About -
South Indian Bank Ltd (SIB) est. in 1929 is a major private sector bank headquartered at Thrissur in Kerala, India. SIB has 926 branches, 1 service branches, 18 Regional Offices spread across India. The bank has also set up 1,275 ATMs & 120 Cash Deposit Machines.
South Indian Bank Ltd (SIB) est. in 1929 is a major private sector bank headquartered at Thrissur in Kerala, India. SIB has 926 branches, 1 service branches, 18 Regional Offices spread across India. The bank has also set up 1,275 ATMs & 120 Cash Deposit Machines.
Financial Summary -
Q2FY23 (YoY)
NII at ₹726 Cr vs 527 Cr ⬆️38%
Op Profit ₹426 Cr vs 170 Cr⬆️151%
PAT at ₹223 Cr vs (187) Cr ⬆️219%
Net Int Margins at 30-qtr high
Q2FY23 (YoY)
NII at ₹726 Cr vs 527 Cr ⬆️38%
Op Profit ₹426 Cr vs 170 Cr⬆️151%
PAT at ₹223 Cr vs (187) Cr ⬆️219%
Net Int Margins at 30-qtr high

Location Wise Break-up -
South Indian Bank earns 53.8% from Kerala, 29.4% from South India & 16.8% from Rest of India.
South Indian Bank earns 53.8% from Kerala, 29.4% from South India & 16.8% from Rest of India.

Strategies -
SIB is committed to achieve its goals by focusing on major areas such as profitability, asset quality, resilient loan book, robust retail liability portfolio, appropriate organizational structure & digital technology.
Improving profitability by focusing on "6Cs"
SIB is committed to achieve its goals by focusing on major areas such as profitability, asset quality, resilient loan book, robust retail liability portfolio, appropriate organizational structure & digital technology.
Improving profitability by focusing on "6Cs"

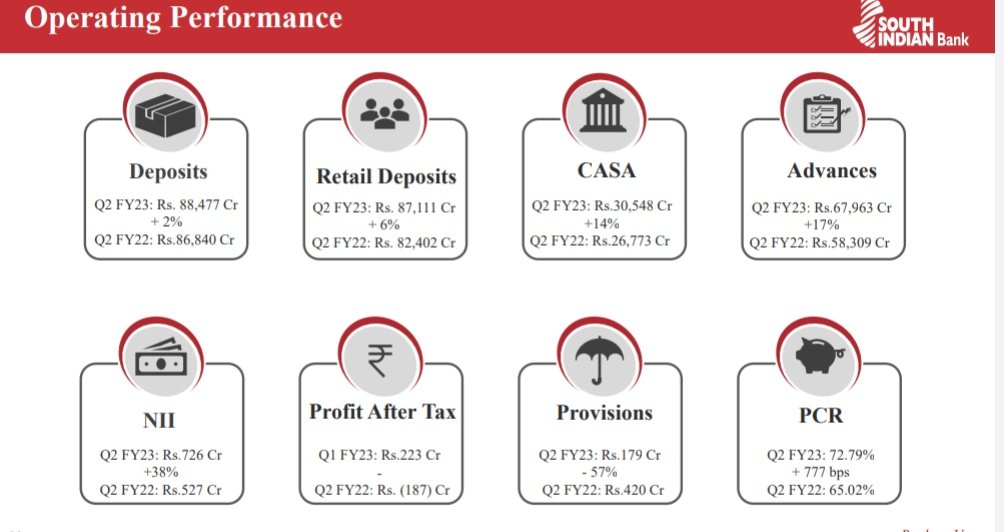
Key Metrics - (YoY)
Deposits ⬆️2%
Retail Deposits ⬆️6%
CASA ⬆️14%
Advances ⬆️17%
NII ⬆️38%
Provisions⬇️-57%
PCR ⬆️ to 72.8% vs 65%
Net NPA ⬇️ to 2.5% vs 3.85%
Deposits ⬆️2%
Retail Deposits ⬆️6%
CASA ⬆️14%
Advances ⬆️17%
NII ⬆️38%
Provisions⬇️-57%
PCR ⬆️ to 72.8% vs 65%
Net NPA ⬇️ to 2.5% vs 3.85%
Digital Banking -
Mobile banking transactions volume increased by (87%) YoY to 85 Million transactions.
Mobile banking transactions volume increased by (87%) YoY to 85 Million transactions.

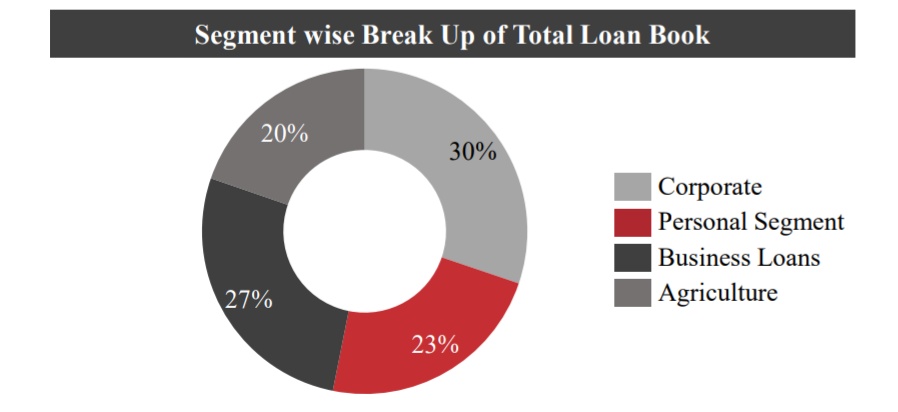
Composite Loan Book -
Business loans account for (27%) of the total loan book, followed by Corporate (30%), Personal (23%) & Agriculture (20%).
Business loans account for (27%) of the total loan book, followed by Corporate (30%), Personal (23%) & Agriculture (20%).
Gold Loans -
SIB has given 76% of gold loans under the Agriculture segment & 24% under the Retail segment.
Personal Segment -
Housing loans account for 31% of personal loans, followed by Gold Loans (20%), Mortgage (17%), Vehicle (7%), Loan against Deposits (8%) & Others (17%).
SIB has given 76% of gold loans under the Agriculture segment & 24% under the Retail segment.
Personal Segment -
Housing loans account for 31% of personal loans, followed by Gold Loans (20%), Mortgage (17%), Vehicle (7%), Loan against Deposits (8%) & Others (17%).
Business Loans -
MSME/SME loan accounts for 72% of business loan & 28% Others.
MSME/SME loan accounts for 72% of business loan & 28% Others.
Management -
Current MD & CEO "Murali Ramakrishnan" has a work Experience of over 34 years. He retired from ICICI Bank as Senior General Manager at Strategic Project Group.

Current MD & CEO "Murali Ramakrishnan" has a work Experience of over 34 years. He retired from ICICI Bank as Senior General Manager at Strategic Project Group.


South Indian Bank post the onboarding of Murali Ramakrishnan in Sep’20, focused on
growing the balance sheet in a calibrated manner with prime focus on NIM & Asset Quality.
growing the balance sheet in a calibrated manner with prime focus on NIM & Asset Quality.
Valuation -
Market Cap : ₹2783 Cr
P/E : 4.97 Vs
10yrs Median PE 9.9
P/BV : 0.48 Vs
10yrs Median P/BV 0.9
Market Cap : ₹2783 Cr
P/E : 4.97 Vs
10yrs Median PE 9.9
P/BV : 0.48 Vs
10yrs Median P/BV 0.9
Conclusion -
SIB is able to showcase improvement in all major business parameters which is in line with management objectives. Improvement is visible in changing advance mix, improving CASA ratio, lowering NPA, etc. These positive developments signals a turn around in long run.
SIB is able to showcase improvement in all major business parameters which is in line with management objectives. Improvement is visible in changing advance mix, improving CASA ratio, lowering NPA, etc. These positive developments signals a turn around in long run.
Please 🙏 like 👍,comment, retweet ♻️ if you find this 🧵 useful.
And follow us on @LnprCapital for more information like this.
@nid_rockz
And follow us on @LnprCapital for more information like this.
@nid_rockz
https://twitter.com/LnprCapital/status/1586297082461454336?t=qjZujBXBFUI-wKydPaxKJg&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh