
saveMany
With the saveMany function, you can save multiple related models in one function call.

25/37
createMany
Similarly to saveMany you can also use the createMany if you don't have models, but arrays instead:
createMany
Similarly to saveMany you can also use the createMany if you don't have models, but arrays instead:

28/37
afterCreating
There's an afterCreating method on the Factory class that you can use to do something after a Model has been created.
When I have Users with profile pictures, I always use this feature:
afterCreating
There's an afterCreating method on the Factory class that you can use to do something after a Model has been created.
When I have Users with profile pictures, I always use this feature:

29/37
Factory For
Instead of creating the category and passing it as an attribute, you can use the for method:
Factory For
Instead of creating the category and passing it as an attribute, you can use the for method:

30/37
Factory Has
With the has method you can do the inverse of the relationship. So you can use this for has many relationships:
Factory Has
With the has method you can do the inverse of the relationship. So you can use this for has many relationships:

31/37
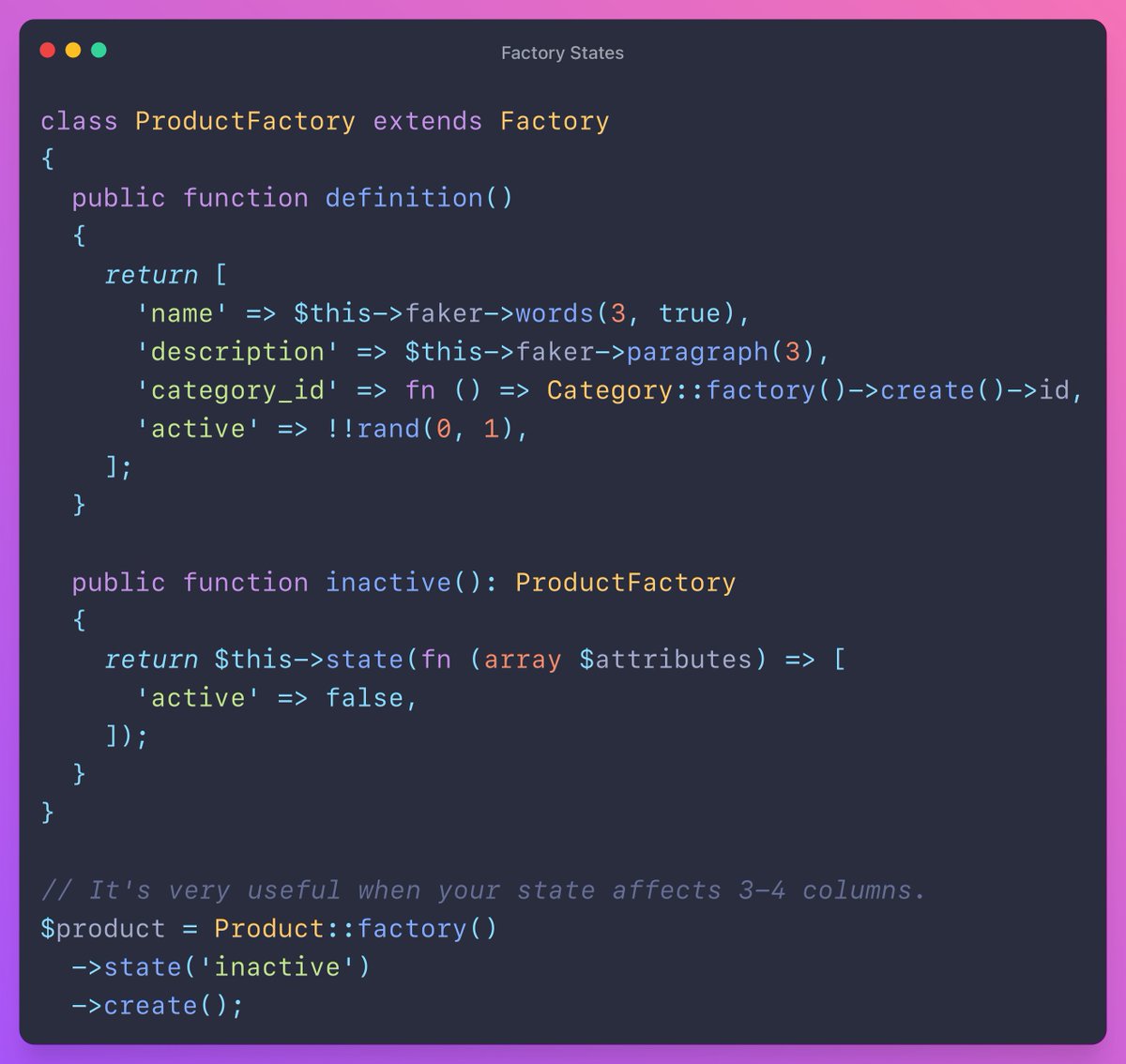
Factory States
When working with factories in tests (or seeders) we often need a specific 'state' in a given model. Let's say we have a Product model and it has an active column.
You can do this:
Factory States
When working with factories in tests (or seeders) we often need a specific 'state' in a given model. Let's say we have a Product model and it has an active column.
You can do this:
32/37
Log Every Database Query
We often want to see every database query that was executed in a request during development. There are multiple solutions, but here's the most simple one:
Log Every Database Query
We often want to see every database query that was executed in a request during development. There are multiple solutions, but here's the most simple one:

33/37
whenLoaded
You can avoid N+1 queries in API resources by using the whenLoaded() method. This will only append the department if it’s already loaded in the Employee model.
Without whenLoaded() there is always a query for the department:
whenLoaded
You can avoid N+1 queries in API resources by using the whenLoaded() method. This will only append the department if it’s already loaded in the Employee model.
Without whenLoaded() there is always a query for the department:

34/37
Pagination Links With Query String
If you have pagination in your project and you want to keep the query string from the request URL you can use the withQueryString() method.
Otherwise, your query string will be lost in the pagination links.
Pagination Links With Query String
If you have pagination in your project and you want to keep the query string from the request URL you can use the withQueryString() method.
Otherwise, your query string will be lost in the pagination links.

35/37
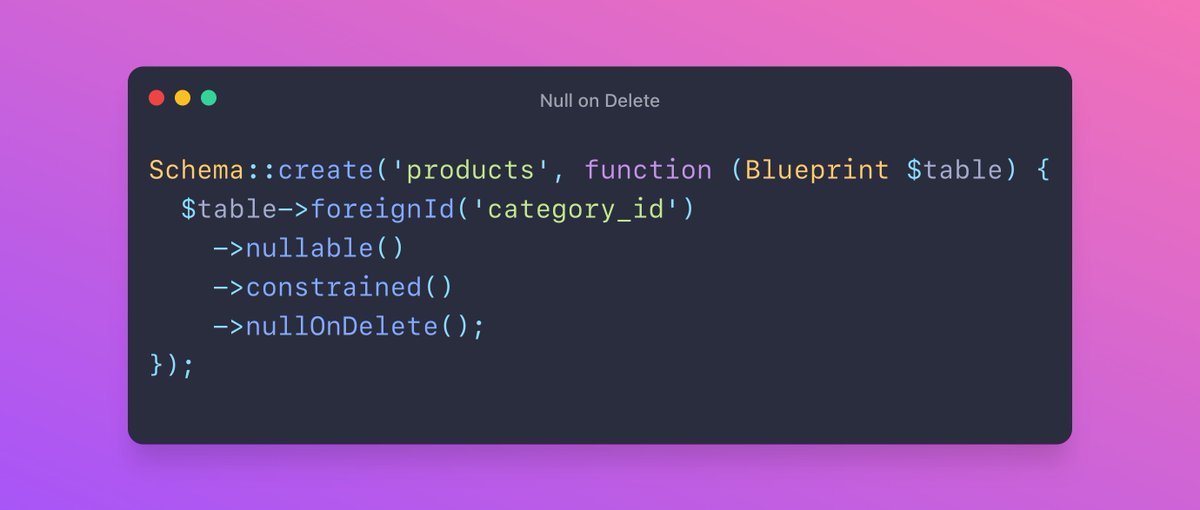
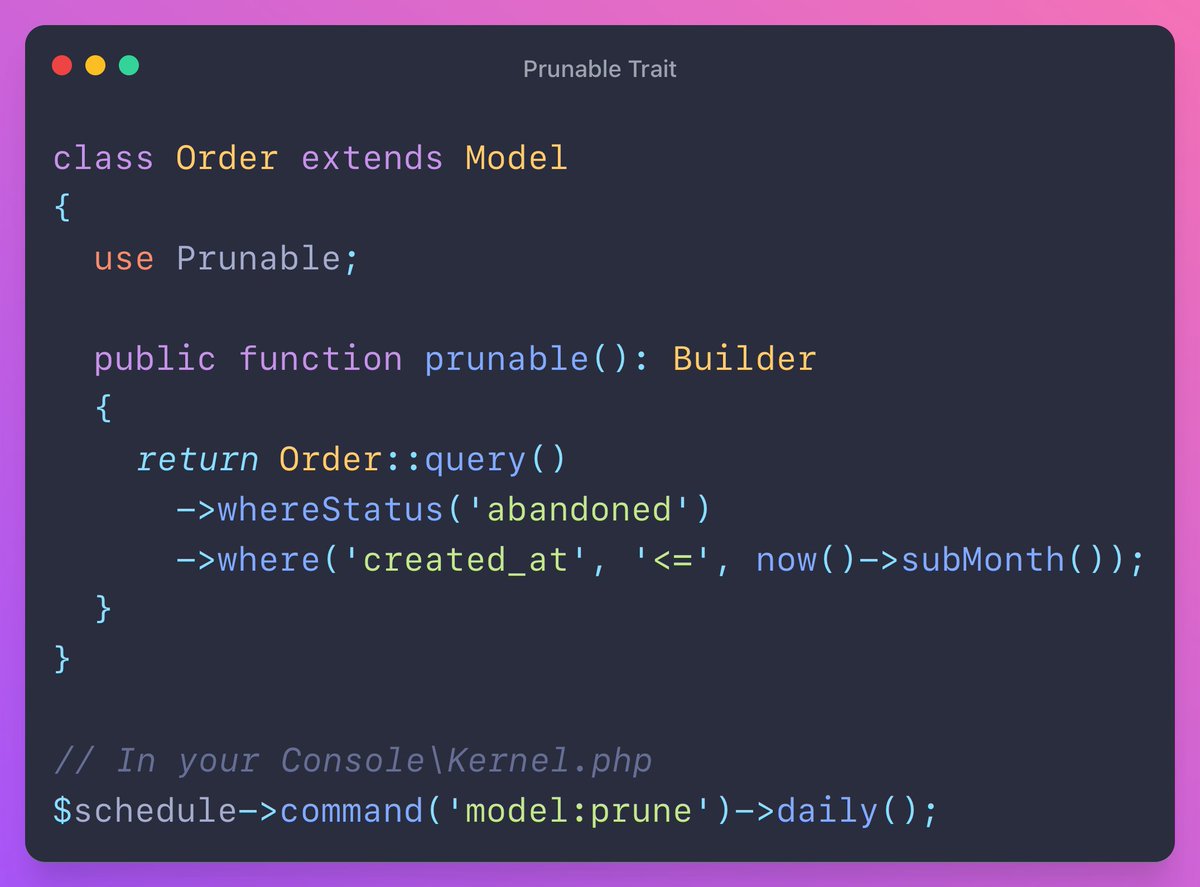
If you have a logic in your application that deletes some old or unused rows from the database, you can use the Prunable trait.
You don't need to write your own command, you can schedule the one provided by Laravel:
If you have a logic in your application that deletes some old or unused rows from the database, you can use the Prunable trait.
You don't need to write your own command, you can schedule the one provided by Laravel:
36/37
Custom Query Builder
With Eloquent you can define your own query builders for your models. By using this you can move your scopes and queries from your models.
Custom Query Builder
With Eloquent you can define your own query builders for your models. By using this you can move your scopes and queries from your models.
https://twitter.com/mmartin_joo/status/1468916731037065218
37/37
You made it... You’re a beast! 💪
I have a ton of other tweets like above so give this guy a follow: @mmartin_joo
You made it... You’re a beast! 💪
I have a ton of other tweets like above so give this guy a follow: @mmartin_joo
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh