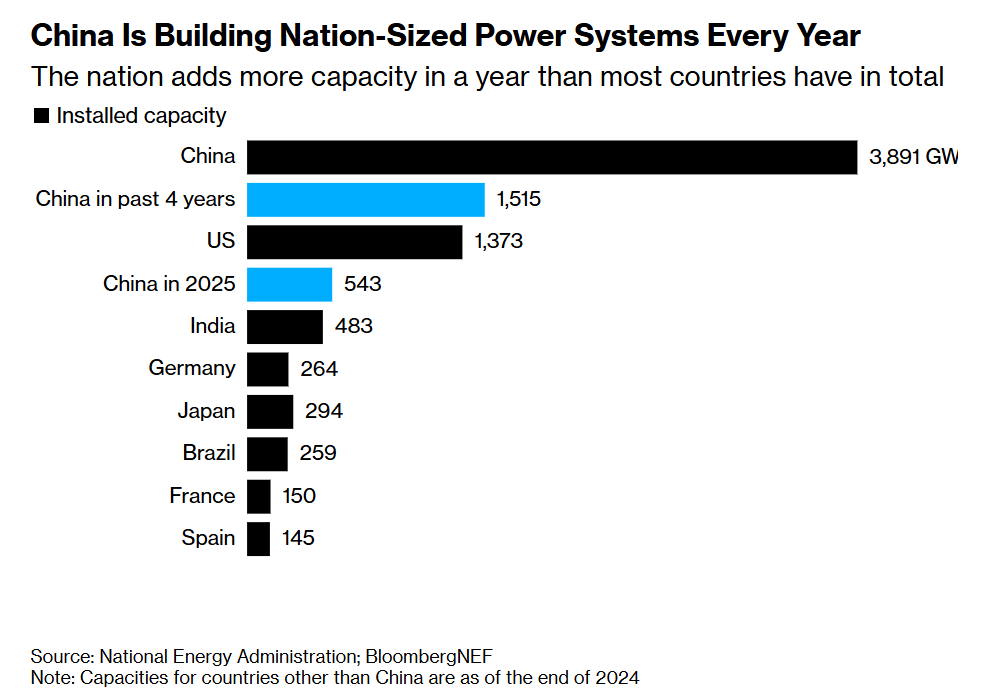
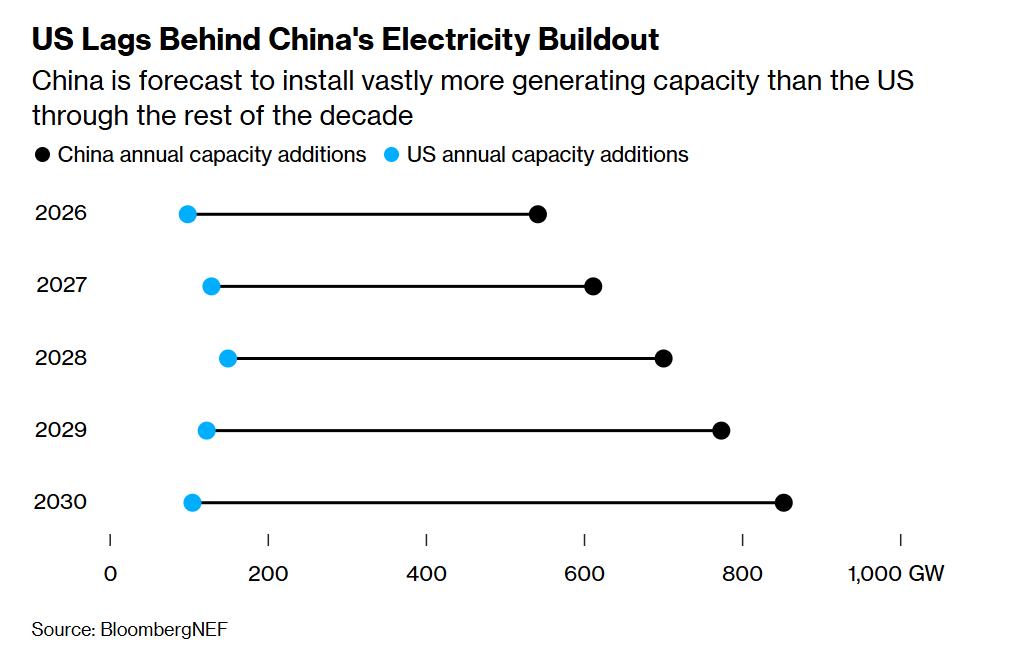
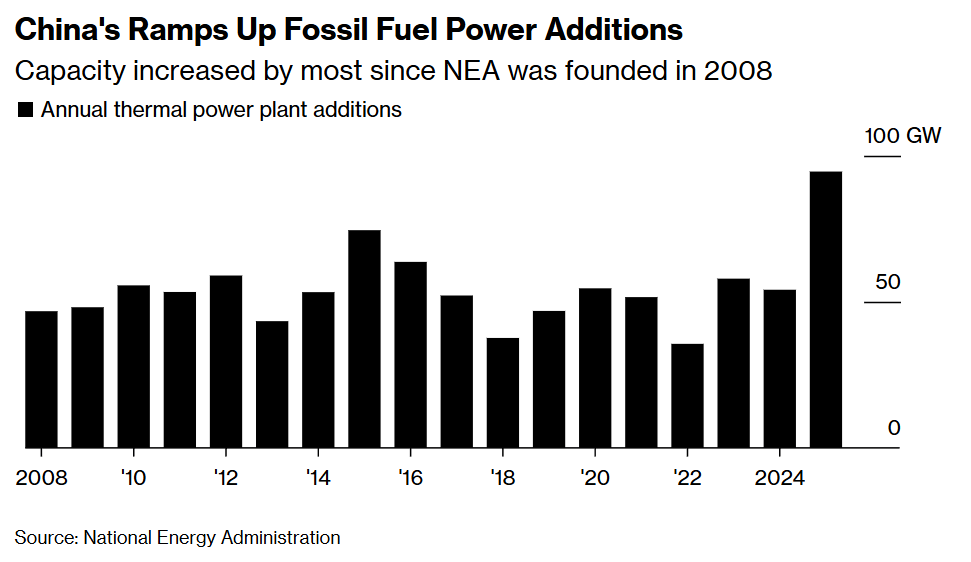
Before the war in Ukraine, China was becoming more reliant on Russian energy, metal and crops
🇨🇳🤝🇷🇺
But relations have become more complicated in recent weeks, raising questions about future trade
Here’s how China’s trade with Russia may change 👇
bloombergquint.com/china/ukraine-…
🇨🇳🤝🇷🇺
But relations have become more complicated in recent weeks, raising questions about future trade
Here’s how China’s trade with Russia may change 👇
bloombergquint.com/china/ukraine-…

Energy (1) ⚡️
Following the invasion, Chinese buyers, and the lenders that finance their purchases, have largely shunned Russian shipments of coal and LNG, as well as crude
While it likely temporary, it reflects companies’ deeper concerns about becoming ensnared in sanctions
Following the invasion, Chinese buyers, and the lenders that finance their purchases, have largely shunned Russian shipments of coal and LNG, as well as crude
While it likely temporary, it reflects companies’ deeper concerns about becoming ensnared in sanctions

Energy (2) ⚡️
China will likely expand imports of Russian LNG
But coal is different. Russian supply is a tiny fraction of what China consumes, and Beijing’s plan to raise the capacity of its coal industry suggests may be doing away with imports entirely
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
China will likely expand imports of Russian LNG
But coal is different. Russian supply is a tiny fraction of what China consumes, and Beijing’s plan to raise the capacity of its coal industry suggests may be doing away with imports entirely
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
Oil 🛢
For crude, the calculation also revolves around freight rates, and the high premiums attached to Russian shipments because of the war. There are a lot of nations supplying China with oil, and even when prices are high, buyers can be more picky
For crude, the calculation also revolves around freight rates, and the high premiums attached to Russian shipments because of the war. There are a lot of nations supplying China with oil, and even when prices are high, buyers can be more picky

Grain 🌾
Russia sells wheat to more than 100 countries, but China has been one of the few big markets it’s struggled to crack
Rising transportation costs are also the likely impediment to Moscow expanding its grain sales, as China can procure cheaper supply elsewhere
Russia sells wheat to more than 100 countries, but China has been one of the few big markets it’s struggled to crack
Rising transportation costs are also the likely impediment to Moscow expanding its grain sales, as China can procure cheaper supply elsewhere
Metals (1) 🪨
China is already buying a lot of Russia’s refined copper exports, according to a note from UBS AG this week, which suggests the upside is limited
China is already buying a lot of Russia’s refined copper exports, according to a note from UBS AG this week, which suggests the upside is limited

Metals (2) 🪨
For palladium, which is used to cut car pollution, Russia’s exports to China have increased, and could rise further
A possible obstacle is that companies listed in Europe produce most of the catalytic converters sold in China, and they may not want Russian supply
For palladium, which is used to cut car pollution, Russia’s exports to China have increased, and could rise further
A possible obstacle is that companies listed in Europe produce most of the catalytic converters sold in China, and they may not want Russian supply

Metals (3) 🪨
For some metals, China’s dependency on Russia has only weakened in recent years. Indonesia has emerged as its main supplier of nickel, replacing Russian imports
For some metals, China’s dependency on Russia has only weakened in recent years. Indonesia has emerged as its main supplier of nickel, replacing Russian imports

Natural gas (1) ⚡️
(Saving the best for last)
Moscow needs to find new customers as Europe shuns Russian gas, and China is best placed to fill that void
Russian pipeline exports to China began in 2019. And Gazprom wants to expand those sales by expanding the pipeline network
(Saving the best for last)
Moscow needs to find new customers as Europe shuns Russian gas, and China is best placed to fill that void
Russian pipeline exports to China began in 2019. And Gazprom wants to expand those sales by expanding the pipeline network

Natural gas (2) ⚡️
Gazprom signed a contract last month to design a pipeline across Mongolia toward China
A new supply deal with China would enable Gazprom to build an interconnect to redirect gas toward China from fields that now only feed Europe
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
Gazprom signed a contract last month to design a pipeline across Mongolia toward China
A new supply deal with China would enable Gazprom to build an interconnect to redirect gas toward China from fields that now only feed Europe
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
Natural gas (3) ⚡️
Russia forged new long-term natural gas supply deals with China at the Winter Olympics last month
Gazprom is currently in talks with China over supplies via a third route, Power of Siberia 2, which would significant boost capacity
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
Russia forged new long-term natural gas supply deals with China at the Winter Olympics last month
Gazprom is currently in talks with China over supplies via a third route, Power of Siberia 2, which would significant boost capacity
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
Natural gas (3) ⚡️
And what’s in it for China?
Well, potentially really cheap gas as Russia searches for a replacement to Europe — its top customer. Beijing has the upper hand in future negotiations
And what’s in it for China?
Well, potentially really cheap gas as Russia searches for a replacement to Europe — its top customer. Beijing has the upper hand in future negotiations
Natural gas (4) ⚡️
To be sure, it will take a long time for Russia to connect its western gas field to China
To be sure, it will take a long time for Russia to connect its western gas field to China
https://twitter.com/chrisbeet/status/1505474077599109127
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh