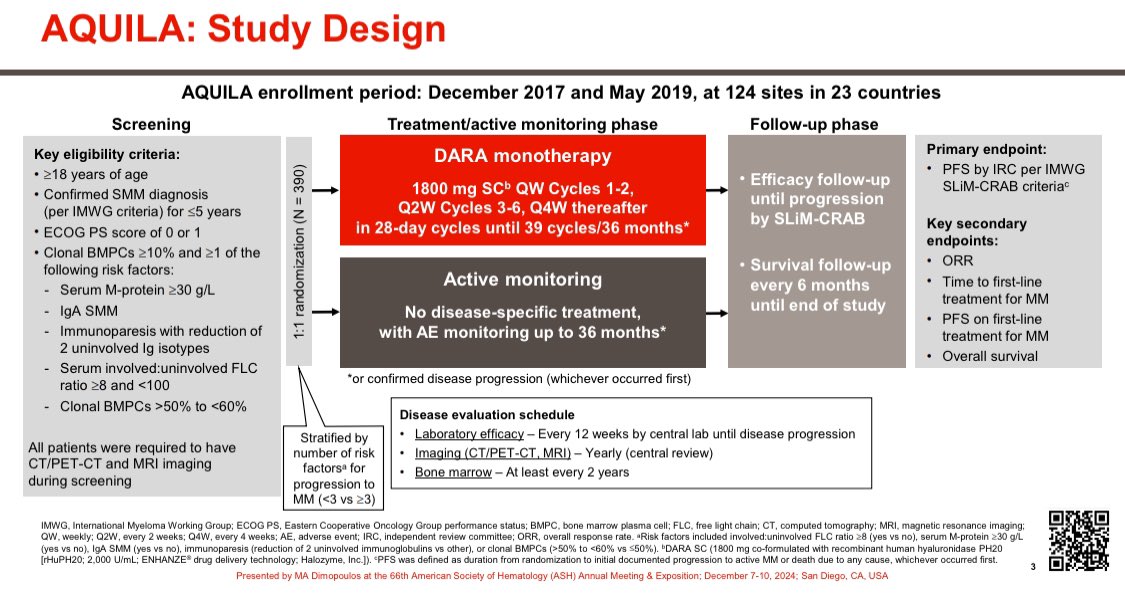
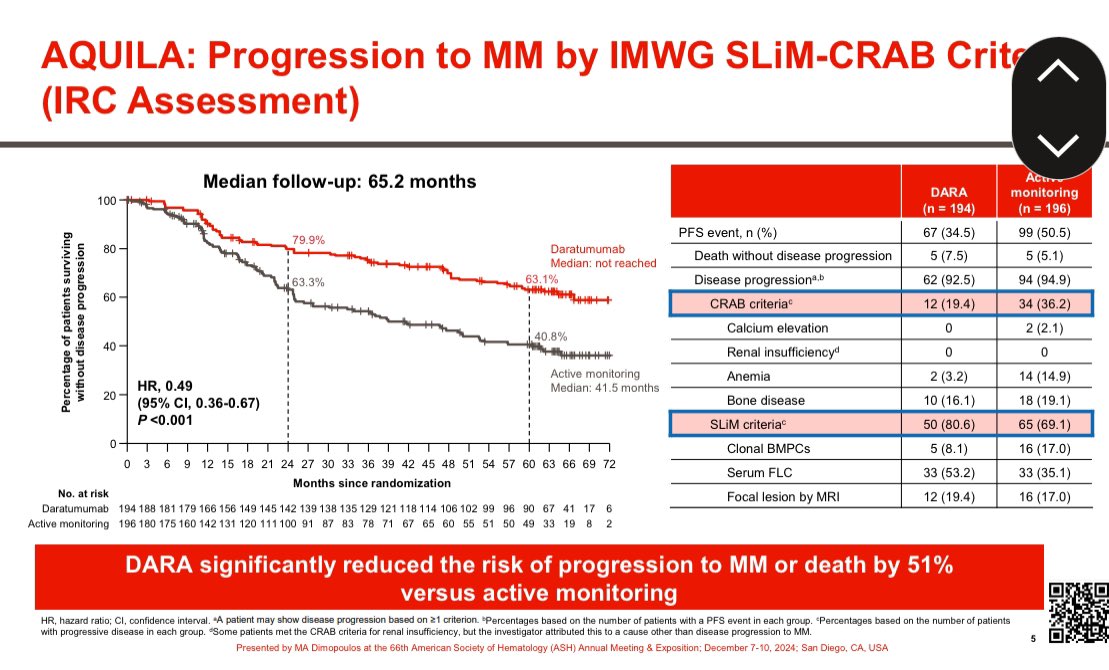
We need to do something about prescription drug prices. I have written and advocated for lower prescription drug prices for years.
I applaud @mcuban for starting @costplusdrugs to provide prescription drugs at low prices.
costplusdrugs.com
I applaud @mcuban for starting @costplusdrugs to provide prescription drugs at low prices.
costplusdrugs.com

Having spoken to many experts and organizations including experts from Costco and @AARP it was clear that even if the intent is there, providing low cost drugs in our system is extraordinarily difficult.
So I'm glad someone is taking the initiative.
So I'm glad someone is taking the initiative.
The fact that your copay with insurance can be higher than paying out of pocket at the pharmacy tells you how broken the system is, how much the entire supply chain except the patient benefits from the current system.
Even when life saving expensive drugs like imatinib become generic, a low price is not guaranteed.
1) Because to enter formularies the generic is also priced high to accommodate all the rebates that go to middlemen. That why you see this kind of disparity in cost.
1) Because to enter formularies the generic is also priced high to accommodate all the rebates that go to middlemen. That why you see this kind of disparity in cost.

Even with @GoodRx coupon the lowest price is $120. Not $17.
And as a patient you wouldn't know that for this drug on this day, there is a much higher price at say Walgreens compared to Walmart.
And as a patient you wouldn't know that for this drug on this day, there is a much higher price at say Walgreens compared to Walmart.

2) Second is having one or two generics is not enough. Need more than 4 generics to have real completion and impact on prices. Many generics are hesitant to enter the US market if there are already a couple on the market because they would find it hard to enter formularies. 

3) Third is Pharma has made it hard for generics to enter the market. And by the time they do, there is already a new and improved brand name version which makes the older one (which still works quite well) appear to seem outdated. We wrote about it here. mayoclinicproceedings.org/article/S0025-… 



*competition
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh