
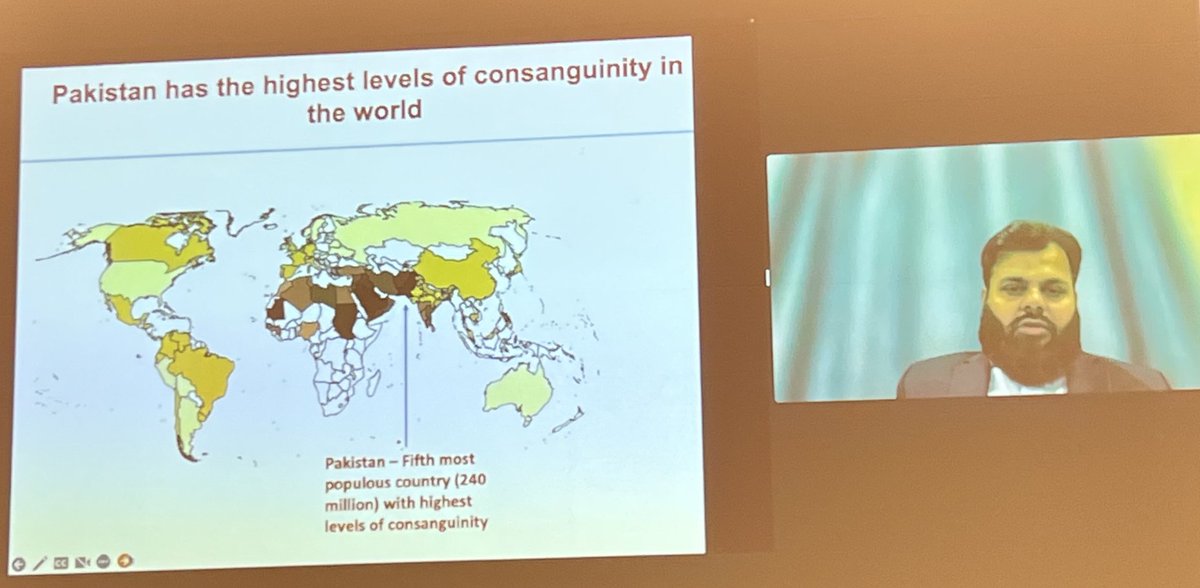
Danish Saleheen stunned the audience with his story of building the world's largest cohort of human knockouts in Pakistan, which is the world's 5th most populous country with highest level of consanguinity ever known. #ASHG22 #DRIFT22 
Starting with around 10k individuals sequenced in 2017, now the cohort comprise of around 200k individuals recruited, of which 80,000 were exome sequenced. Goal is to sequence 1 Million.
nature.com/articles/natur…
nature.com/articles/natur…
Based on these data, they have identified so far >14000 human knockouts for >5000 genes. To achieve the same in European populations, you'll have to sequence >11 million individuals. 

Such a high prevalence of knockouts is due to the extremely high rate of consanguineous unions in the communities. In the current sample, around 40% are born to first cousin unions. Marrying outside the family circle is considered a 'taboo' in certain communities.
Extensive phenotyping of these individuals are being done by linking to clinical records, administering questionnaires and through physical and clinical examinations at the site of recruitment.
The most powerful of all these approaches is the call back study--ability to recontact the individuals, do a cascade screening of the family members and perform an in-depth phenotyping of the whole family.
Danish shared a mind blowing experience where he recontacted an individuals who was a knockout for APOC3. It turned out his wife was also a knockout and as a result, all their 9 children. It was jaw dropping moment to see the pedigree of this family.
Cascade screening this family and their relatives identified 33 knockouts and hundreds of heterozygous carriers of APOC3 mutation. For context, there is zero KO in the gnomAD database.
This motivated them to test for cardio protective effect of APOC3 homozygous mutations, given the previous reports in heterozygous individuals. And this led to a shocking revelation.
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
Unlike the heterozygotes, the homozygotes for APOC3 are not protected from heart attack. Instead they seem to be at increased risk. Exemplified by the fact that the fisherman through whom all these KOs were traced died few months later of heart attack.
An important lesson to learn here: our predictions of the full picture based on the half we see don't turn out always right. It also highlights the extreme value of having such a genetic database.
How can we use this resource to gain insights into the GWAS findings? Danish and colleagues took all the GWAS loci identified for NAFLD and prioritized a list of 82 genes that are likely to be causal using different methods.
Of which, for 22 genes human knockouts are present in the Pakistani Genomic Resource database. Now they are planning to study these KOs extensively.
I am stunned to learn how extremely valuable this genetic resource is to the genomics community. While Danish concluded his talk, I was lost in thoughts wondering if it'll be ever possible to establish such a resource in India.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh














