You could add Russia to the list. Strange it may sound, its pattern of expansion was similar. Except it was potamic rather than oceanic. In this respect it kinda resembled Portugues expansion in what is now Brazil. And yes, Russia struggled to go far away from the rivers, too
https://twitter.com/simongerman600/status/1548307732070932481
Consider the map of Russian admiralties till 1680-1800s. Some of them look "logical" being located at the cost, like in St Petersburg or Arkhangelsk. But Kazan or Voronezh are deep inland. They would build ships there and then go down the river to the sea. Irkutsk is even better 

Irkutsk admiralty didn't build ships. But it prepared all the equipment & components for the Okhotsk shipyard. It was a very northern Okhotsk that was the initial Russian stronghold on the Pacific. Alaska was colonised from there. What is now Vladivostok was annexed only in 1850s 
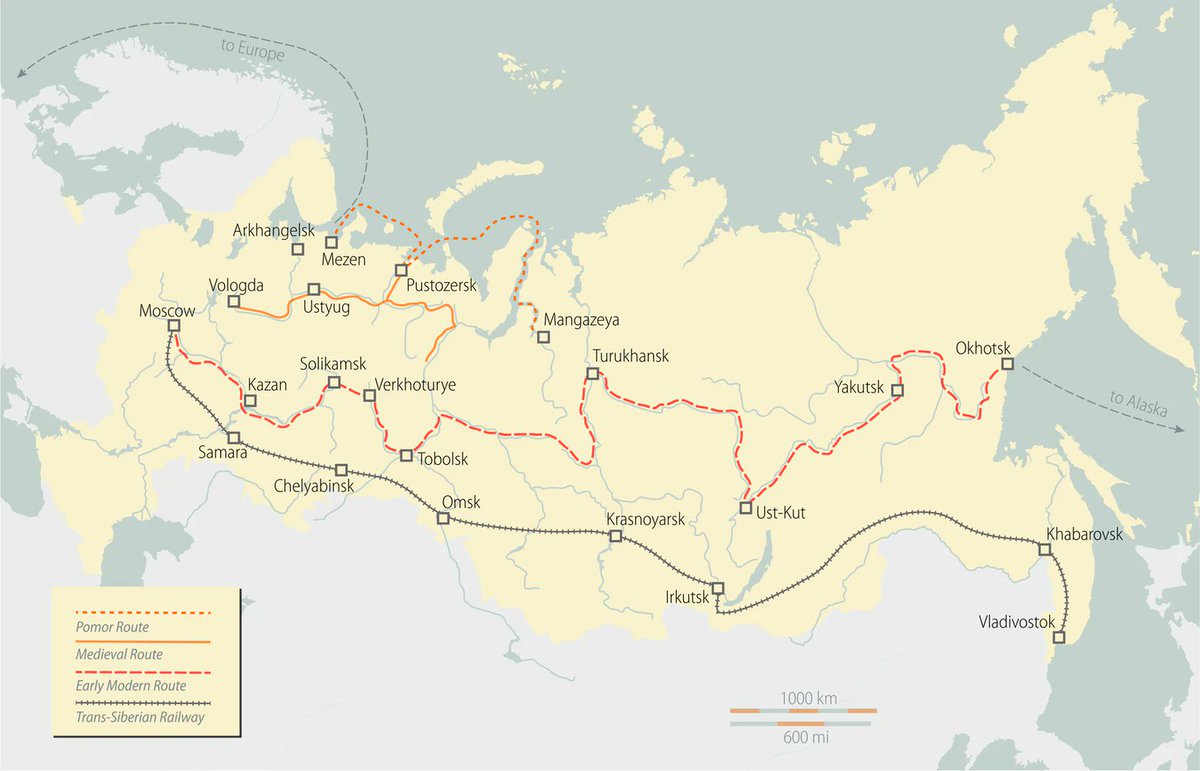
That's a very sketchy map of how Russian transport routes changed over time. It reflects the general trend of Russia going south. Older centres of population and economy were situated much further north than they lie now. That happened in Siberia with the Transsiberian railway 

European Russia used to be a much more northern country, too. Consider a single parameter - a number of households from provincial cities who paid the musketeers tax in 1682-1683. That doesn't reflect the population numbers but may kinda reflect the size of the middle class 

Until 1700s Pomorye, literally the "land by the sea" located by the White Sea and the Arctic Ocean was by far the richest and the most commercial part of Russia. Then the St Petersburg was founded and Peter I prohibited foreign trade through Pomorye, so it gradually declined 

Pomor people are the exception being the only originally seafaring culture the Russia had. They were indeed sea going and ocean going people. Russia however was super potamic and overwhelmingly relied on rivers as the means of communications. At least till the railways were built 

What is important to understand is that historically since at least 1600 Russia has been going south, with its demographic and economic centre shifting closer and closer to equator. But back then it was *expanding* south, expanding not only geographically but also demographically 

Now Russia is shrinking. It's ageing and depopulating. But it is depopulating unevenly. The North, Siberia and the Far East are getting empty with people leaving en masse, while Krasnodar is the fastest growing city not only in Russia but possibly in Europe. Russia's moving south 
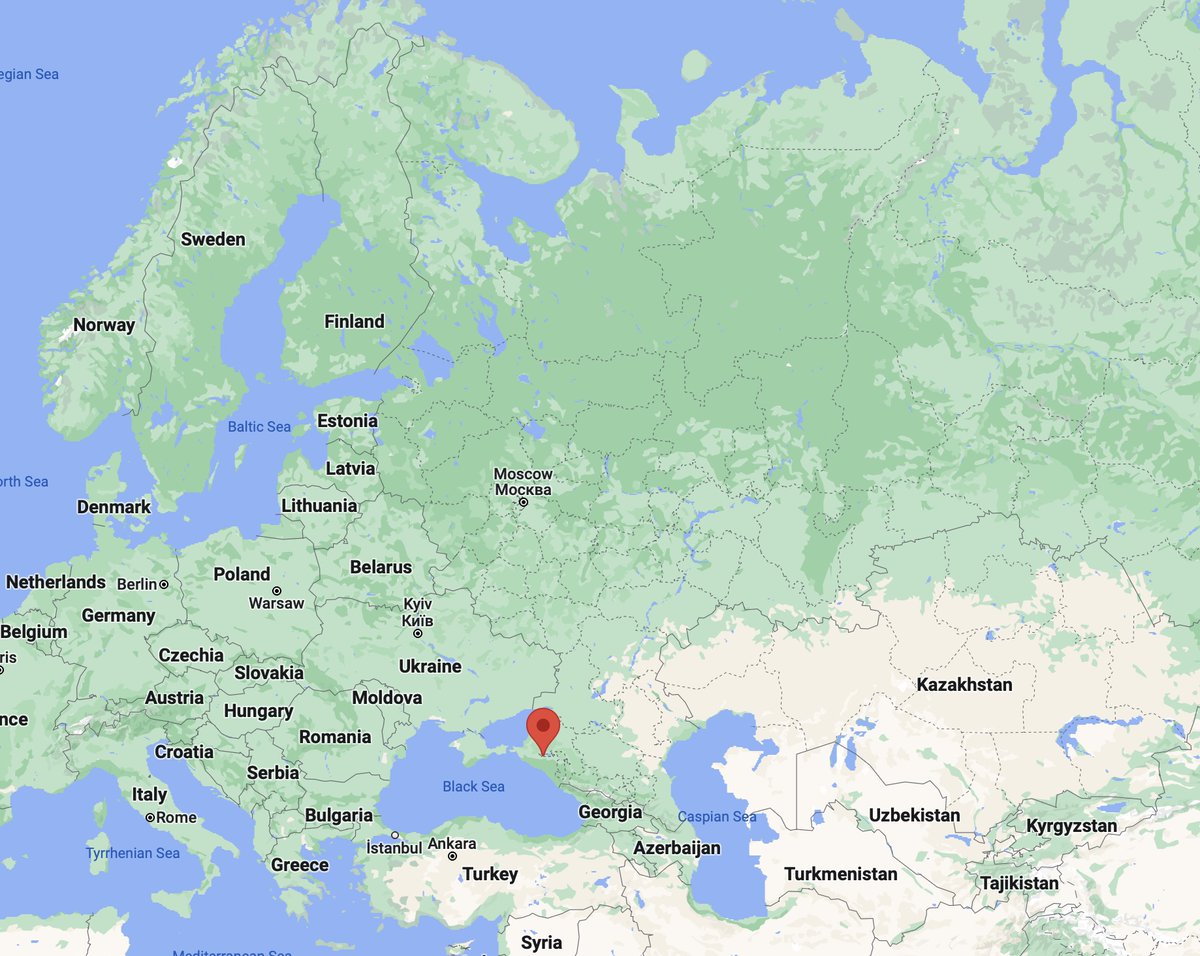
That makes total sense. First, climate. Siberia is hard to live in. Yes, it has tons of resources and industry, but with Moscow taking everything, it keeps Siberia in poverty. As a result people are voting with legs and moving to the warmer places. Like the Black Sea coast 

Second, logistics. Most all of Russian trade is being done via seaports located in only three regions - St Petersburg, Vladivostok and Krasnodar. Three points of access to the relatively warm seas that Russia has. And Krasnodar is the warmest of all. It's usually not freezing 

No wonder that now most of Russian internal migrants go to one of three centres. It's either Moscow, St Petersburg or Krasnodar. While Moscow and St Petersburg are old imperial centres and Moscow is super unsustainable, being a geographic anomaly, Krasnodar grows naturally 

Siberia getting empty, Russia is shrinking southwest. In this context war with Ukraine makes sense. It lies too close to new Russian demographic and economic centres. Indeed, Krasnodar & Rostov interest groups are major beneficiaries and supporters of this war. They're doing well 

Two conclusions. First, policy makers hoping to use Russia against China may be delusional. The war in Europe is natural with Russia shrinking southwest. Conflict with China though would be unnatural. The rule of Moscow depopulates Siberia leaving it empty. No ground for conflict
With the demographic and economic centres shifting southwest, Southwest has too powerful interest groups, which Moscow now has to negotiate with. Which is not the case with Siberia. Krasnodar has way more saying in Kremlin than any Siberian region
Second. Many presume that the disintegration of Russia should it take place, will start with some ethnic republics. I don't think so. It will probably start in one of these ones. The end of🧵 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





