Let's talk of political, institutional and legal culture of the Horde. Firstly, to understand how did the Horde impact others we need to check how it was organised
Furthermore, this case has broader significance when considering the imperiogenesis effect of the Steppe
(thread)
Furthermore, this case has broader significance when considering the imperiogenesis effect of the Steppe
(thread)

Let's start with a question. What are the four largest inland capital cities of Eurasia? Well, obviously, Beijing, Delhi, Tehran and Moscow. What is in common between these inland megacities that also serve as the political cities of huge empires/states? 

They all four rose to prominence as the fiscal and administrative centers of nomadic conquerors, specialising on collecting taxes from the subjugated sedentary population 

Moscow was a tiny and unimportant principality until princes of Moscow got the right to collect the taxes (выход) for the Horde from all the other Russian polities. We now ofc think of Muscovy as of political and military power. But at first it was just a fiscal intermediary 

It is quite telling that the prince who made Moscow the most powerful Russian state was nicknamed Ivan Kalita (= the Wallet). Collecting taxes for the Horde, he got rich and purchased tons if fiefs. Yes, at first Moscow wasn't conquering much, it was mostly buying land for cash 

Tehran was chosen as a capital of Iran by Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar. This Turcoman leader chose Tehran, because he wanted to avoid former capital Isfahan associated with the previous also Turkic and originally nomadic dynasty - the Safavids 

With Delhi it's even more interesting. It was the capital of Slave Dynasty. Around 1190 Eastern Iranian ruler Muhammad Ghor sent his Turkic slave armies on the conquest of Indostan. And these slave generals indeed conquered the Indo-Ganghetic valley 
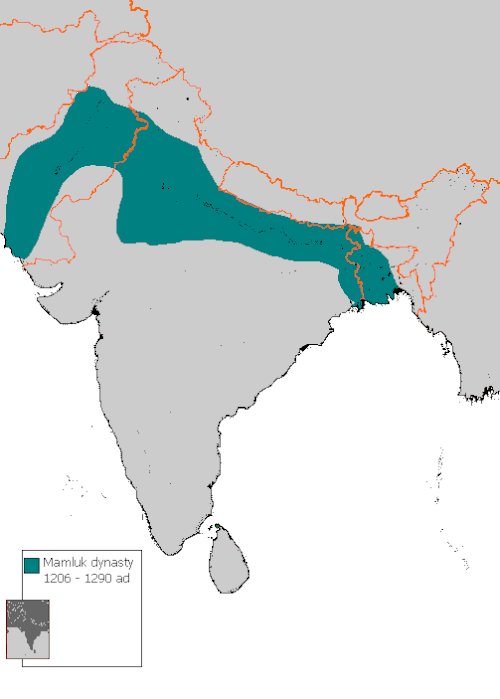
Where were these slave generals garrisoned? Yildiz sat in Ghazni, Bakhtiyar Khilji in Bengal, Qabacha in Punjab. And Aibak in Delhi. In the fight for power that followed Muhammad Ghor's death Aibak won. That's the beginning of the Slave Dynasty and of the imperial ascent of Delhi
The case of Slave Dynasty where one slave succeeded to another highlights an important sociopolitical pattern - slave-elites. Bernard Lewis called it 'a peculiar social structure of Muslim society', I prefer to talk of the Inner Asian Military Bondage. But I'll cover it later
Finally, Beijing was am unimportant city until it became a capital of Inner Asian conquerors. First of Khitans, then of Jurchens, then of Mongols and finally of Manchus. To put it in other words, Beijing rose to prominence as the HQ of mounted horse archers from beyond the wall 

What do these cases show? They show the imperiogenesis effect of the steppe. Those who live near the steppe will be conquered by nomads and will spend much of their history under the nomadic overlords. And these nomadic overlords tend to create very large empires 
This imperiogenesis argument raises a question of how did nomadic rule impact the conquered. Russian intelligentsia traditionally ascribed Russian imperial despotism to this nomadic legacy. Kinda 'Russians were liberals, but under the Asian rule they picked up the Asian ways' 

Interestingly enough very similar arguments were raised in China circa 1900. Now we find it self-obvious that the Qing Empire would just transform to Republic and then PRC keeping the same terrirory. But many of early 20th c Han nationalists would disagree 

Some of them argued that China would be better off dropping the Qing conquests such as Mongolia, Xinjiang, Tibet and possibly even Manchuria and returning to the old borders of Ming empire. Basically to its Han core, limited by the Great Wall 
Zhang Binglin went even further. He argued that the entire imperial structure - centralisation, bureaucracy, provincial system are the legacy of the nomads to be dropped. Instead China should break into many independent states - to break with the alien past 

In the past this was casually admitted by the rulers. In 1957 Zhou Enlai, the first Prime Minister of the People's Republic of China explicitly stated that 'The extensive territory of our country today is the legacy of the Qing dynasty'.= China is so big, because it was conquered 

Let's summarise. Sedentary people living by the steppe will be conquered. It's not a 'risk', it's the certainty. And they will spend much of their history within huge empires created by the nomadic conquest elites. So one effect of nomadic conquest legacy = very, very big state
What are other, may be less obvious effects? To meditate on this question, next time I will cover the political, institutional and legal culture of one specific nomadic empire - which is now a-historically called the Golden Horde. See you on Monday 
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





