Many wondered: why during the Chechen wars many families opposed the war, while now almost nobody does? Well, one answer is that during the Chechen wars monetary compensations to families were negligible, while now the "coffin money" (гробовые) are quite good. You can buy a car
Also notice the location. It's Saratov. There is a major gap between more successful Middle Volga regions like Tatarstan, Samara and Ulyanovsk (green) and much poorer Lower Volga such as Saratov (yellow) or Volgograd (red). Socioeconomic situation in the latter is *way* worse 
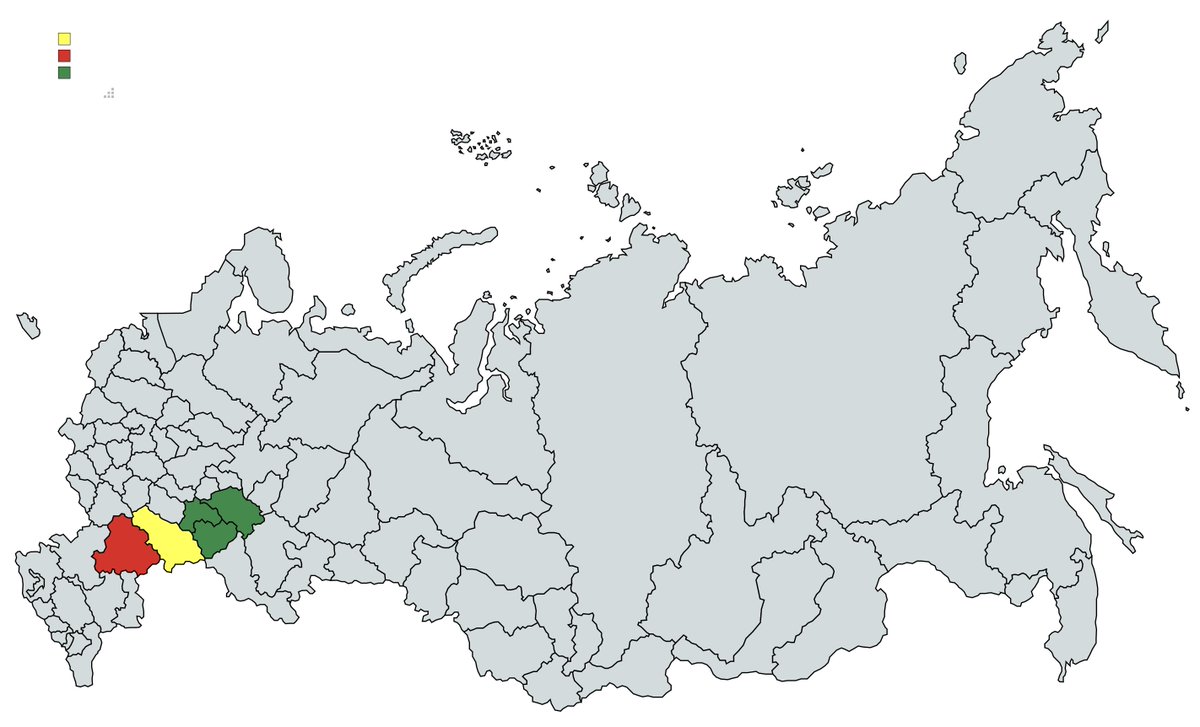
The gap is not only economic, but also cultural. In some respects the Middle vs Lower Volga dichotomy resembles the nanfang vs beifang dichotomy in China. Saratov and Volgograd are paradoxically much more "beifang", Muscovite and Great Russian than regions to the north of them 

Strange it may sound, around 1900 Saratov was the third biggest city of Russia proper after Moscow and St Petersburg. It was a big and rich merchant city that still has the memory of its former glory and a certain imperial vibe. It also has a nice old city, horribly maintained 

If Saratov is mentally stuck in the age of Russian empire, in terms of local identity and public imagination, then Volgograd is stuck in the WWII era. There is probably no other city or region where the Victory-worshipping (победобесие) cult takes such exaggerated forms 
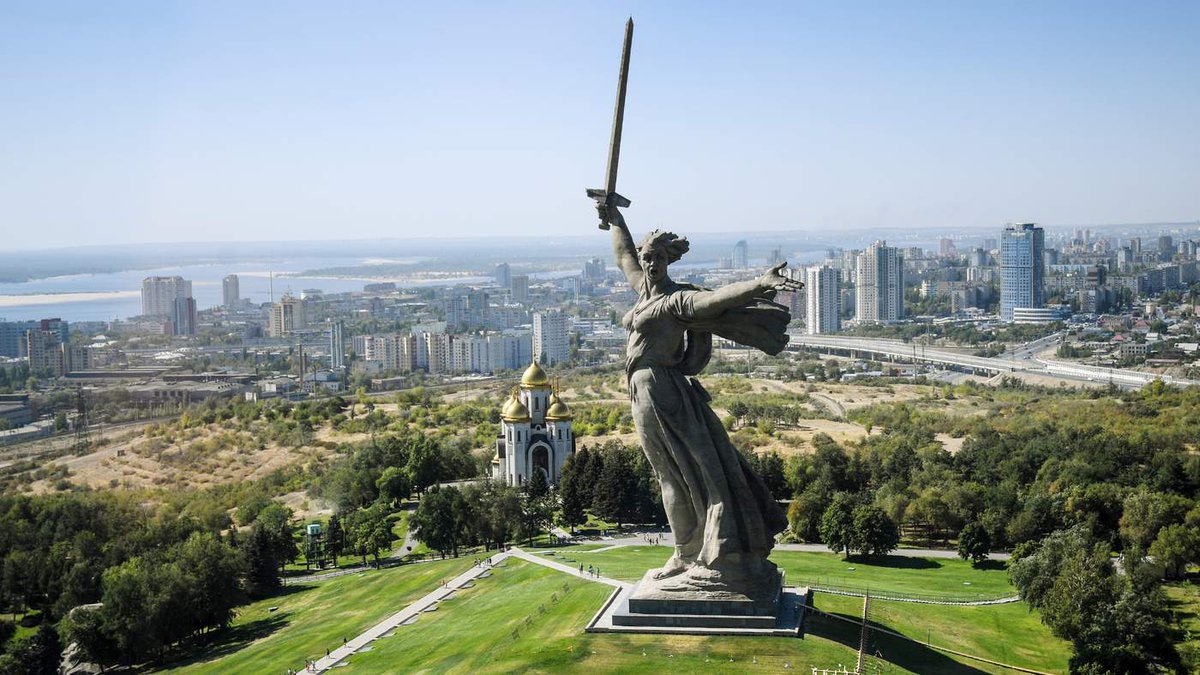

Volgograd doesn't have much of history. In the imperial era it was a relatively small and unimportant Tsaritsyn city, way less relevant than Saratov. After the revolution it was renamed as the Stalingrad and then completely razed during the Stalingrad battle 

As a result of subsequent population change, nothing of the old city remained either in terms of culture or in terms of identity. While later renamed to Volgograd in the process of de-Stalinization, the city fully identifies itself with the WWII. It has no memory of the past 

Stuck-in-the-USSR Volgograd is repeatedly earning the title of the poorest large (over a million population) city in Russia. Stuck-in-the-empire Saratov is doing not much better having very low salaries or quality of life for a large regional centre
ria.ru/20211004/zarpl…
ria.ru/20211004/zarpl…
There's a big contrast between poorer beifang Lower Volga and richer nanfang Middle Volga. Tatarstan, Samara and Ulyanovsk form one economic cluster, both in terms of commercial ties and in terms of pursuing a successful FDI-oriented industrial policy. Well, till February 24 

In fact, after February 24 the Middle Volga industrial cluster has some of the worst economic prospects in the entire European Russia, at least in terms of employment. They all three get obliterated because in economic (and partially in institutional) terms they were very similar 

With this richer Middle Volga cluster going down, some of the neighbouring poorer regions that depended upon the former economically will go down, too. In the previous era, Moscow would act as an arbiter redistributing from winners to losers. Now it won't do that
Kremlin will invest all available resources in maintaining the economy in Moscow. In such a hypercentralized country, Moscow is the only city that truly matters. Economic collapse of Moscow created revolutionary risks, while collapse of province has no risks to regime at all
This however, makes the imperial structure much more fragile. For decades provinces had a big grudge on the imperial metropoly which lived so much wealthier. Now the gap gonna only increase, with the provincials seeing less and less benefits in staying within the empire. The end
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





