You have probably heard about Web3 and decentralisation. Decentralization means you have the complete right to your own content. It means instead of centralized entities; ownership gets distributed amongst users. Every user that the ownership over their content.
Now let's go through the architecture of a Web3 dApp and how they works?
The heart of Web3 dApps are smart contracts, they are program that responds to events by executing business logic and they run on a Blockchain.
The heart of Web3 dApps are smart contracts, they are program that responds to events by executing business logic and they run on a Blockchain.

Think of smart contract as a backend code, where the logic for the application happens. These smart contract should be compiled into the binary format and then deployed on any blockchain. The complied file or ABI can be used in the frontend to interact with smart contracts.
We also have EVM which executes the logic defined in the smart contracts. To get or post any data on the smart contract which is deployed on a blockchain, we should be using a Node. You can either deploy our own node or use any node providers such as Chinstack, Alchemy. 
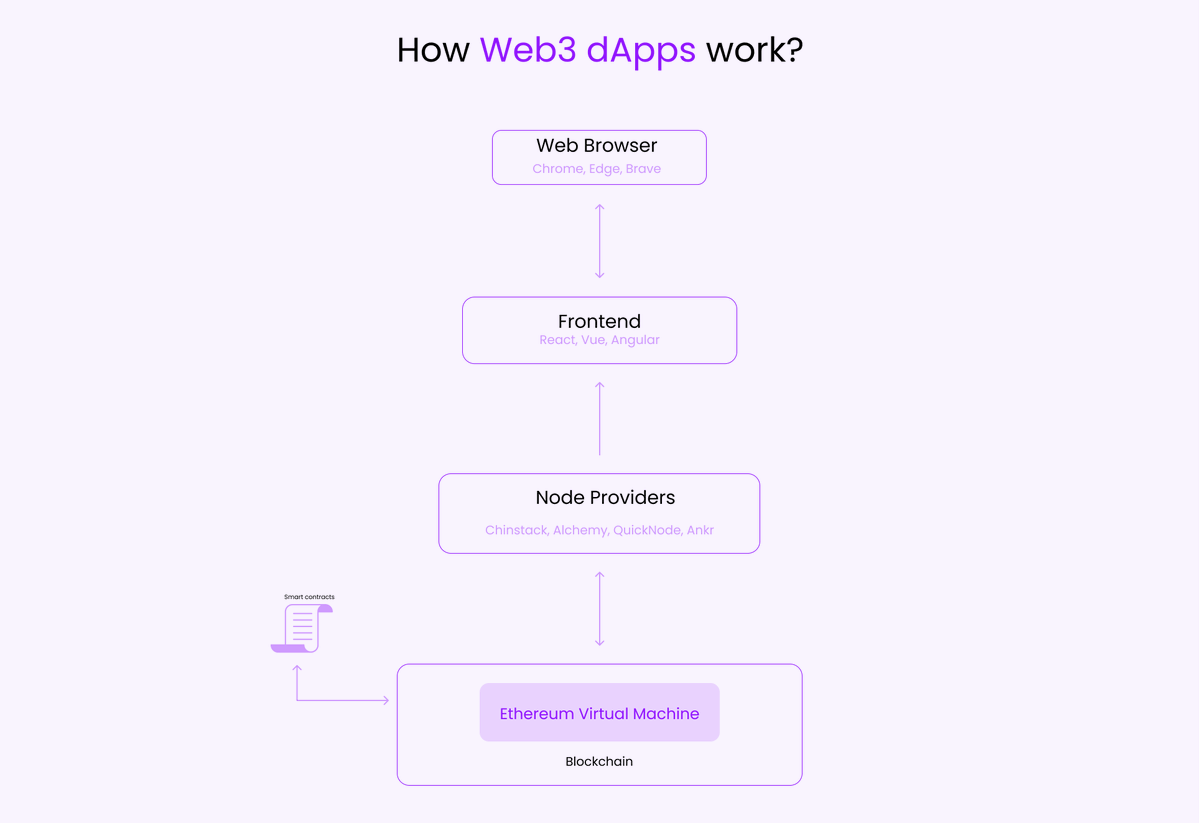
Every Ethereum provider implements a JSON-RPC to connect to blockchain, and then you can read the stored data on blockchain. However if you want to store anything on blockchain, you need to submit a signature using your wallet. 

Coming to storage, popular storage solutions are IPFS and Arweave. IPFS is a distributed file system for storing and accessing data which means instead of storing your files on a centralized database, IPFS stores them on a peer-to-peer network. 

Now let's talk about querying the data. You can either use smart contract events with help of packages like ethers.js or you can use @graphprotocol.The Graph is an off-chain indexing solution which can help you query data in a much easier way. It uses GraphQL query language. 

So, we have talked about many things such as Querying data, Sign ing transactions, storages, providers but there is one more important thing that we need to consider. Scaling!!!
As you know Ethereum doesn’t scale properly. There are a few problems with Ethereum scaling, due of so many transactions, it is a bit slow and have high gas fees.
Here is why, @0xPolygon comes in. Polygon is a L2 scaling solutions that is fast and cheap than Ethereum.
Here is why, @0xPolygon comes in. Polygon is a L2 scaling solutions that is fast and cheap than Ethereum.

Conclusion
Of course this is such an overview of it and it is just the beginning of Web3. I believe that we might see many better tooling in the future. I didn't mention anything about Oracles, because I have another separate thread for it, stay tuned :)
Of course this is such an overview of it and it is just the beginning of Web3. I believe that we might see many better tooling in the future. I didn't mention anything about Oracles, because I have another separate thread for it, stay tuned :)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh