
Many Long Covid and more recently ME/CFS sufferers have turned to natural clot busters (nattokinase, lumbrokinase) since new studies have revealed that many with these diseases have microclots. A few words on their dosing, efficacy and safety. 🧵
Funnily, nattokinase is not a kinase; instead, it is a serine protease. Proteases are enzymes that cleave (break) peptide bonds in proteins. Another example of a serine protease is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). tPA cleaves plasminogen to plasmin and plasmin dissolves clots. 



This double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study in 12 young & healthy Japanese men found that a single 2000 FU dose of NK activated multiple fibrinolytic & anti-thrombotic pathways: aPTT ⬆️, D-dimer ⬆️ & tPA activated. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P… 



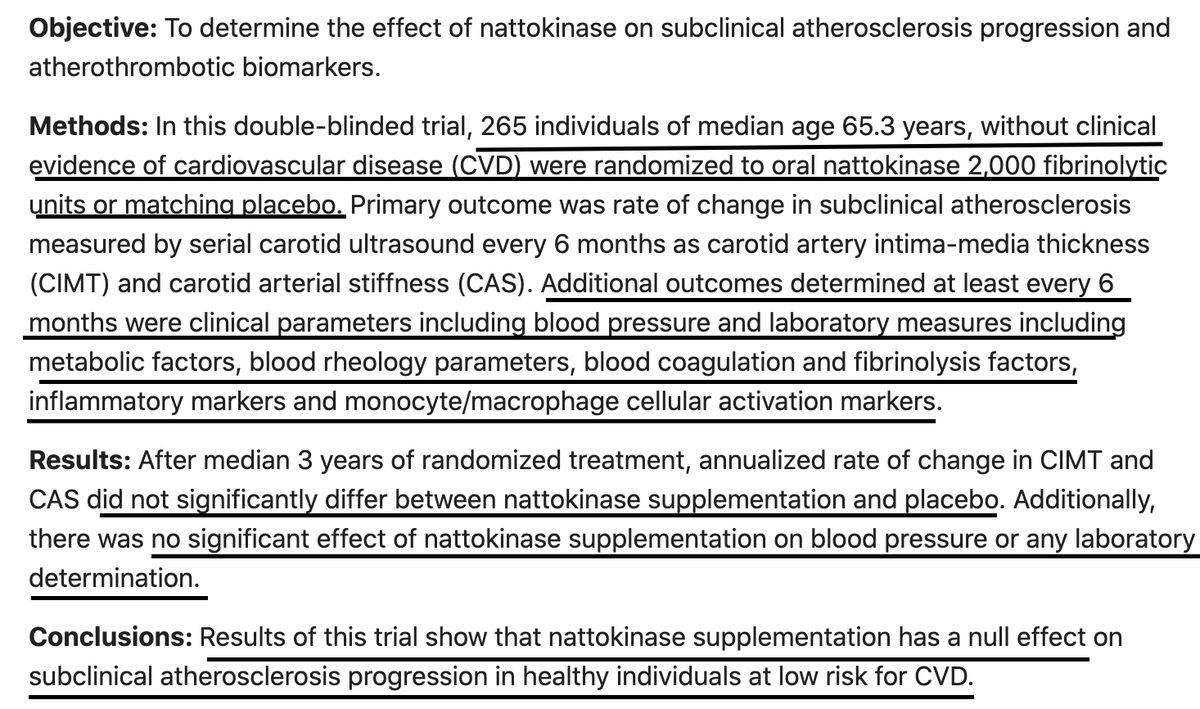
However, this larger RCT from 2021 concluded that after a median 3 yrs, daily 2000 FU NK showed no significant effect on blood coagulation and fibrinolysis factors, blood pressure or any other tested labs, & didn't decrease pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33843667/ 
SAFETY:
My primary worry = bleeding. While study 1 does not assess bleeding risk, all the fibrinolysis/coagulation parameters remained in normal range following NK administration, which is promising. However, that study only looked at one single dose.
My primary worry = bleeding. While study 1 does not assess bleeding risk, all the fibrinolysis/coagulation parameters remained in normal range following NK administration, which is promising. However, that study only looked at one single dose.
SAFETY, cont
The 2021 NK atherothrombotic prevention study (study 2 above) compared daily 2000 FU NK to placebo for a median of 3 yrs, not just 1 single dose. They did not report any adverse effects or bleeding, but of course, they also reported no efficacy whatsoever.
The 2021 NK atherothrombotic prevention study (study 2 above) compared daily 2000 FU NK to placebo for a median of 3 yrs, not just 1 single dose. They did not report any adverse effects or bleeding, but of course, they also reported no efficacy whatsoever.
SAFETY, cont
"Consumption of 10 mg/kg-day nattokinase for 4 weeks was well tolerated in healthy human volunteers...Oral consumption of nattokinase [appears] of low toxicological concern."
2000 FU = ~100 mg
60 kg x 10 mg/kg = 600 mg NK = 12,000 FU max dose
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26740078/
"Consumption of 10 mg/kg-day nattokinase for 4 weeks was well tolerated in healthy human volunteers...Oral consumption of nattokinase [appears] of low toxicological concern."
2000 FU = ~100 mg
60 kg x 10 mg/kg = 600 mg NK = 12,000 FU max dose
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26740078/
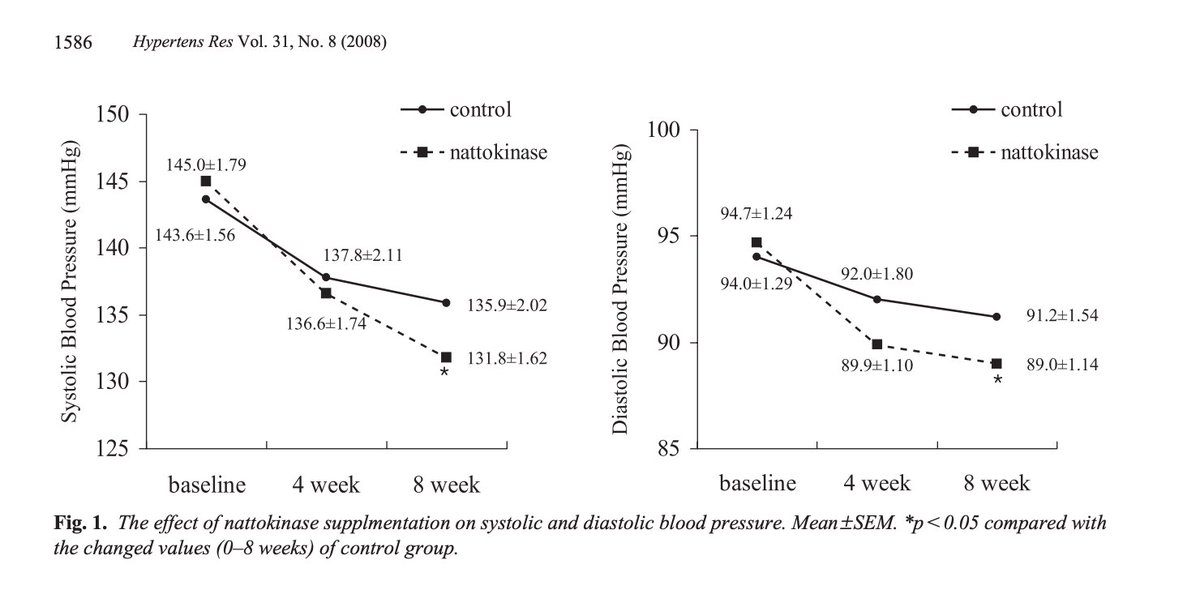
This RCT examined the effects of NK on blood pressure. Unlike the above 2021 study which showed no effect on BP, here, NK induced a statistically significant decrease in BP after only several weeks on 2000 FU NK daily.
Monitor BP. nature.com/articles/hr200…
Monitor BP. nature.com/articles/hr200…
DOSING:
It appears that 2000 FU once daily is the most clinically studied. In this 2013 NK pharmacokinetics study (see below), pts took one dose of 2000 FU NK following baseline blood samples, then returned at 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, and 48 hours post-dose for subsequent blood draws.
It appears that 2000 FU once daily is the most clinically studied. In this 2013 NK pharmacokinetics study (see below), pts took one dose of 2000 FU NK following baseline blood samples, then returned at 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, and 48 hours post-dose for subsequent blood draws.
Peak serum levels of NK were observed ~13.3 h ± 2.5 h post-dose. Dosing interval therefore may be 12-24 hours (2000 FU once daily or 2000 FU every 12 hrs in more aggressive dosing). pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23709455/
LUMBROKINASE
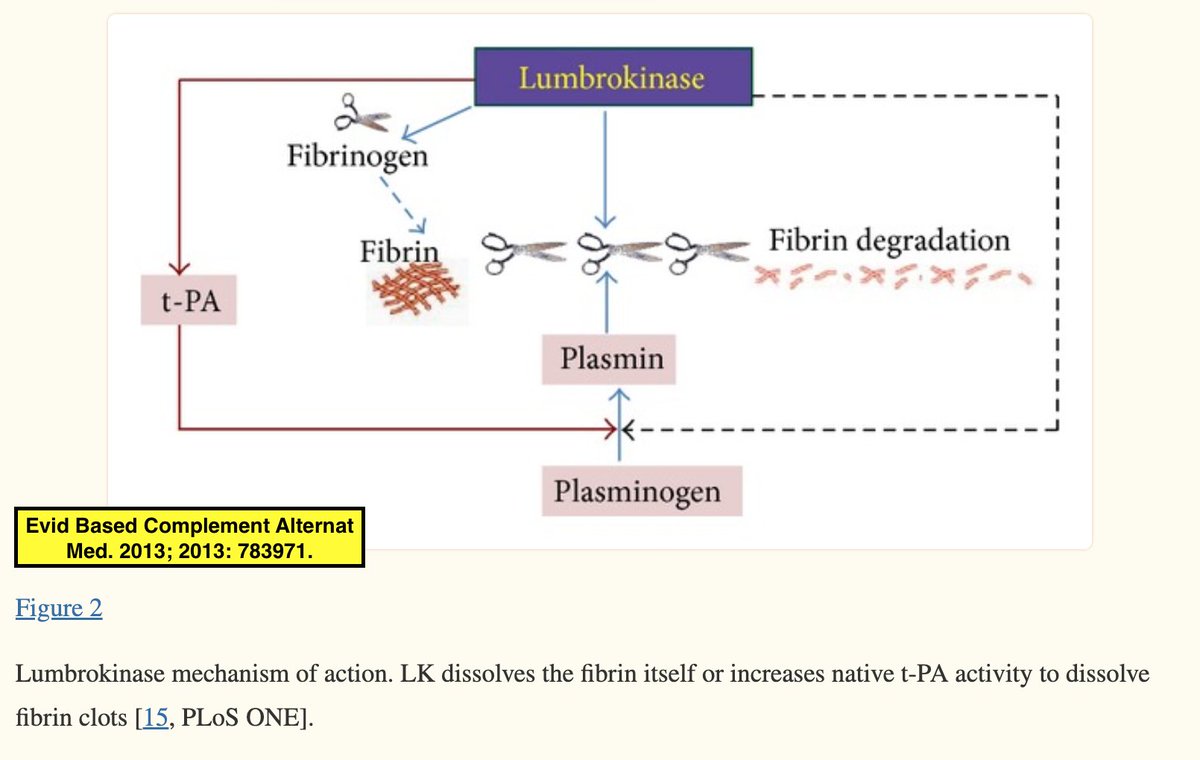
Interestingly, lumbrokinase is named after the genus name of earthworm: lumbrokinase = a group of fibrinolytic enzymes isolated & purified from earthworms.🪱 Lumbrokinase's mechanisms of action are depicted here (similar to NK).
Interestingly, lumbrokinase is named after the genus name of earthworm: lumbrokinase = a group of fibrinolytic enzymes isolated & purified from earthworms.🪱 Lumbrokinase's mechanisms of action are depicted here (similar to NK).
SAFETY (lumbrokinase)
This study explored the efficacy and safety of lumbrokinase in the treatment of acute & moderate risk PE. Authors compared lumbrokinase + heparin + warfarin vs heparin + warfarin and found similar safety & better efficacy. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29093246/
This study explored the efficacy and safety of lumbrokinase in the treatment of acute & moderate risk PE. Authors compared lumbrokinase + heparin + warfarin vs heparin + warfarin and found similar safety & better efficacy. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29093246/
Overall, nattokinase seems more studied than lumbrokinase. I'd personally feel more comfortable trying nattokinase for this reason. I wouldn't combine w/ aspirin. However, everyone is different based on their individual medical history, medications, & risk-benefit analysis!
According to Stephen Buhner in his book Herbal Antivirals, lumbrokinase is 30 times more potent than nattokinase and 300 times more potent than serrapeptase. Serrapeptase is a weaker fibrinolytic but has other benefits like anti-inflamm & removal of cellular debris & toxins.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh







