Yes. That's a complete misunderstanding of how categorisation and statistics work in Russia. My family used to have relatives: three brothers from the same parents: Kurt, Walter and Horst
According to their passport data, Kurt was German, Walter was Tatar and Horst was Bashkir
According to their passport data, Kurt was German, Walter was Tatar and Horst was Bashkir
https://twitter.com/kynakwado/status/1553786946140397569
Discussions on "percentage" miss one key factor. In most regions population is heavily mixed. In reality you gonna have many ancestries and many bloodlines. So who you identify with is mostly a matter of choice. And the question is - on basis of what is this choice made
For example, in Tatarstan around half marriages are mixed marriages. Who will the children identify with? USSR era was characterised by the heavy domination of ethnic Russians, so almost all children from mixed marriages would become "Russian" - the higher status community
In 1989-1991 the ethnic hierarchy changed quickly. That partially resulted from the renegotiation of political balance and partially from the fact that till 1991 Tatarstan was poor, but after 1991 it lived way better than most regions in Russia. The hierarchy changed accordingly
This is the only author that I am aware of that managed to adequately describe what happened in Tatarstan after 1991. She noticed that the program of Beautification of Kazan for example wasn't merely "urbanism". It was a political project of massive importance 

Beautification of Kazan (and smaller towns) was political because it helped to renegotiate the ethnic hierarchy. Let's be honest, if Tatarstan cities objectively look better than most Russian ones, that does lead to renegotiation of status, both internally and externally 
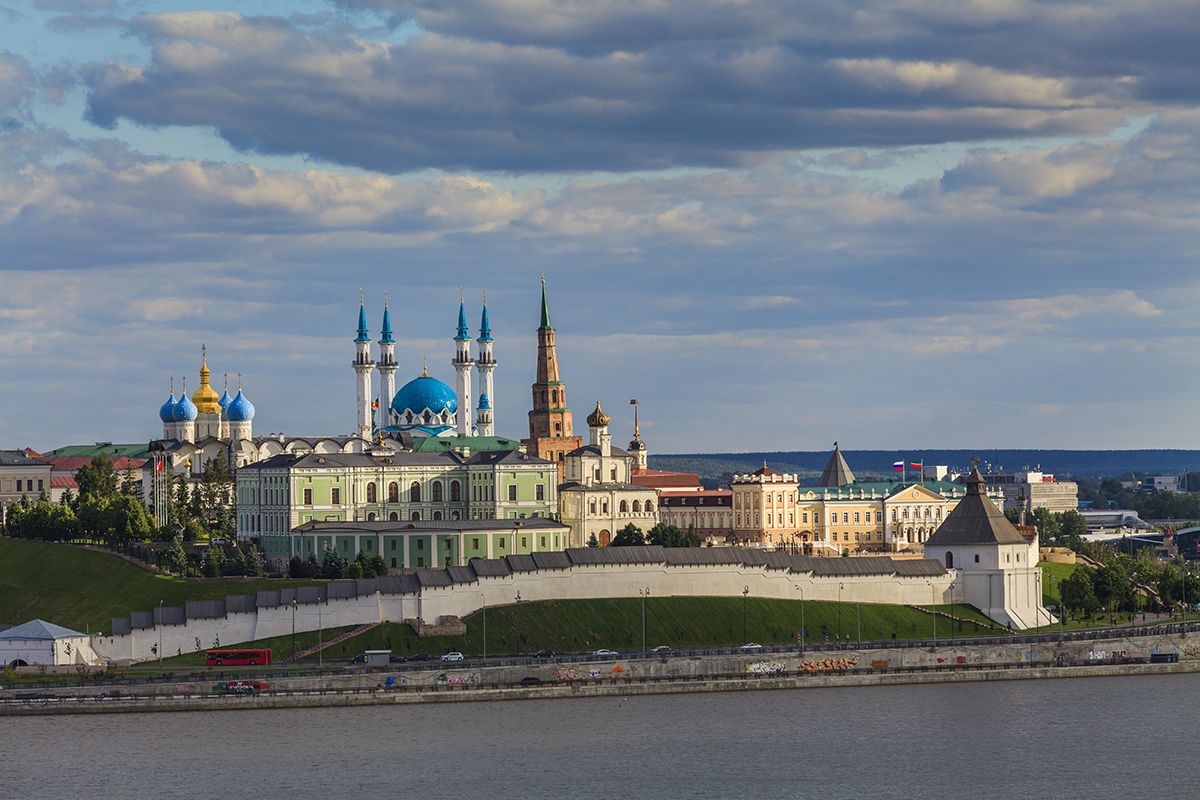

With the renegotiation of ethnic hierarchy, behaviour changed accordingly. Previously almost 100% of Tatarstan kids from mixed marriages had Russian names. But not anymore. In a heavily mixed area ethnicity is a matter of choice. In the unmixed area, too, it's just less obvious
That becomes even more obvious if you go in Siberia. Consider a very popular "chanson" (criminal songs) singer Ivan Kuchin. You can hear him very often in provincial cabs or cafes. On this photo he looks more "European" 

Which makes total sense if you consider that he is from the Chita region. Almost on the border with Mongolia and with heavily mixed population. When you think of Russia, think about the Iberoamerica. Much of the Urals and Siberian hinterland is the country of Mestizos 

When you think about Russia imagine the following. Imagine that we still have the Spanish empire that is run by the Bourbon king from Madrid in the same old ways with peninsulares ruling over everyone else. That wold be the closest analogue to the modern Russia 
Arguing that Russia should remain intact because "80% are Russian" is like saying that 90% of the Spanish Empire are actually Spanish, because they are all Castilian speaking Catholics and therefore should stay under the power of Madrid forever. Sounds good, doesn't work. The end 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






