An unexpected monarch faces a revolution.
An accidental battle frees a nation.
The monarch ponders over a question while a concert stops its play.
Story in the evening ...
An accidental battle frees a nation.
The monarch ponders over a question while a concert stops its play.
Story in the evening ...
https://twitter.com/Arby_K/status/1484352552749740032
Nikolai Pávlovich was born in 1796 to Pavel Petrovich, Emperor of Russia and Maria Feodorvna (Sophie Dorothea) of Württemberg. His brother, Aleksándr Pávlovich, became Emperor in 1801, when their father was killed by Russian nobles. 1/10 

Emperor Aleksándr led Europe at the Congress of Vienna to a "system restore" and formed an alliance with Austria and Prussia. His death in 1825 brought an ambiguity to the throne since unknown to most Russians Nikolai's elder brother, Constantin, had renounced the throne. 2/10 

Nikolai waited for his brother to become Emperor but Constantin refused to do so, remaining in Poland. Eventually Nikolai became Emperor, but not after having to deal with a revolt. But no sooner had he got hold of the throne, he had to defend against a Persian invasion. 3/10 

Meanwhile, the Greeks, who had been rebelling against the Ottoman Empire, had to face reinforcements from Egypt. Emperor Nikolai wanted Greeks to be independent under Ottoman rule. Russia, Britain & France, while blockading the Greek coast, ended up destroying Ottoman fleet. 4/10 

War between the Ottomans and the Russians soon followed. It ended with Greece becoming independent of Ottoman rule, while Wallachia and Moldavia fell under Russian protection, though under Ottoman rule. In the meantime, Russia had removed Persians from the Caucasus. 5/10 

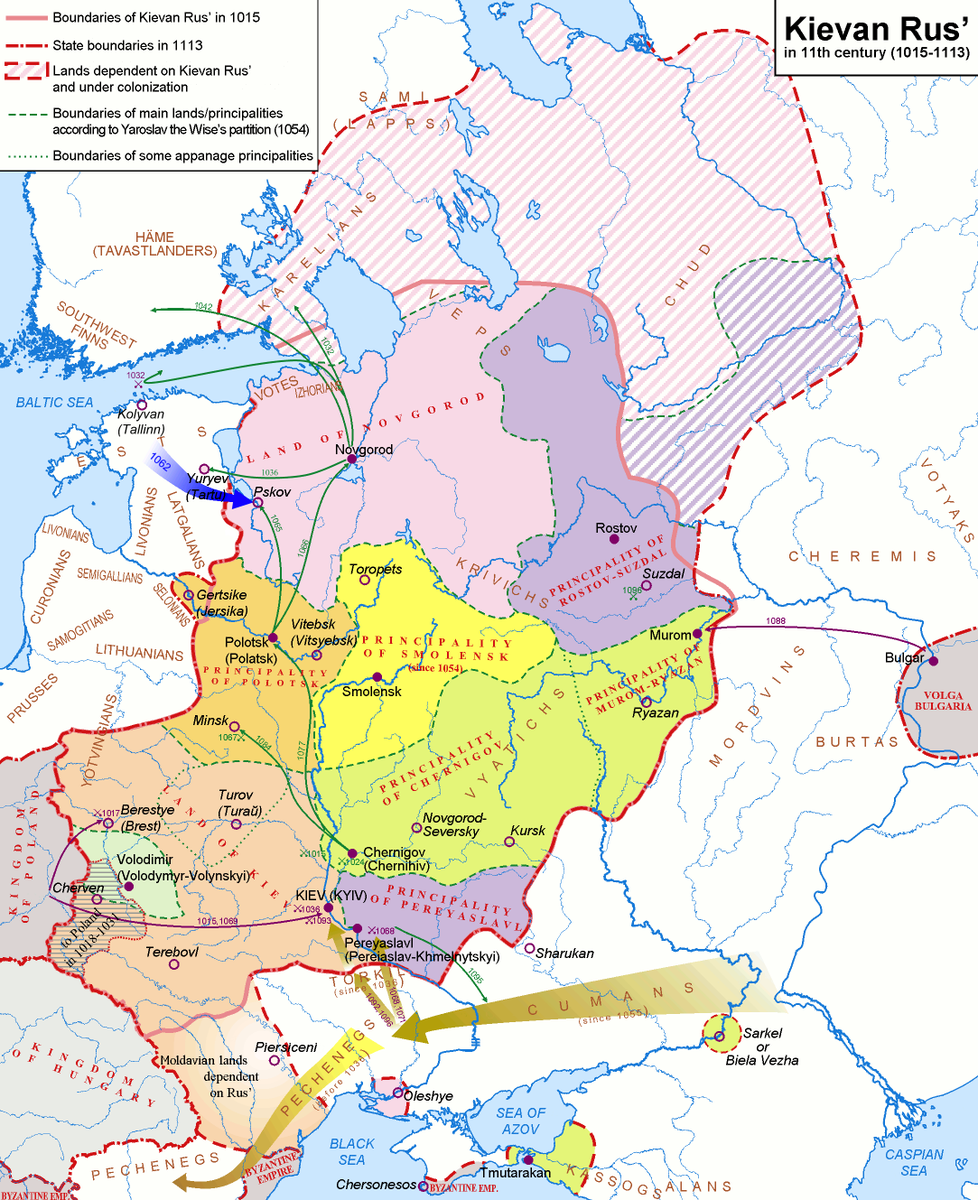
In 1830, Constantin faced an uprising in Poland. The regions of the former Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth staved off Russian recovery efforts for a year. But ultimately, Russia saw it through and Emperor Nikolai removed Polish autonomy and integrated it into his Empire. 6/10 

In 1833, the Emperor centralized his Empire on tenets of Orthodox Christianity, autocracy and nationality. The same year Russia concluded a peace treaty with the Ottomans in return for support against the rebellious governor of Egypt. Britain and France would not be happy. 7/10 

In 1848, Emperor Nikolai watched the revolutions of Europe with concern. He was keen on maintaining the old order. In 1849, he assisted Austria in putting down revolution in Hungary. He was also worried about the question of the future of the declining Ottoman Empire. 8/10 

Emperor Nikolai saw himself as the protector of the Orthodox Christians, who had once ruled Constantinople and formed a significant minority in the once great Ottoman Empire. But a French intervention in 1851 went against the Orthodox leading to Russia replying in kind. 9/10 

The destruction of the Ottoman fleet by Russia led to a joint Ottoman-British-French invasion of Russia, centred on the Crimean peninsula in the Black Sea, but also elsewhere. As the Russians struggled to hold their ground in Crimea, Emperor Nikolai died in 1855. 10/10 



• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh