OTD - 1941 - Operation Barbarossa - Nazi Germany’s invasion of Soviet Russia. A thread about different German photo collections and sources.
Warning: some people might find some of the content in this thread distressing.
#CultureofWar
Warning: some people might find some of the content in this thread distressing.
#CultureofWar
Hitler’s war of extermination unleashed a militarized genocide and the Holocaust. From the outset, German soldiers inflicted the ‘Holocaust by Bullets’ on several million people. The legacy has deeply scarred Europe. 



Photography played a very important part in the campaign. The official newsreels, newspapers and journals all carried photographs. They were essential in the visualisation of ideological enemies - to be exterminated under Hitler’s directives.
Images: @USNatArchives @BundesarchivD



Images: @USNatArchives @BundesarchivD




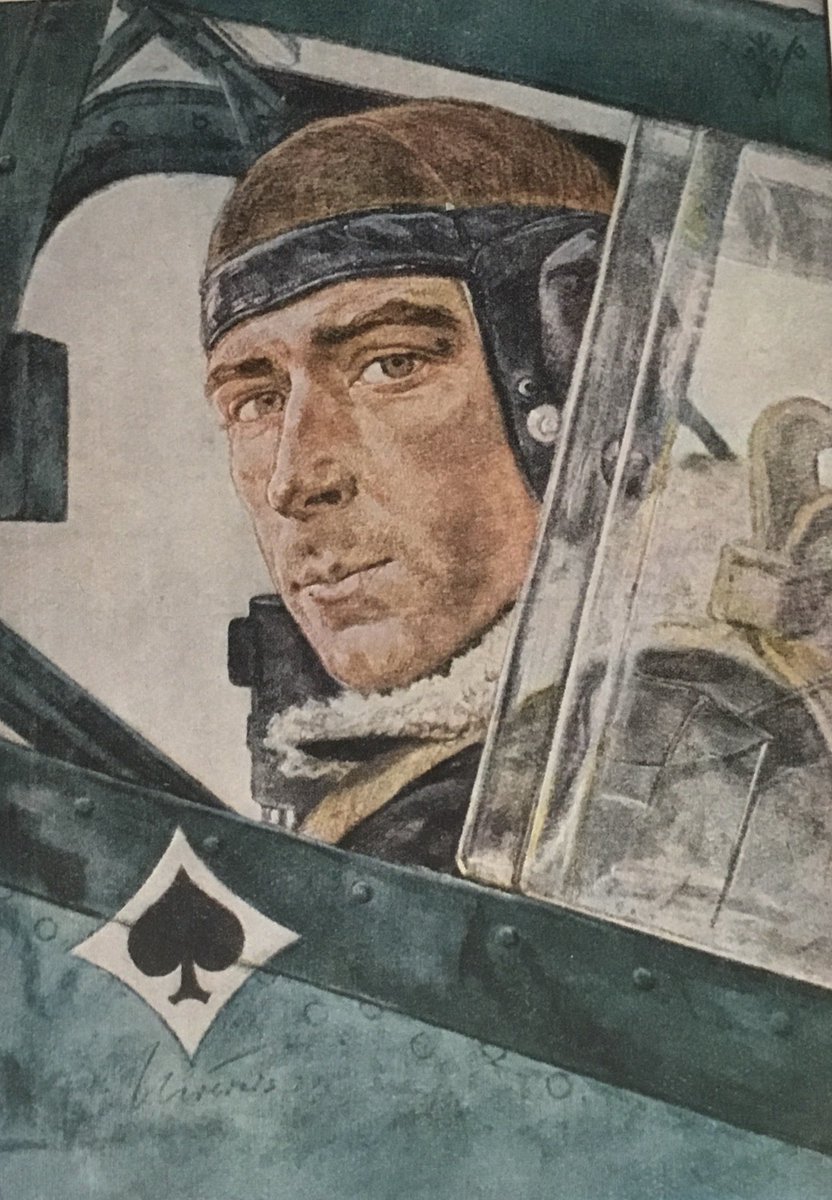
Official Nazi photographs reflected institutional cultures. For example, the heroic realism of the Luftwaffe’s culture was a common picture pose. Typical also was the glorification of individuals like Werner Mölders, the fighter ace.
Images: W.Haupt / PWB

Images: W.Haupt / PWB


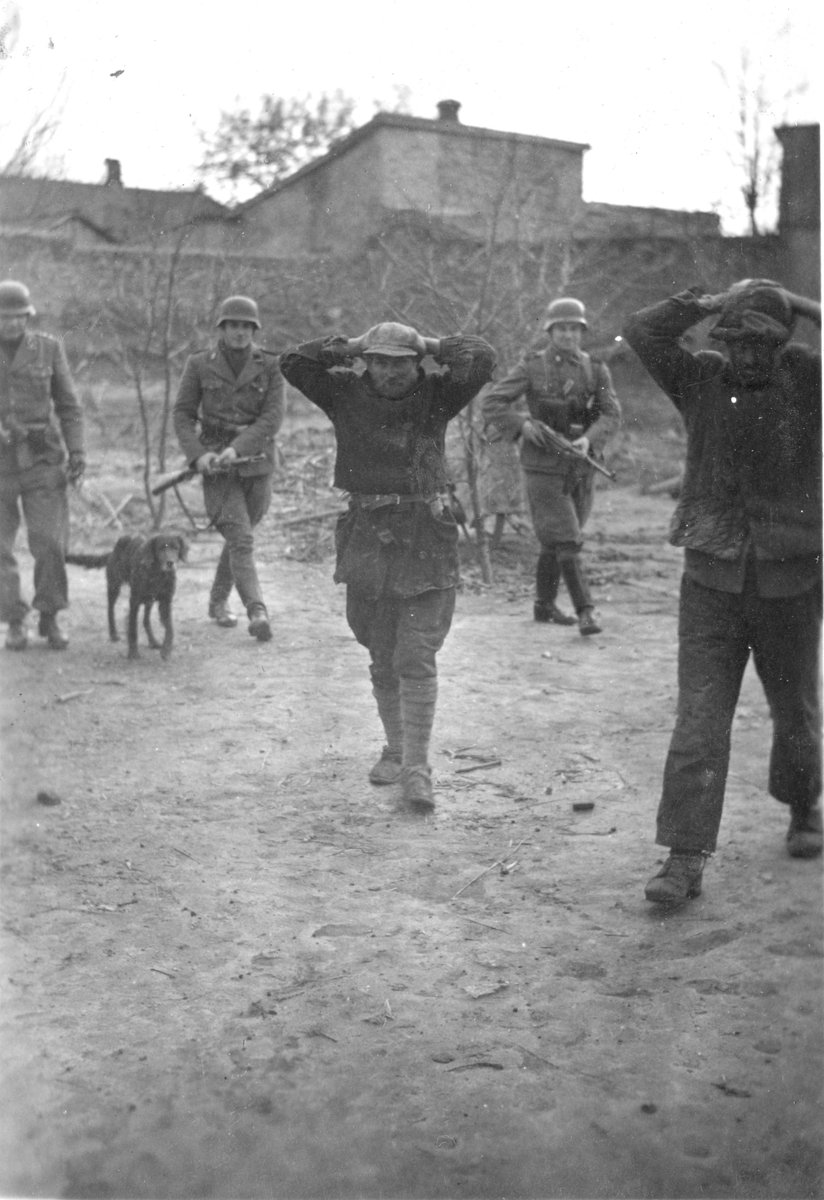
Official army reports about the fighting, as in Bialowieza Forest (Soviet-occupied Poland) were framed by photos. The photos of the 137th Infantry Division during Barbarossa were accompanied by reports of hard fighting, first published in 1942, and then republished in 1961.
PWB



PWB




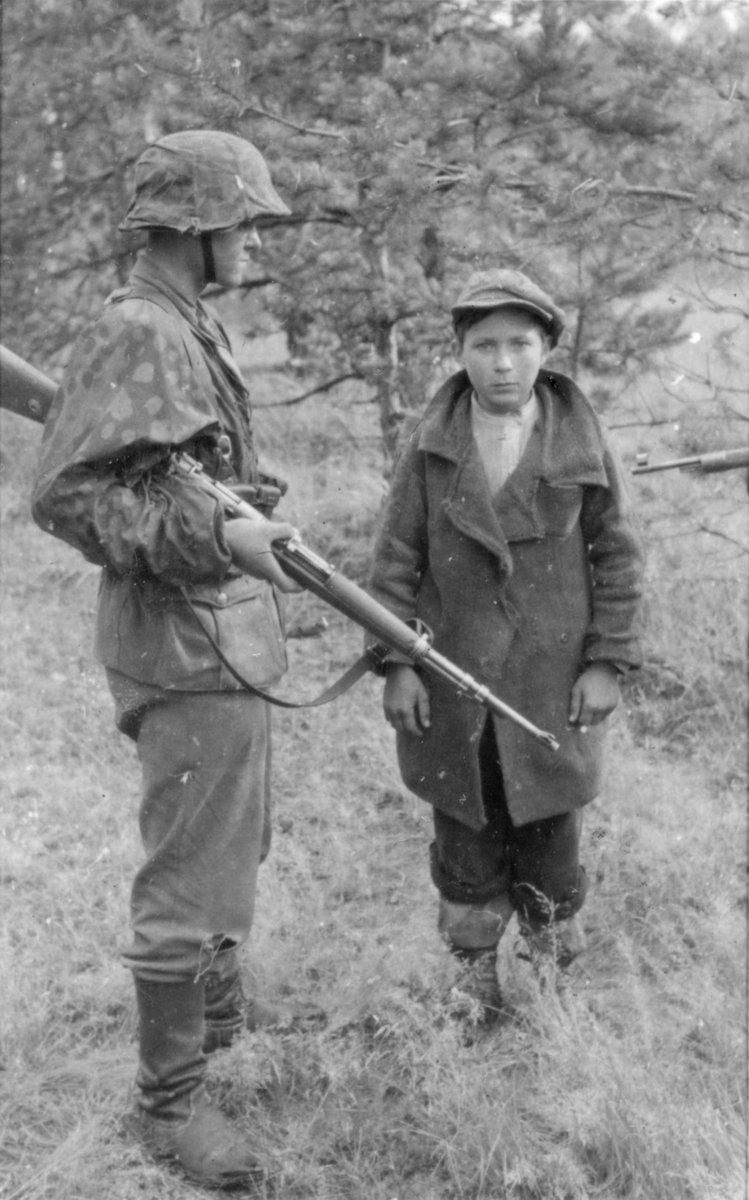
Many photographs were not official or by war journalists. Ordinary soldiers were encouraged to take cheap cameras to war and record their memories. A powerful collection of images that range from soldiers under stress to killers.
W. Haupt, Claus Hansmann, @BundesarchivD



W. Haupt, Claus Hansmann, @BundesarchivD




This was possible because of the small, cheap reliable cameras. Adverts for them appeared long before the war in many popular magazines for the military, gun sports and photography.
Images: Deutsch-Russisches Museum (Berlin) exhibition book


Images: Deutsch-Russisches Museum (Berlin) exhibition book



The story of photography and war memory was not just a WW2 phenomenon. Many families have photographs from the Great War. A bland photo album from the 1920s can disguise another story about the memories of war.
Image: PWB

Image: PWB


Most striking about the Nazi photo story was the ideology underpinning the collection of memories. For one album, the family pictures were slotted into sleeves at the back, after the official photographs/citations - creating a Volksgemeinschaft of memories.
Images: PWB



Images: PWB



Tucked away in the back of family albums are forgotten men - killed or missing. Sometimes identified with an arrow pointing to a relative. No names or places on the back, but nonetheless remembered.
Images: PWB



Images: PWB




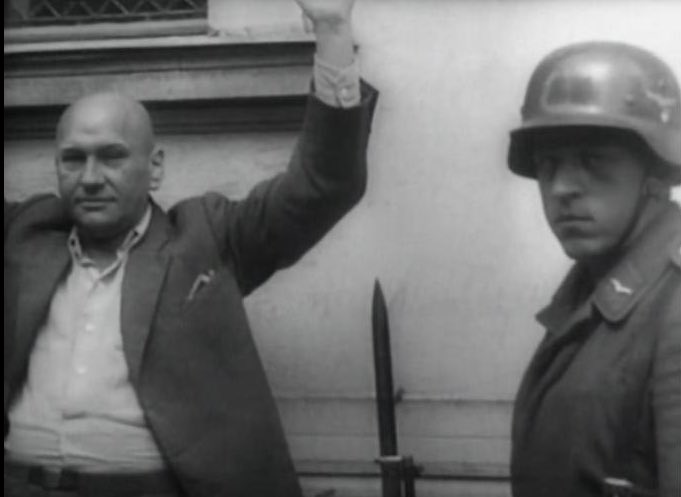
The ordinary soldier stares back defiantly. The vast collection of ordinary photos is an important resource in the historical reconstruction of German military culture and Nazi crimes.
Image: @BundesarchivD
Image: @BundesarchivD

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh































