When IAF had a legal Branch!
Yes, a separate branch just like GD(P), SIGS, A&SD. While the exact date of formation of the branch is not known, it can be surmised that the branch was setup between October 1945 and January 1946. Three more officers transferred on 22 April 1946 +
Yes, a separate branch just like GD(P), SIGS, A&SD. While the exact date of formation of the branch is not known, it can be surmised that the branch was setup between October 1945 and January 1946. Three more officers transferred on 22 April 1946 +

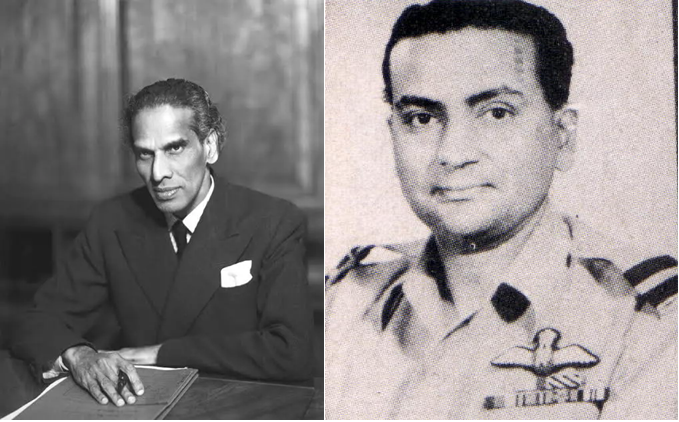
The first officer to be in the Legal Branch was then F/O (later Gp Capt) Syed Mohammad Aslam (1889). He later transferred to PAF. Three officers served in the Legal branch at the time of independence – Wg Cdr Basant Singh (2723), F/L PK Shastri (2878) and S/L BD Mistry (2728)+
After Independence – PK Shastri and BD Mistry were seconded to the JAG branch (Army) serving as Deputy Assistant JAGs. PK Shastri returned to AirHQ and became the first Chief Legal Advisor (1949-51) of the IAF. This post is now known as JAG (Air). +
Wg Cdr Basant Singh, after independence was sering as AD (PS1) within the Dte of Personnel Services. This likely was the section handing Legal issues at that time. He continued to serve in various legal role capacities and served as JAG (Air) in the mid-60s before retiring. +
Incidentally, for nearly 15 years (1951-67) the CLA/ JAG (Air) was Gp Capt Mani Poonem (1686). Mani Poonem was originally commissioned as an Observer, transferred to A&SD branch and within that trained in the legal profession. +
The Legal branch was formally disbanded in September 1949 and the members of the branch (three officers) transferred to other branches, though the legal profession continued to exist as a stream of the A&SD Branch.
@IAF_MCC
@IAF_MCC
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh