Let's talk about Russian demography. As you see vast spaces in Siberia & European Russia are depopulating. There are two factors behind. First, low fertility. The only places with natural growth are Muslim areas of Caucasus, Idel-Ural and clusters of indigenous Siberians (thread) 
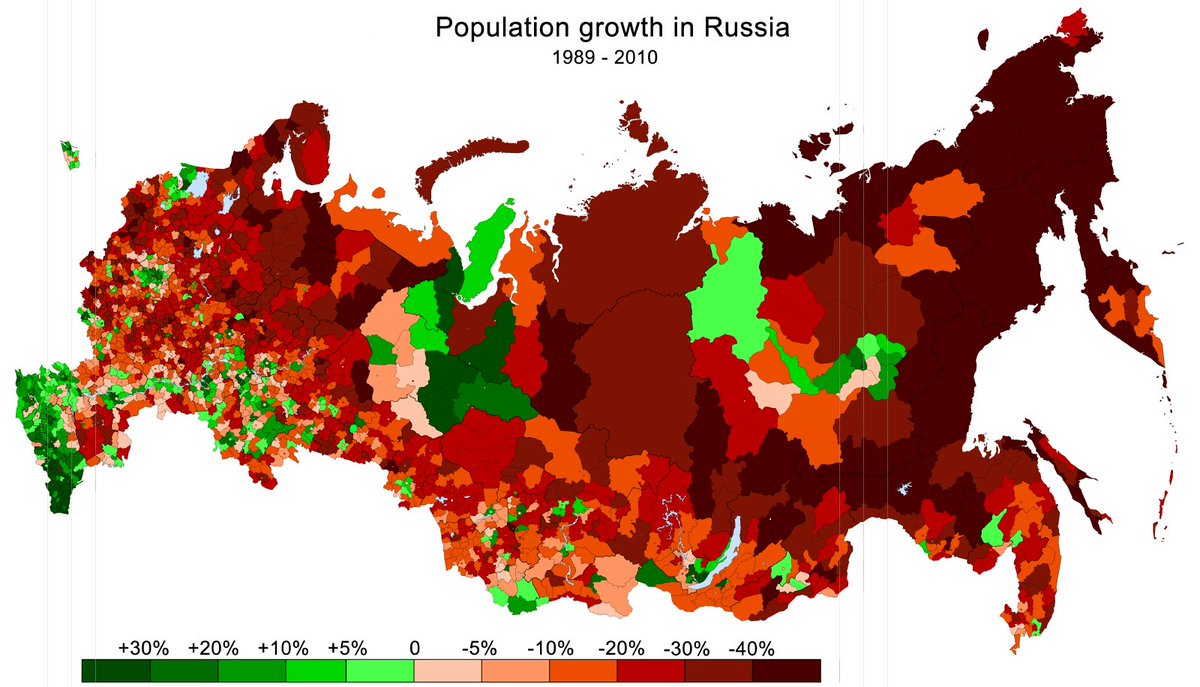
Secondly, migration. Huge areas are depopulating because people are moving elsewhere. Where exactly? Over 90% move to just three locations:
1. Moscow (that large city inland)
2. Krasnodar (Black Sea, near Crimea)
2. St Petersburg (Baltic shore, near Finland)
in that order
1. Moscow (that large city inland)
2. Krasnodar (Black Sea, near Crimea)
2. St Petersburg (Baltic shore, near Finland)
in that order
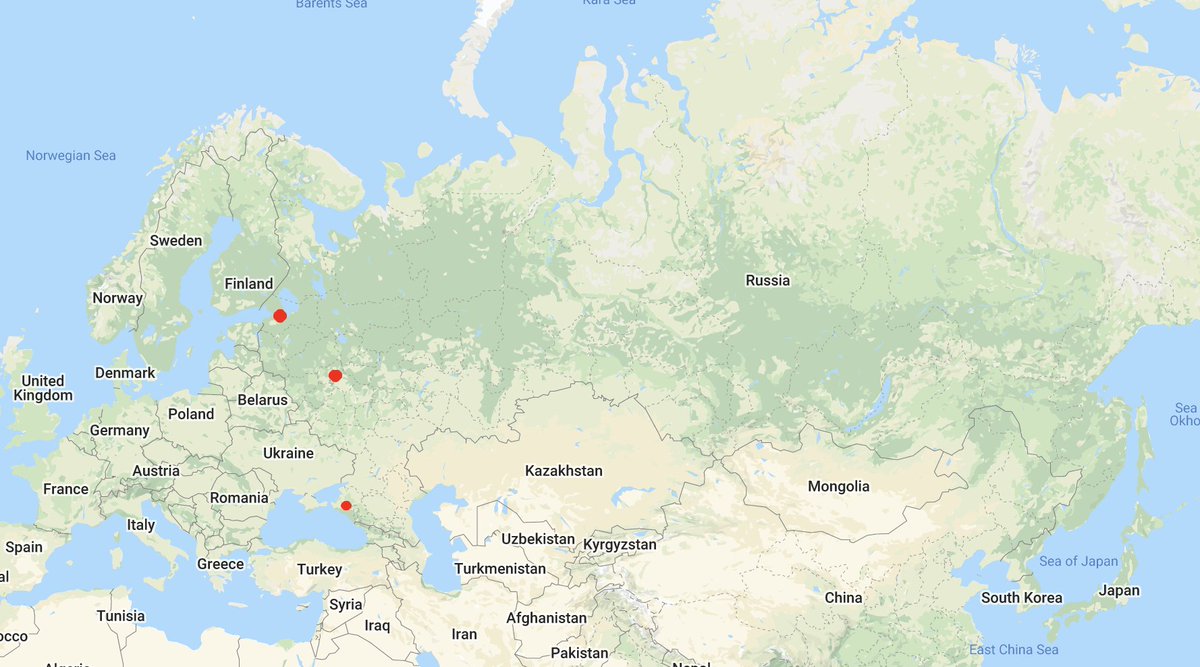
Let's talk of them. The case of Moscow is simple: it's by far the biggest and richest city. Moscow agglomeration alone attracts between 50-55% of all internal migrants. All the power's in Moscow -> all the money -> all the economic opportunities. Like in some LatAm countries 

Another important attraction spot is St Petersburg. The second largest city, the biggest seaports cluster, the former imperial capital. Locals usually look down upon Muscovites considering them too uncouth and unsophisticated. And yet, it's poor, very much poorer than Moscow 

Why? Petersburg's been long suffering from unpopular, and incompetent governors who don't do the basic stuff - like cleaning the city from snow and ice. As a result, touristic downtown tends to look like this every winter - city center is often impassable. And so on 

Some argue Moscow is purposefully keeping St Petersburg in desolation. Why? Because it's a rival. St Petersburg is the only city that can realistically compete with Moscow as an alternative seat of power. Therefore, any popular and competent governor'd be too much of a threat
This might be parallel to the situation in China. For the past 500+ China had two capitals: northern or southern, Beijing or Nanjing. Some argue that for this reason Beijing is purposefully obstructing the development of Nanjing. It's the only potential alternative seat of power 

But let's talk of Krasnodar. It's located in the very south, near the Black Sea coast. It doesn't have much of history, architecture or as Muscovites would argue - culture. It was built in 1792 as a frontier fort in sparsely populated land and till recently was very small 

And yet's now it's the fastest growing city in Russia. According to official data, it's population increased by 74% for the recent seven years. Unofficially - much faster. Which creates problems - enormous traffic congestions, electricity and water supply, etc. Problems of growth 
Why do people move here? First, Krasnodar is the Russian sunbelt. Let's look at this map classifying climate zones of Russia. It goes from 'absolutely uncofortable' deep purple to 'the most comfortable' orang). And Krasnodar is the warmest, sunniest, closest to the warm Black sea 

I'll take a pause, gonna continue in an hour or two
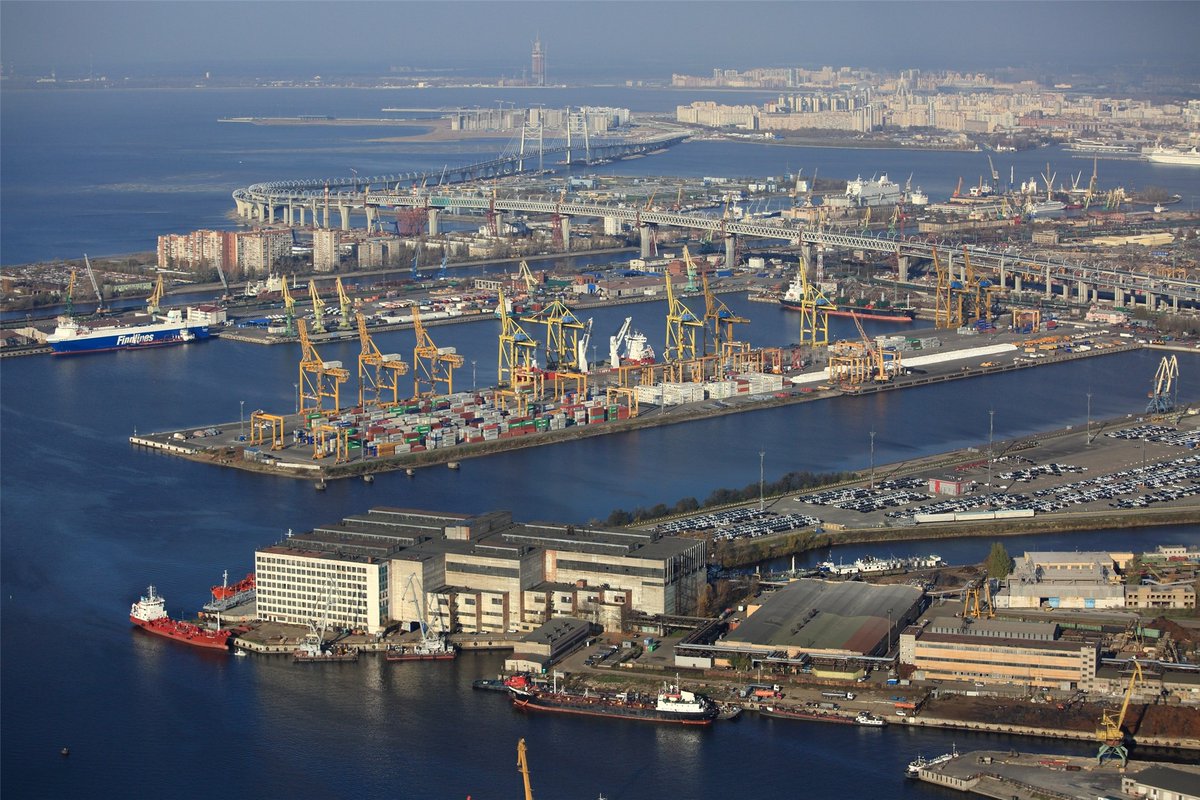
Second, geography. As you see, Krasnodar region (red) covers the entire Black Sea shore. Theoretically Russia theoretically has lots of seas, but they freeze. The navigation across the Arctic is really possible only with expensive ice-breakers 

Which means there are only three convenient areas for seaports, connecting Russia with the World Ocean. St Petersburg on Baltic (upper left), Krasnodar on the Black Sea (lower left) and Vladivostok on the Pacific (lower right). Other waters just freeze too much 

Which is why three busiest seaports of Russia are located in these three regions.
1. Novorossiisk (Krasnodar) 156 million tons
2. Ust-Luga (St Petersburg) 103 million tons
3. Vostochny (Vladivostok) 73 million tons
1. Novorossiisk (Krasnodar) 156 million tons
2. Ust-Luga (St Petersburg) 103 million tons
3. Vostochny (Vladivostok) 73 million tons

But the Pacific seaports like Vladivostok have a problem. They r too disconnected from the rest of Russia. The only real link is the Transsiberian railway. Which is now busy shipping cargo from China to Europe: trains can go as often as every 3 minutes. The railway is overwhelmed 

That's why in the view of economic geography Krasnodar is uniquely well-positioned. It's one of only three viable access points to the world ocean, and is located near the warmest sea which Russia has 

With best soils and climate in Russia, Krasnodar is highly agricultural. At this moment top 3 farming regions are:
1. Krasnodar
2. Rostov
3. Tatarstan
But Tatarstan is deep inland, while Krasnodar's on the shore and thus can easily export domestic and Rostov-produced grain
1. Krasnodar
2. Rostov
3. Tatarstan
But Tatarstan is deep inland, while Krasnodar's on the shore and thus can easily export domestic and Rostov-produced grain

Being located in the sunbelt and on the sea shore it became a region of heavy government investments. Sochi olympics, a number of SEZs, the Putin's palace where he spends more time than in Kremlin - they're all located here. Because it has sun and the only warm sea in Russia 

Interestingly enough, while growing so quickly and attracting huge number of migrants, the region has quite bad reputation. First of all, northerners consider them as Russian rednecks - uncultured rustic ppl. A common slur is 'Kubanoid', Kuban being the main river of Krasnodar 

Which can partially result from the ethnic differences. Krasnodar was colonised only since around 1800 and predominantly from Ukraine. If you look at this Soviet ethnic map of 1941 you'll see that ethnic Ukrainians dominate in the region 

Consider Bastrykin, Chief of Investigation Committee of Russia. He publicly told to his staffer, a Krasnodar native:
«You're not a Petersburg (Leningrad) man. In the past they wouldn't allow you here and now they do. Go back to Kuban, to your Cossacks. Y'all just flocked here"
«You're not a Petersburg (Leningrad) man. In the past they wouldn't allow you here and now they do. Go back to Kuban, to your Cossacks. Y'all just flocked here"

Ofc that was considered extremely rude and provocative. But what one person will say, very many think, they just keep silence. In a sense that might reflect the attitude of originally St Petersburg ruling class - the close circle of Putin are all from there - to the southerners
Which might be mutual. Anecdotally, a friend of mine, a very Nordic looking (blonde, blue eyes) girl from Taganrog which is in nearby region was teased by her family as 'katsapka', кацап being a Ukrainian slur for Russians 

Another stereotype about the region is that it's very criminal. And that the entire south of Russia is super criminal. That's not completely wrong. However, the main difference is not the scale of organised crime, but rather its institutional organisation and culture
To put it simply, Russia has two very different and largely incompatible organised crime cultures - thieves and bandits. Btw here's a nice book with good conceptualisation of this phenomenon 

Let's start with thieves who dominated till 1991. Thieves culture originated in the Stalinist era. The thing about thieves is that they're very networked, very cooperative and very ideological. Their (public) agenda is not money-making but building parallel state and institutions 

If you listen to thieves, they don't care about money at all. They care only about justice. And true justice can be found not in the official laws (= Law of Cops), but in the criminal tradition (= Law of Thieves). Which is very much superior and based on true Christian principles 

Ofc it's cheap propaganda. But the thing with propaganda is that it works. If it doesn't fool everyone, it fools very many. Quite a lot of people sincerely believed they could find justice with thieves who are legalistic and rigorous Christian paladins (if you listen to them)
E.g. two business partners have dispute and come to thieves for justice:
- Will you demand payment?
- No, I care only about justice
But after making a judgment he says:
- I don't need money. But our brothers in prison do. So you must contribute 100 000 bucks
Many such cases
- Will you demand payment?
- No, I care only about justice
But after making a judgment he says:
- I don't need money. But our brothers in prison do. So you must contribute 100 000 bucks
Many such cases
I gave this as an illustration of thieves' logic and thieves' propaganda. We are selfless, virtuous men who don't need money. Why do we do crime then? Largely because we need to help our brothers in prison.
Sounds stupid? Well, if it works, it ain't stupid
Sounds stupid? Well, if it works, it ain't stupid
Thieves largely held monopoly on the organised crime all over the former USSR till late 1980s. By the late 1980s with the Soviet system crumbling and the opportunities for shady business schemes booming, a new culture emerges from almost nothing. The bandits 

Unkile thieves, bandits were openly about money. While thieves developed complex ideology and presented them as the warriors of light, whose sufferings in prison are parallel to the passions of the Christ (as shown in the screenshot below), bandits didn't really care to do that 

According to thieves logic, these new upstarts could enter the criminal world. But they had to do it be entering existing thieves' organisations and doing the long arduous apprenticeship in a hope that may be one day that could rise. These guys didn't care 

What followed next was a pretty brutal fight. Bandits who didn't care about the Law of Thieves but cared a lot about physical exercise, gunnery and business were mostly winning. However, the outcomes varied over the different regions 

St Petersburg was the place of the most clear and unconditional victory of the bandits. Which is reflected in culture - e.g. in a super popular TV series 'The Bandit Petersburg'. That's not a fiction - here they exterminated the opposing forces almost completely 

Of course there were casualties. For example, Putin's judo coach Usvyatsov who probably organised his admission to the prestigous St Petersburg university was killed by thieves:
translation
"The grave. On the grave there's an epitaph
I died, but the mafia is immortal'
translation
"The grave. On the grave there's an epitaph
I died, but the mafia is immortal'

And Russian ruling elite originated in the Bandit Petersburg. See funerals a mafia boss in 2004. They're attended by (1) Zolotov, then chief of Putin's bodyguards, now of the National Guard, (3) Vanichkin, Chief of St Petersburg Police, and Kumarin (2) the leader of Tambov gang 

Also - do you see a guy in a green coat? That's Andrey Konstantinov, the author of the book 'Bandit Petersburg' on which the series was based. He's very well-connected and well-informed 

While the rise of bandits made the devastating effect upon thieves, there were two regions, where they did beat off all incursions. They were 1) the Far East 2) the South of Russia, including Krasnodar. The criminal culture of these regions remains super thief-style even now
While the Far East is contracting, depopulating and apparently is not gonna make any difference in the foreseeable future, Krasnodar is skyrocketing. So, when thinking of the future of Russia we should keep in mind, that demographic and economic center will gradually drift south
And it will drift to the regions which are:
1) recently colonised
2) ethnically different from the heartland
3) don't have much imperial legacy or tradition
4) overlooked by the state
5) looked down upon
6) have different institutional culture
7) economically self-sufficient
1) recently colonised
2) ethnically different from the heartland
3) don't have much imperial legacy or tradition
4) overlooked by the state
5) looked down upon
6) have different institutional culture
7) economically self-sufficient
The end of thread. I think that's enough for today. This time I described how Russia is changing sociospatially-wise. Next time, I'll cover how did it come to this sociospatial distribution in the first place. On Friday I'm planning to write
Why Russia became so large
Why Russia became so large
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





