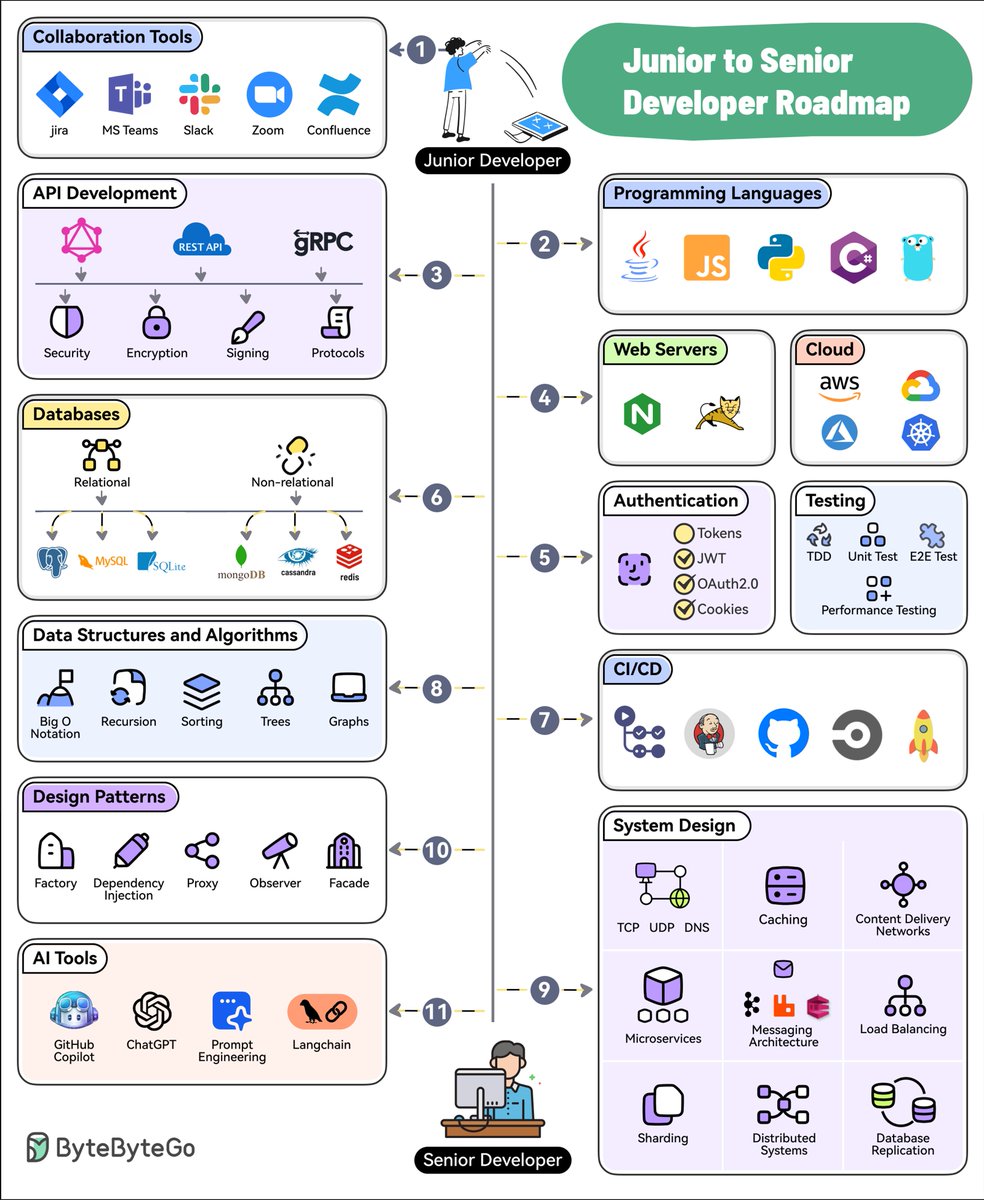
/1 Why is PostgreSQL voted the 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐥𝐨𝐯𝐞𝐝 𝐝𝐚𝐭𝐚𝐛𝐚𝐬𝐞 by Stackoverflow 2022 Developer Survey?
The diagram shows the many use cases by PostgreSQL - one database that includes almost 𝐚𝐥𝐥 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐮𝐬𝐞 𝐜𝐚𝐬𝐞𝐬 developers need.
The diagram shows the many use cases by PostgreSQL - one database that includes almost 𝐚𝐥𝐥 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐮𝐬𝐞 𝐜𝐚𝐬𝐞𝐬 developers need.

/2 🔹OLTP (Online Transaction Processing)
We can use PostgreSQL for CRUD (Create-Read-Update-Delete) operations.
We can use PostgreSQL for CRUD (Create-Read-Update-Delete) operations.

/3 🔹OLAP (Online Analytical Processing)
We can use PostgreSQL for analytical processing. PostgreSQL is based on 𝐇𝐓𝐀𝐏 (Hybrid transactional/analytical processing) architecture, so it can handle both OLTP and OLAP well.
We can use PostgreSQL for analytical processing. PostgreSQL is based on 𝐇𝐓𝐀𝐏 (Hybrid transactional/analytical processing) architecture, so it can handle both OLTP and OLAP well.
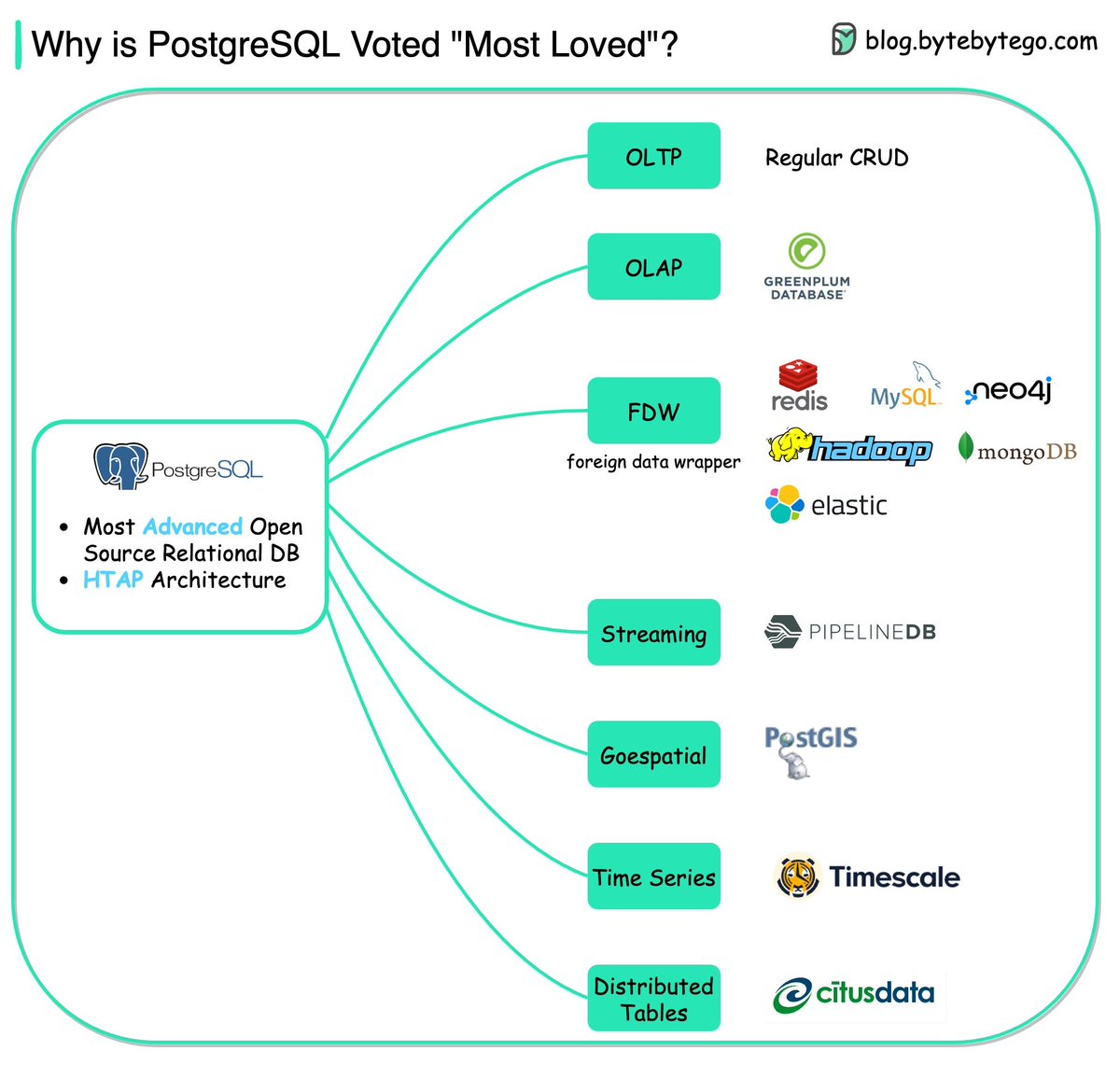
/4 🔹FDW (Foreign Data Wrapper)
A FDW is an extension available in PostgreSQL that allows us to access a table or schema in one database from another.
A FDW is an extension available in PostgreSQL that allows us to access a table or schema in one database from another.

/5 🔹Streaming
PipelineDB is a PostgreSQL extension for high-performance time-series aggregation, designed to power real-time reporting and analytics applications.
PipelineDB is a PostgreSQL extension for high-performance time-series aggregation, designed to power real-time reporting and analytics applications.

/6 🔹Geospatial
PostGIS is a spatial database extender for PostgreSQL object-relational database. It adds support for geographic objects, allowing location queries to be run in SQL.
PostGIS is a spatial database extender for PostgreSQL object-relational database. It adds support for geographic objects, allowing location queries to be run in SQL.

/7 🔹Time Series
Timescale extends PostgreSQL for time series and analytics. For example, developers can combine relentless streams of financial and tick data with other business data to build new apps and uncover unique insights.
Timescale extends PostgreSQL for time series and analytics. For example, developers can combine relentless streams of financial and tick data with other business data to build new apps and uncover unique insights.

/9 👉 Over to you: Which database do you like the most?
/10 I hope you've found this thread helpful.
Follow me @alexxubyte for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
Follow me @alexxubyte for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
https://twitter.com/alexxubyte/status/1585296460072919040
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh