New work out in PNAS with @BlairShevlin @stephsmithphd and Jan Hausfeld! We find that high-value decisions are both fast AND accurate contradicting the ideas of diminishing value sensitivity and satisficing. Summary thread below. #neuroeconomics
doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2… 1/10
doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2… 1/10
We already knew that decisions between high-value foods, gambles, and other rewards are made quickly. But there’s a debate about why. Some argue that it is adaptive – satisficing makes sense when all the options are good enough. Others think it is due to increased noise. 2/10
We tested these explanations across three tasks. In each, people made binary choices and we assessed both their response times (RT) and accuracy as a function of the value (both subjective and objective) of the options. The results may surprise you…
3/10
3/10
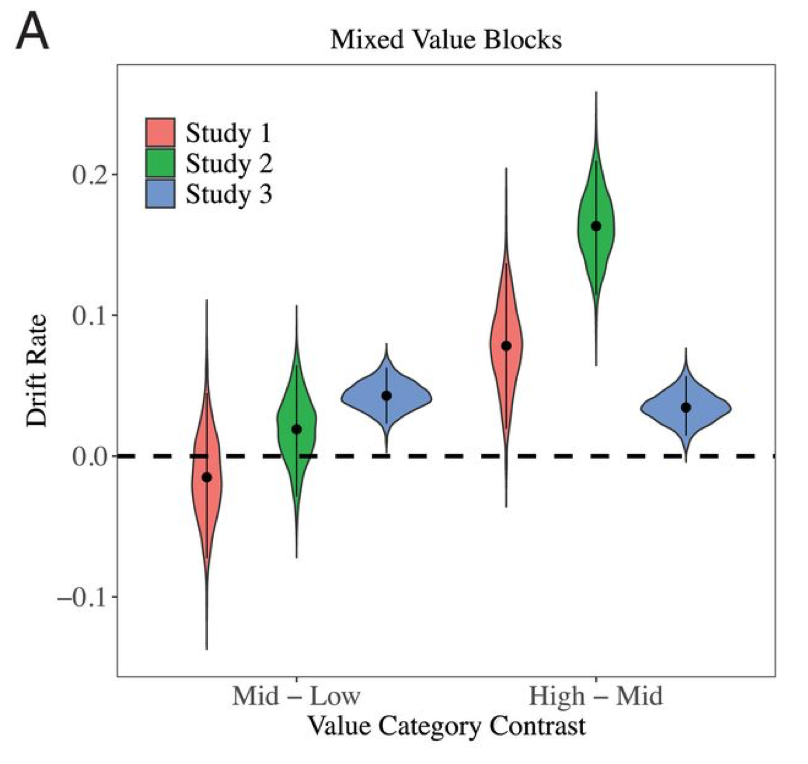
While we replicated the negative effect of value on RTs, we also found that accuracy rates increased as value increased! People didn’t seem to be settling or guessing at all – they were actually just better at making high-value decisions! 4/10 

While Studies 1-2 used subjective ratings to measure value, Study 3 used objective values. We trained people that colors = cash. Each option was a mix of colors and each trial there was an objectively better option. Trials were simply mean-shifted across value levels. 5/10 

We also explored how expectations influence choices. If people know that upcoming choices are all high-value, do they choose randomly because the options are all good enough? We found the opposite: responses slowed for cued, high-value trials 6/10 

We then modeled these decisions using the DDM, which allows us to evaluate discriminability while controlling for response strategy. We found that value increased the rate of evidence accumulation (drift rate), suggesting that high-value options are more discernible. 7/10 
We also found that expectations affected response strategy. High-value cues cause people to be more cautious (use wider boundary separation) in how they respond. This contradicts the satisficing hypothesis. 8/10 

In summary, we found that high-value decisions are easier; they are faster and more accurate. People also want to get them right. This suggests that there may be nuances when applying ideas from perception like Weber-Fechner or divisive normalization to value-based choice. 9/10
Thanks for following along! For more details about the design, computational modeling, and connections to economics, psychology, and neuroscience, you can read the paper here doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2…. Here’s the press release: news.osu.edu/people-are-fas… 10/10
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




