The only station named as a “Staging Post” in the @IAF_MCC was the No. 1 Aircraft Staging Post at Car Nicobar in 1956. This is the fascinating read of how Car Nicobar was the only RAF base in independent India & later became an accidental IAF “Staging Post” #IAFHistory (1/23) 

A Staging Post is simply an airstrip where transport aircraft can land. It can be a tiny airstrip used for refueling/ navigation or a large transport base. During WWII the RAF Transport Command set up 100s of Staging posts across the world from the US to the Far East. 2/ 

Back to Andaman. In 1858, the British setup Andaman & later in 1869 Nicobar (Nancowry Island) as penal colonies. Nicobar was shut down in 1888, but Port Blair persisted with a small presence. It was not intended to be a Military Post prior to WWII. 3/ 

A&N Islands had poor communication with Mainland Indian. Only connection to A&N and Mainland was a steamer that moved 4 times a year in the 1940s (SS Maharaja). This was the only way to sustain the island with food and other provisions. 4/ 

By Jan ’42, it was apparent that Rangoon would fall to the Japanese. While the British did have a Battalion of Gorkhas at Port Blair, they started evacuating. Evacuations were done via SS Maharaja, with a capacity of 500 per trip, and made a trip every 3 weeks or so. 5/ 

A&N was strategic. Situated at the head of Indian Ocean, access to both SE Asia & India. Japanese could target British ac out of Burma & British Fleet in Indian Ocean, submarines in the Strait of Malacca. Later, Japs attacked Trincomalee and Vishakapatnam from the A&N Islands. 6/ 

Japanese attacked Andaman Island in Feb 42. On 23 Mar 42, 13,000 Jap soldiers took control of A&N islands. By Aug 43, they controlled Car Nicobar Islands and stationed 1,000 troops. Troop concentration was mainly in Port Blair (South Andaman) and Car Nicobar. 7/ 

Japs invested in air raid shelters, AA guns, bunkers, roads, jetties & airstrip. In 1937, the British had constructed airstrip at Port Blair but left it unpaved. In 1943, Japs paved the airstrip & put-up lighting for night landing. Today the civil airport stands at this place. 8/ 

Churchill was keen to retake A&N Islands as the Americans & Chinese were keen for a British forward move in Indian Ocean. Operation Buccaneer was planned by SEAC to attack A&N Islands in late 1943 but canceled on 9 Dec 43 by Churchill to focus on other fronts of the war. 9/ 

Island was given over to the nominal administration of Netaji Bose’ INA in end 1943 by the Japanese. Jap occupation was characterized by fortifications, air raids, famine. Food was always imported into the Island and due to the fighting, supply ships could not reach. 10/ 

From 44, Eastern Fleet started to attack A&N Islands & choke-off supplies. Mar 45 – HMS Rapid, Suamarez & Volage attack in Steward Sound. Hellcat strikes on Nicobar Islands & Mosquito Photo-recce was done ex-ceylon. British took control of A&N back from Japs on 26 Sep 1945. 11/ 

Post-independence, India hurriedly colonized A&N Islands with displaced Bengali refugees. A&N was depleted, had minimal population density, climate similar Bengal and for strategic reasons needed to be occupied by Indians before any other country. 12/ 

The RAF Transport Command in 1945 decided extra capacity was needed on the Indian Ocean route, with an intent to extend the Trunk Route from UK to Ceylon to Australia. This would keep the British colonies in Ceylon – Malaya – Australia connected. 13/ 

In May 1947, RAF setup a meteorological and radar station in Car Nicobar on the airstrip that the Japanese had constructed. Car Nicobar was made a RAF Staging post for refuelling/ Navigation aids between Ceylon & Singapore with a motley staff of RAF personnel. 14/ 

As India became an independent country, in a rare move it allowed RAF to keep this staging post on the Island, thereby making it an RAF base on Indian territory. In return, it got access to RAF Staging posts in Europe which it did use when its aircraft traveled west. 15/ 

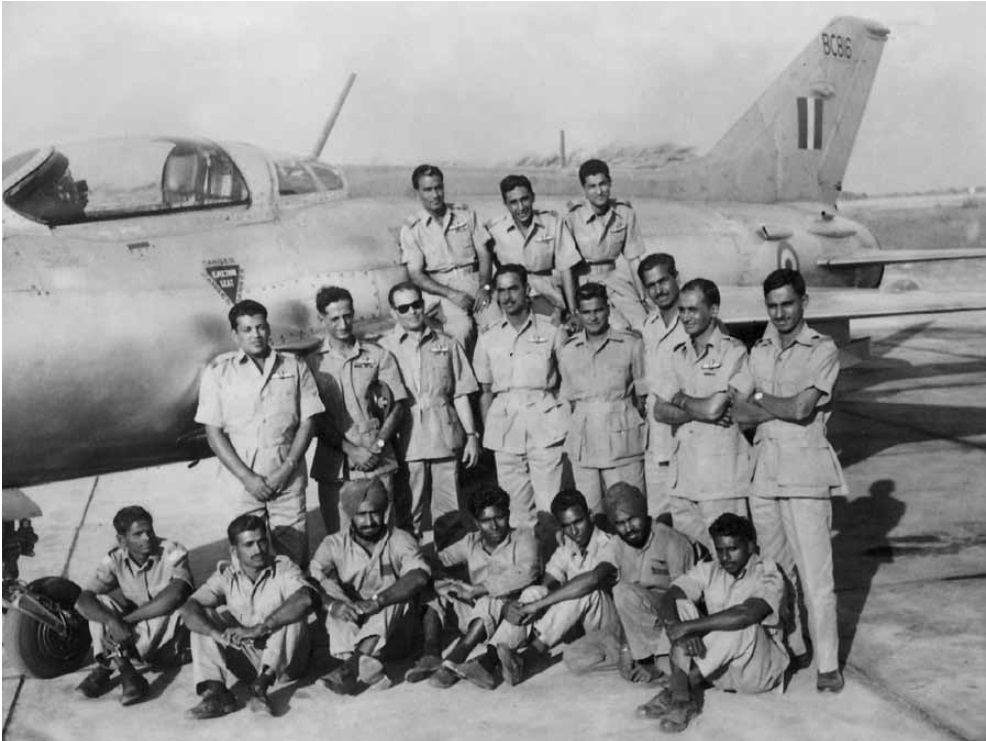
Over the next few years, multiple RAF crews and squadrons visited Car Nicobar Staging post for varying periods of time. The 52/110 Sqn Valetta crews that flew the Changi/ Butterworth/ Car Nicobar/ Negombo/ Gan 'Air Bridge' were lightly referred to as Gan Air or Gan Pig Run. 16/ 

In May ‘53, the RAF Staging Post caused a furor in the Parliament of India when a member puzzled the Govt on the use of the staging post to potentially wage war on another colony, namely Malaya. Pt. Nehru personally had to answer and satisfy the member. 17/ 

In Feb 54, the question came up in Parliament again & the Minister of Defence had to handle some tough cross-questions. It seems this triggered the Govt into taking over the base. The IAF took over, renaming it as No.1 Staging Post, IAF even though it had nowhere to stage to! 18/ 

The IAF decided to have the Staging Post under the charge of its 6 Wing based at Barrackpore. However, it needed to first send equipment to Car Nicobar, which was still reliant on SS Maharaja for regular transit. This turned out to be a tougher job than anyone had imagined. 19/ 

The challenge presented was limited facility to transport heavy equipment (MT vehicles weighing 4 to 25 tons each) by Sea as the only ship operating was small/old. In addition, the crane at Calcutta could not haul up such load and the monsoon rains delayed matters further. 20/ 

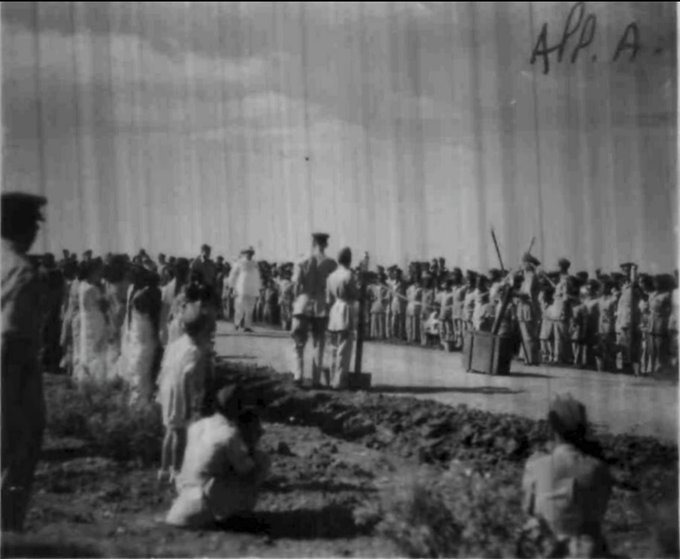
IAF airlifted some men and light material and the RAF and local administration provided facilities. Thus the IAF reached the far end of India’s boundaries and occupied the Car Nicobar base on 1st July 1956. 21/ 

IAF started running Dakota Couriers between Barrackpore and Carnic once a week with 11 Sqn taking up the role. The route was via Rangoon for safety reasons. This triggered a discussion to rebuild the airstrip at Port Blair for both defence and Civil benefits. 22/ 

In '67, the runway was extended to 9,000 ft. In '85, 122 HF moved in as the first permanent IAF flying unit at Car Nicobar. IAF ran it as a Staging Post till 1986, after which it became 15 FBSU & 37 Wing in 1993. Now it has emerged as the IAF's strategic foothold in the IOR. 23/ 

Sources: @IN_Archives, The Vulnerable Andaman and Nicobar Islands(Punam Tripathi, 2018), Imperial Gazette of India (1909),The War Against Japan(Stanley Woodburn Kirby, 1957), Japanese occupation of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, 1942-1945(TR Sareen, 2014)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh