
What exactly is an HTTP cache.
Thread 🧵👇🏻
Thread 🧵👇🏻
An HTTP cache is crucial for making your website fast.
Most websites you visit fetch data from the backend to display it on the web page.
Continuous calls to the server can make your website slow and hence worst User Experience.
Most websites you visit fetch data from the backend to display it on the web page.
Continuous calls to the server can make your website slow and hence worst User Experience.
This is where cache comes into the picture.
Cache is a technique using which the browser can store the resources in the local storage, reducing the number of round trips to the server.
Cache is a technique using which the browser can store the resources in the local storage, reducing the number of round trips to the server.
Cache reduces the latency and number of calls, resulting in a fast and performance-optimized website.
There are two broadly divided categories of cache.
1. Shared cache
2. Private cache
1. Shared cache
2. Private cache
Shared cache, as the term suggests, can be used by multiple users.
Whereas, private access is dedicated and accessible by the single user only.
Whereas, private access is dedicated and accessible by the single user only.
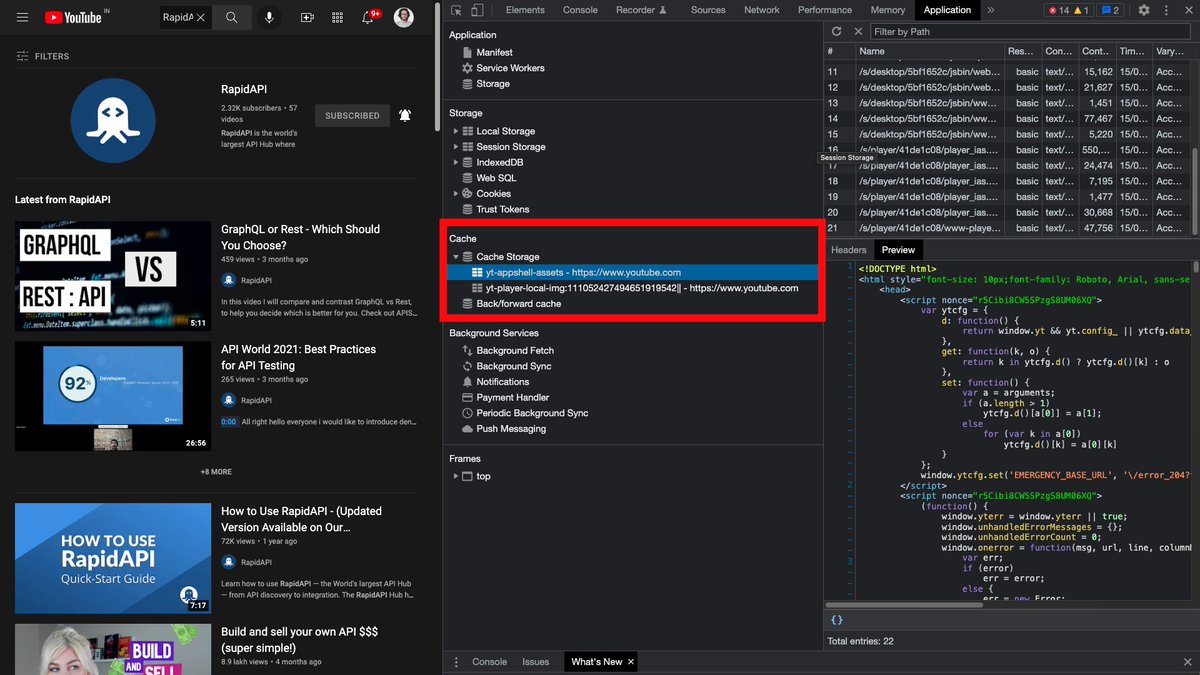
Private cache exists in your browser. You can check by following the steps below.
Inspect > Select Application from the top navbar > Check Cache on the left tree.
Inspect > Select Application from the top navbar > Check Cache on the left tree.
The shared cache is accessible to multiple users. For example, Internet Service Provider serves resources to multiple users via shared cache.
You can handle the entire cache mechanism using the `Cache-Control` HTTP header.
It holds instructions for both request and response.
It holds instructions for both request and response.
For example, if you want to revalidate the cached response each time with the origin server, use
`Cache-Control: no-cache`
`Cache-Control: no-cache`
You can also define the lifecycle of cache data using the `max-age` directive.
For example,
`Cache-Control: max-age=100`
The cached response will be considered fresh for 100 seconds.
For example,
`Cache-Control: max-age=100`
The cached response will be considered fresh for 100 seconds.
When a client makes a GET request, the request first goes through a cache and then to the server.
The freshness of data is decided by `Cache-Control: max-age=X` and `age=Y` headers.
Data is fresh if `max-age` is greater than `age` else stale.
The freshness of data is decided by `Cache-Control: max-age=X` and `age=Y` headers.
Data is fresh if `max-age` is greater than `age` else stale.
With that being said, this is pretty much it for this thread.
Follow @Rapid_API for more exclusive content. 🐙💙
Follow @Rapid_API for more exclusive content. 🐙💙
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




