I started my substack with a text "How Russia got so big and so cold"? History of Russian imperial expansion, teaches some important lessons about Russian big strategy. Media focuses too much on its ideological context and too little - on economic one
kamilkazani2.substack.com/p/how-did-russ…
kamilkazani2.substack.com/p/how-did-russ…
Let's look at the map of Muscovite expansion. The rise of Muscovy was a chain of hostile takeovers oriented northward - to control the supply of furs from the North and Siberia (orange line). They would push their representatives into local administrations and then impose control 

That's how Moscow secured the supply of the main tradable good it could get, the furs, and cut off its main rival of Novgorod from its supply lines. After Novgorod was isolated from its eastern lands, which supplied it with tradable goods, the fall of this republic was determined
Over the centuries, the main concern of Russian power was:
1. Secure the supply lines of tradable goods (natural resources)
2. Secure their export flows to the West
Export was vital for funding technological import. And technological import was vital for the imperial expansion
1. Secure the supply lines of tradable goods (natural resources)
2. Secure their export flows to the West
Export was vital for funding technological import. And technological import was vital for the imperial expansion
Consider the map of Oprichnina - the lands Ivan the Terrible took under his direct rule. We see its economic context. Control the routes to Siberia in order to get the natural resources and control the export lines to Europe to ship them off. So he moved his residence to Vologda 
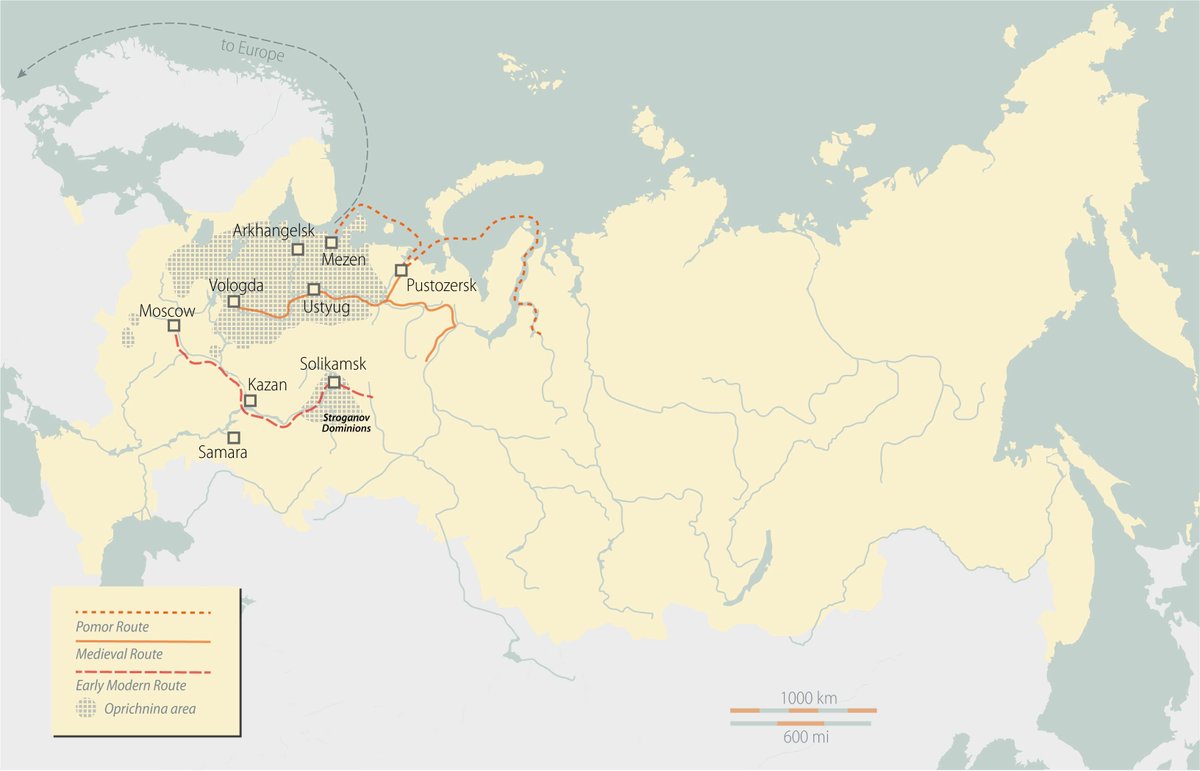
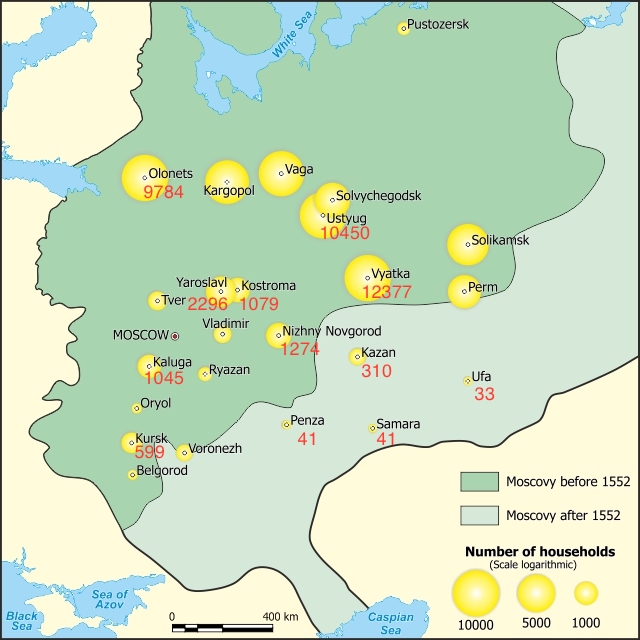
Russian expansion northward was motivated by these trade concerns = supply + export of natural resources. The North which controlled both was the richest region of Russia. Consider the number of taxpaying (= free and rich enough) households in 1682-1683. Only the North had cash 
But then Russian communication lines were shifting south. Through the internal waterways Russia reached Okhotsk (red) - the first Pacific base from where the expansion to Alaska started in the 18th c. The real rise of the south started circa 1900 with the Trans-Siberian (grey) 

That's why construction of Trans-Siberian was so important. Heir apparent personally oversaw and opened it
Tip: If you wanna know priorities of Russian rulers, check what their kids are doing. Nicholas - railways, Stalin's sons - army. And Putin's daughters? High-tech healthcare
Tip: If you wanna know priorities of Russian rulers, check what their kids are doing. Nicholas - railways, Stalin's sons - army. And Putin's daughters? High-tech healthcare

These new communication lines reshaped the country - decline of the north, rise of the south. The old capital and trade hub of Siberia Tobolsk dropped. While Novosibirsk which emerged in 1893 as a construction workers' camp emerged as new capital and third largest city in Russia 

Only with completion of the Trans-Siberian Russia gets its current configuration, with population being concentrated along the southern border, Canada-style. That hasn't been the case historically. In fact, this shift to the south continues and will reshape Russia even further 

Lessons
Russian imperial expansion is dependent on technological import. And import is funded by the export of natural resources. Hence priorities
1. Secure supply lines for these resources
2. Secure their export lines
In this respect Putinomics is no different from Oprichnina
Russian imperial expansion is dependent on technological import. And import is funded by the export of natural resources. Hence priorities
1. Secure supply lines for these resources
2. Secure their export lines
In this respect Putinomics is no different from Oprichnina
Furthermore. LOTR style battles played less role in Muscovite expansion than we presume and hostile takeovers - far larger. Main wars were won by expanding Muscovite influence within existing institutions through pressure and blackmail. Army was used later, to finish them off
The biggest point of failure in the entire expansion mechanism is the export flow. No export revenue -> no technological import -> no expansion. That's why Russia is aggressive while the fossil fuels are expensive, and docile when they're cheap. Russia is not self-sufficient
And finally. For the past 400 years, Russia has been continuously moving south. Its centre of gravity shifted from the sub-Arctic to Volga. In the future we should expect it to move even further south to the Russian sunbelt on Krasnodar coast. That's already happening. End of🧵 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





